"Understanding the importance of staying current with COVID-19 vaccination is
essential for protecting our most vulnerable population. The Australian
experience with COVID-19 demonstrates the profound vulnerability of our older
In the early 2000s I was in my mid 20s, working a dead end job as a Windows programmer, and had two very young kids who were not super good at sleeping. I had worked as what I would now call a systems programmer for the Australian patents and trade marks office for a few years in the late 1990s doing low level image manipulation code — we had a for the time quite impressive database of scanned images of patents and trademarks, and sometimes we need to do things like turn them into PDFs or import a weird made up image format from the Japanese patents office.
So when you combined those things — previous experience in a field I found interesting, a job I did not currently find interesting, and a lot of spare time very early in the morning because the kids wouldn’t sleep but my wife really did need a rest — you end up with a Michael who spent a lot of time writing image manipulation code on his own time. Even back then I was pretty into Open Source, so I released what I think was probably the first Open Source PDF generation library, as well as a series of imaging tools such as pngtools. pngtools was modeled on the libtiff tifftools which I had used extensively at work.
And then things changed. I wrote a couple of books. I got hired by Google and moved to California. The kids got a bit older and life got a bit more complicated… And pngtools just sort of sat there. Except, many Linux distributions had packaged it by then. I guess I had kind of hoped that someone else with more time or passion for the project would reach out and ask to take it over, but that simply never happened. A few years ago I felt sufficient guilt to dig out the SVN repo from backups and convert it to a git repo on github, but apart from occasionally merging a PR from some random on the internet nothing has really happened to pngtools in literally decades.
I think this is where we get to the “mental health” bit of the title — I’ve been actively contributing to Open Source for nearly 30 years, but I can’t really explain what I got in return apart from the occasional dopamine hit. I think I could argue that Google wouldn’t have hired me without my Open Source work, but that’s probably also not entirely true. They hired lots of other people with no history of Open Source contributions. I think overall my lived experience is that I would often have been better off personally not contributing my code publicly — I grow tired of people’s poor social skills and having to fight to get bugs fixed. In a world where its much easier to write non-trivial things with LLM tooling, I am genuinely unsure if its worth the effort of trying to collaborate with people who clearly do not want to collaborate with me. I am sure some of this is my fault, certainly I think I am more sensitive to rejection that your average bear probably because of ADHD, but it can’t all by my fault.
So why would I pick pngtools back up now? Well there’s a latent sense that it needs some love and that no one else is going to do it, but also those LLM tools from the previous paragraph actually make it a lot easier to rebuild state than previously. I don’t really need to deeply understand all the code in a language I haven’t written in for 20 years. I can just supervise a robot that does it. I know its fashionable to hate on the LLM development tools, but honestly that always seems to come from someone who hasn’t actually tried them and is ultimately scared for their job. I don’t think the tools replace me, they simply make me a lot more productive — just like web search did when first introduced.
I should be clear to say I see a distinction between tightly bounded problem spaces with clear definitions of correct like coding, and AI generation of art or English essays. I think those later fields are much more complicated both in terms of correctness and ethics.
And anyways, that’s how you end up with pngtools v1.0 after a mere 25 years.
A SWAY session by Joanne of Royal Far West School. http://sway.org.au/ via https://coviu.com/ SWAY is an oral language and literacy program based on Aboriginal knowledge, culture and stories. It has been developed by Educators, Aboriginal Education Officers and Speech Pathologists at the Royal Far West School in Manly, NSW.
Category: Array
Uploaded by: Silvia Pfeiffer
Hosted: youtube
Category: 2
Uploaded by: Silvia Pfeiffer
Hosted: youtube
This screencast shows how a user of the PARADISEC catalog logs in and explores the collections, items and files that the archive contains.
Category: 2
Uploaded by: Silvia Pfeiffer
Hosted: youtube
Screencast of how to use the PARADISEC catalog for managing and publishing collections.
Category: 2
Uploaded by: Silvia Pfeiffer
Hosted: youtube
Screencast of how a PARADISEC administrator uses the PARADISEC catalog for managing the consistency of metadata and staying on top of uploaded files.
Category: 2
Uploaded by: Silvia Pfeiffer
Hosted: youtube
 Continuations 2026/06: Mailer rebuild
Continuations 2026/06: Mailer rebuildThe highlight of this week was sharing my Hanami Mailer rebuild. If you’re interested in how our mailers will fit alongside actions and views (and reuse the latter!), check it out. I wrote up all the different ways you can use the API, so you can get a sense of it all without even going into the code.
My next step here is to wait for any feedback from the other Hanami maintainers. In a week or so I’ll merge this and sort out the full framework integration story. Once that’s done we can start to make more noise about it and hopefully get some real user testing.
I made some releases this week! Hanami CLI v2.3.5 includes a fix to make asset paths work better with “sandboxed” Node.js setups. Thanks Hailey for the fix! Dry Operation v1.1.1 enhances our transaction support and makes it possible to provide extra transaction options at both class and per-transaction levels. Thanks Armin for this improvement! And Dry Types v1.9.1 includes a workaround for a JRuby bug. Thanks Paweł for continuing to improve our JRuby support!
Last week, I filed a bug with Parklife about a peculiarity with the way we were using it (using dotted version numbers in our URLs). This week, I got to test the fix! It works brilliantly, and now I’ll get to remove this patch from our codebase. Thank you Ben for one of my favourite bits of software!
Still on the site, I reviewed our backend-focused tickets and shared a bunch with Jojo for the time she’s continuing to spend on it (there’s actually not much left on the critical path for launch, which is great!). And Max has come back with a revision to our designs, which I’ll review tomorrow.
I finally got to spend some time properly reviewing Aaron’s validation extension for Dry Operation. I know this is going to be a much loved feature (thank you Aaron for building it!), so I’m glad I can spend the time to help make it as good as possible.
We hit a major milestone this week. I ported Hanami Assets, DB, Releoader, RSpec, Utils, Validations, and Webconsole (oh my!) over to repo-sync, and now every Hanami repo is synced! That’s the entirety of our Dry and Hanami organisations, both fully synced. This also means their releases all come via release-machine, which is what allowed me to link to those nice GitHub release pages earlier in the dotpoint above :)
To celebrate, I took the chance to make a couple nice little improvements to these automation repos. I moved repo-sync’s listing of repos/files to a dedicated config file, and added a scheduled workflow to clean up stale preview branches. I also updated our forum release announcements so they auto-link to GitHub resources, like usernames, PR numbers and commits.
Andrew Pam spoke about new developments in Linux gaming and about hardware and OS support for games etc. He also described some interesting developments with Linux support for SMR disks [1].
Then we discussed Everything Open 2026 [2]. We had some discussion about some of the lectures including the final one which generated controversy (here is the playlist for EO 2026 lectures [3]).
We discussed ideas for running a more effective BOF on a difficult topic like FOSS on mobile phones. The main conclusions seemed to be to have more than 2 people chairing the BOF and more than 1 hour to run it. Maybe a BOF as an introduction to a hack evening.
Then we had discussions about the future of LUGs, the difficulty in getting interest in attending meetings, and to what extent YouTube replaces meetings. One conclusion was that we should publish videos of meetings even if they aren’t going to be interesting to most people. If 99% of people find that watching a meeting they can’t contribute to is boring then we get 1% who are interested and if the number of people who see the video is large enough then 1% becomes a good number.
We finished with discussing Linux promotion. There was a general feeling that a Linux Australia subcommittee dedicated to promoting Linux would be a good thing, I didn’t poll the people do determine who of the people who agreed it was a good idea were actually interested in doing the work.
I (Russell Coker) used my Furilabs FLX1s for the meeting and it worked well running Firefox talking to the Big Blue Button server but unfortunately Firefox wouldn’t work with the camera. This was a reasonable result and the 3 hour meeting used slightly over 50% of the phone’s battery which is much better than a Librem5 or PinePhone Pro could manage. For as yet unknown reasons my desktop PC didn’t want to talk to the webcam that I have been using for years.
The meeting had 10 people attending which isn’t a large meeting but was enough for many interesting discussions.
Topics for future meetings include using storage technology such as SMR disks which we also agreed was a good topic for ongoing discussions in the Matrix room over the course of weeks. Changing storage options is not a trivial thing and not something that can be done quickly or easily.
How to best run BOFs and workshops at conferences was agreed to be a topic that needs more discussion. We are talking about how to get things done efficiently for Everything Open 2027 aleady!
Digital sovereignty was briefly discussed in the meeting and agreed to be a topic for future meetings. It is a complex topic and we will break it down and address separate parts in different meetings. A meeting about “digital sovereignty” on it’s own is probably not going to have enough focus to achieve things. A meeting about a specific topic such as “which cloud to use” can get some good results.
I’ve been experimenting with Claude Code quite a bit recently, and found myself wanting to be able to view my usage at a glance. Unfortunately, Anthropic don’t yet provide this information in a format consumable by a status line helper, so I’ve hacked together a little script that’ll do it for you.
I have it set to show me how much of my 5 hour cap I’ve used (the solid bar), how far through the 5 hour window we are (the * in the progress bar), as well as my 7d usage and how full the context currently is. It’ll change colours to warn you when you’re potentially going to hit your limit.
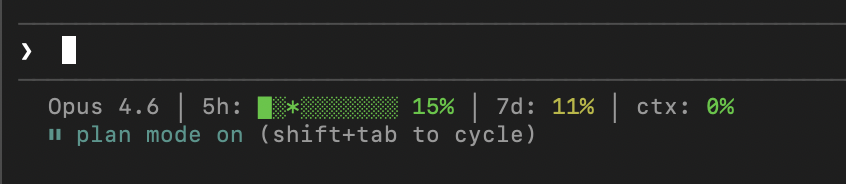
Here’s a gist with the files you need: copy the scripts to your ~/.claude/scripts directory, and add the settings to your ~/.claude/settings.json. Run ~/.claude/scripts/refresh-usage.sh --force to get fresh data immediately.
Given that it’s unofficial behaviour, it may break or get you banned at any time, but I hope not. 
 Continuations 2026/05: Fit of passion
Continuations 2026/05: Fit of passionA slightly slower week, this one. My regular OSS day was spent instead with the kids on their last Friday of the summer holidays.
Some good movement on the site. Reviewed, tweaked, and merged this new status page from Jane Sandberg. Thank you Jane! Aaron is also back on the job and taking a last pass over our logo and type colours. I think we’ve managed to get past all the outstanding issues, and should hopefully be free to lock in our final site design.
In a few spare moments, I took the chance to bring more Hanami repos under repo-sync management. Now we have it for hanami, cli, router, controller, and view! Porting the latter three was very easy, so I’m confident we should be able to get the whole set moved across soon. I also enabled release-machine for all synced Hanami repos, so we’ll get to enjoy a nice streamlined release process soon, too.
One part of rolling out the repo-sync is switching to our new shared RuboCop config, and in doing this this week I discovered what I thought was a bug in RuboCop, resulting in the downloaded remote config files no longer being hidden files. Turns out this was an intentional change and TIL RuboCop’s path relativity feature. Will likely need to rename our shared RuboCop config to account for this.
Paweł is continuing his work on the JRuby rollout, making it so JRuby becomes a required version in the CI matrix for the projects where we’ve restored support. And he managed to fix the local tooling for our repo sync at the same time. Thanks Paweł.
Today, in a fit of passion, I fully built out a first cut of a Hanami Minitest gem. I hope to share it in the coming week. I’m not a Minitest user, so I’ll definitely need the community’s help to make sure our config is nice and idiomatic.
 Continuations 2026/04: i18n support
Continuations 2026/04: i18n supportAfter my code-a-thon last weekend, this week I was able to polish up Hanami’s built-in i18n support and share it as a PR (also on the forum). Please take a look, I’d love to hear your feedback!
I spent a few more hours continuing to refine my Hanami Mailer rebuild. That one will hopefully be ready to share soon too.
While I was poking at things during the week, I discovered that hanami new (and any other outside-of-a-project hanami CLI innovations) were crashing on recent Rubies with Gem::LoadErrors, due to bundled gems already being activated, but being in conflict with the required versions for Hanami’s own dependencies. I fixed this nice and promptly and our CLI is back in action again.
This fix allowed me to make the first-ever automated release of a Hanami gem! I got hanami-cli activated for our release-machine and it all went very smoothly. I’m excited to finish the rollout to the rest of the Hanami gems and use this for all our releases.
I also released a small fix to hanami-rspec to ensure its command callbacks continue to run smoothly with recent Dry CLI releases. Thanks to Sebastjan Hribar for raising this issue!
With release-machine clearly working smoothly, I enabled it for all the Dry gems, while also reviewing the RubyGems.org ownership for each of those gems to make sure it’s current.
Up next for me is getting the v2 of Hanami Mailer ready to share and helping make sure our website work is heading in the right direction (our other Aussie contributors are now back from their respective summer holidays and ready to help again!).




 Continuations 2026/03: Bonus weekend
Continuations 2026/03: Bonus weekendThis edition is going out a couple days later than usual, because I had Bonus Weekend of open source work, and I wanted to be able to share everything with you all at once!
Here’s the background: one of our ambitions for 2026 is to begin a twice-yearly release cadence for Hanami. Since our last release was November, I chose May and November as a starting point. Right now, we’re now getting close to the end of January. We have a new site to ship in February sometime. I’m taking a family trip in April. The team overall has been pretty quiet for the last couple of months. So all of this has had me a bit worried that we wouldn’t have much to share come May.
This weekend the rest of my family went away for a retreat, leaving just me at home. So I took an extra day off work and sat down for two full days of Hanami feature development.
What I got done was the foundation of streamlined i18n support (drop a translations yaml in your project and then Hanami.app["i18n"].t("greeting", name: "Alice") will just work for you), as well as a prototype rebuild of Hanami Mailer to fit in our Hanami 2 ecosystem.
All up, I’m very happy with that outcome! Neither thing is quite ready to share yet, but I should be able to get that done towards the end of this week. This should allow a good couple of months for feedback and testing from our maintainer team and community, and puts us in good stead for a May release.
Aside from that, I did spend my regular Friday working on the site. The biggest change was making our version selectors link directly to the equivalent page in the other version, if it exists. This is exactly the kind of behaviour users would expect, and it also allowed us to get rid of a per-version guides index page, which is no longer necessary now that we show all guides in our left hand side navigation. One less page to design means one step closer to shipping.
I also added some missing Dry guides and tweaked a Parklife config to allow our internal linking to self-versioned guides (mostly the Dry guides) to work properly in production.
Monday, 20th Jan 2025, 6:00pm (ACDT)
Recording is available at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4clkwhrXImY
Attendance record is available upon request
Meeting started at 6:00pm ACDT.
MR JOEL ADDISON, President
Acknowledgment of the traditional owners of the lands on which we meet, particularly the Kaurna people who are the traditional owners of the land that Everything Open 2025 was held on.
MOTION by JOEL ADDISON that the minutes of the Annual General Meeting 2024 of Linux Australia be accepted as complete and accurate.
Seconded by Sae Ra Germaine
Motion Passed with 4 abstentions, no nays
MR JOEL ADDISON – President
The full reports is attached to the annual report, so only a few highlights here:
Questions:
MR NEILL COX – Secretary
Call for people to fill in the attendance sheet.
Again the full report is contained in the Annual Report so just a few highlights here.
MR RUSSELL STUART – Treasurer – Includes presentation of the Auditor’s Report
Questions
Question from Steve Ellis: The 25% is that on revenue or profits?
Response: Profits. There are also other implications [This is a summary of the answer Russell provided see [33:43 of the recording for the full Q&A]
Question from the floor: Of the eight or so what category of non profit seems appropriate or possible?
Response: It turns out we are a scientific institution [again a summary see the recording at 36:01 for the full answer]
Q: You said that if Everything Open didn’t run next year that you would make an $80,000 loss. How could that happen if you don’t run an event.
A[Russell]: No, we wouldn’t make a loss, but we would miss out on the $18,000 profit which is what it made this year. It ranges between that and $40,000 for the last 27 years. [Full answer at 37:18]
Q from Josh Hesketh: What did we provide to Drupal Singapore – was it banks, insurance or other and would we extend that to other conferences in Singapore and further would we consider other countries in the APAC region?
A[Joel]: With that one it was bank accounts and insurance as you mentioned. It’s not certain that we will continue the agreement with the Drupal Association for future conferences. There can also be tax implications. We will assess future conferences as they come up [Full question and answer at 38:48]
Q: Alexar: Is Linux Australia considering having an impact in the APAC region as a strategy or will this just be a case by case approach?
A[Joel]: We’ve always done stuff across Australia and New Zealand and we have supported some other events in the region. We are not ready to commit to a strategic approach without more investigation. For now we are predominantly focussed on Australia and New Zealand but there are opportunities to work with other organisations in the region.
Follow up Question: Can subcommittees pursue similar opportunities?
Follow up Answer: We always say to our subcommittees feel free to bring any ideas to us and we will discuss them with them and go from there.
[Full question and answer at 43:00]
Q [Cherie Ellis]: Is there some way that things can be turned or twisted so that it’s still Everything Open but that LCA or the Linux Australia name is bonded to it so that it becomes the recognizable icon that our sponsors know?
A[Joel]: The sponsors we spoke to understand the alignment.The challenge is that sponsors like IBM are no longer operating in the same way anymore in Australia for that particular area. We managed to find a number of new sponsors this year. Every conference has found that a number of recurring sponsors have said no this year because they can’t afford it or they don’t have the budget. We’ve also had a number of sponsors who signed up and then pulled out in the last two weeks prior to a conference. We expect these challenges to continue over the next 12 months, but we are better prepared for them now. As to bringing LCA back one idea that has been considered is to turn the Linux Kernel Miniconf into LCA as part of Everything Open. That was the intent but we haven’t had enough people step up to make it happen. We do have Carlos from the Open SI institute at the University of Canberra who would like to bring Everything Open to Canberra next year.
[46:45]
Q[Steve Ellis]: Thank you for your support of the community. Do we need a group in Linux Australia focused on sponsorship across all of the events?
A[Joel]: Building a pool of organisations is definitely something we need, not just for sponsorship but also to promote the awareness of the events internally in their organisations. We have discussed setting up some sort of central thing. We could set up a working group and go through some of that. Some of the other conferences have also expressed interest.
[53:48]
Not a Question: Russell forgot to mention that there will be no grants program this year as thet are no profits to pay them from.
[57:31]
Q[Paul Wayper]: Question for the Treasurer: How can the community help Everything Open survive from the ticket price perspective?
A [Russell]: I don’t actually set the budget for the conferences. That’s done by the conference treasurers. I try to give them as much freedom as possible beyond “don’t make a loss”. I don’t have an easy answer for your question.
[58:06]
Returning Officer Julien Goodwin gives his report.
He notes that on examination of the stats Russell and Sae Ra are tied for length of time on the LA Council.
This is Julien’s third time as returning officer.
We have a well-dialed in system now.
The only two things of note are:
Results
Joel: Thank you for coming along to the AGM. I want to say one more thank you to Sae Ra because you have been a big help to me.
Meeting closed at 19:05 ACDT
AGM Minutes Confirmed by 2025 Linux Australia Council
| Joel Addison President |
Jennifer Cox
Vice-President |
Neill Cox
Secretary |
| Russell Stuart
Treasurer |
Lilly Ho
Ordinary Council Member |
Elena Williams
Ordinary Council Member |
| Jonathan Woithe
Ordinary Council Member |
The post 2025 Linux Australia AGM Minutes appeared first on Linux Australia.
I have just got a Furilabs FLX1s [1] which is a phone running a modified version of Debian. I want to have a phone that runs all apps that I control and can observe and debug. Android is very good for what it does and there are security focused forks of Android which have a lot of potential, but for my use a Debian phone is what I want.
The FLX1s is not going to be my ideal phone, I am evaluating it for use as a daily-driver until a phone that meets my ideal criteria is built. In this post I aim to provide information to potential users about what it can do, how it does it, and how to get the basic functions working. I also evaluate how well it meets my usage criteria.
I am not anywhere near an average user. I don’t think an average user would ever even see one unless a more technical relative showed one to them. So while this phone could be used by an average user I am not evaluating it on that basis. But of course the features of the GUI that make a phone usable for an average user will allow a developer to rapidly get past the beginning stages and into more complex stuff.
The Furilabs FLX1s [1] is a phone that is designed to run FuriOS which is a slightly modified version of Debian. The purpose of this is to run Debian instead of Android on a phone. It has switches to disable camera, phone communication, and microphone (similar to the Librem 5) but the one to disable phone communication doesn’t turn off Wifi, the only other phone I know of with such switches is the Purism Librem 5.
It has a 720*1600 display which is only slightly better than the 720*1440 display in the Librem 5 and PinePhone Pro. This doesn’t compare well to the OnePlus 6 from early 2018 with 2280*1080 or the Note9 from late 2018 with 2960*1440 – which are both phones that I’ve run Debian on. The current price is $US499 which isn’t that good when compared to the latest Google Pixel series, a Pixel 10 costs $US649 and has a 2424*1080 display and it also has 12G of RAM while the FLX1s only has 8G. Another annoying thing is how rounded the corners are, it seems that round corners that cut off the content are a standard practice nowadays, in my collection of phones the latest one I found with hard right angles on the display was a Huawei Mate 10 Pro which was released in 2017. The corners are rounder than the Note 9, this annoys me because the screen is not high resolution by today’s standards so losing the corners matters.
The default installation is Phosh (the GNOME shell for phones) and it is very well configured. Based on my experience with older phone users I think I could give a phone with this configuration to a relative in the 70+ age range who has minimal computer knowledge and they would be happy with it. Additionally I could set it up to allow ssh login and instead of going through the phone support thing of trying to describe every GUI setting to click on based on a web page describing menus for the version of Android they are running I could just ssh in and run diff on the .config directory to find out what they changed. Furilabs have done a very good job of setting up the default configuration, while Debian developers deserve a lot of credit for packaging the apps the Furilabs people have chosen a good set of default apps to install to get it going and appear to have made some noteworthy changes to some of them.
The OS is based on Android drivers (using the same techniques as Droidian [2]) and the storage device has the huge number of partitions you expect from Android as well as a 110G Ext4 filesystem for the main OS.
The first issue with the Droidian approach of using an Android kernel and containers for user space code to deal with drivers is that it doesn’t work that well. There are 3 D state processes (uninterrupteable sleep – which usually means a kernel bug if the process remains in that state) after booting and doing nothing special. My tests running Droidian on the Note 9 also had D state processes, in this case they are D state kernel threads (I can’t remember if the Note 9 had regular processes or kernel threads stuck in D state). It is possible for a system to have full functionality in spite of some kernel threads in D state but generally it’s a symptom of things not working as well as you would hope.
The design of Droidian is inherently fragile. You use a kernel and user space code from Android and then use Debian for the rest. You can’t do everything the Android way (with the full OS updates etc) and you also can’t do everything the Debian way. The TOW Boot functionality in the PinePhone Pro is really handy for recovery [3], it allows the internal storage to be accessed as a USB mass storage device. The full Android setup with ADB has some OK options for recovery, but part Android and part Debian has less options. While it probably is technically possible to do the same things in regard to OS repair and reinstall the fact that it’s different from most other devices means that fixes can’t be done in the same way.
The system uses Phosh and Phoc, the GNOME system for handheld devices. It’s a very different UI from Android, I prefer Android but it is usable with Phosh.
Chatty works well for Jabber (XMPP) in my tests. It supports Matrix which I didn’t test because I don’t desire the same program doing Matrix and Jabber and because Matrix is a heavy protocol which establishes new security keys for each login so I don’t want to keep logging in on new applications.
Chatty also does SMS but I couldn’t test that without the SIM caddy.
I use Nheko for Matrix which has worked very well for me on desktops and laptops running Debian.
I am currently using Geary for email. It works reasonably well but is lacking proper management of folders, so I can’t just subscribe to the important email on my phone so that bandwidth isn’t wasted on less important email (there is a GNOME gitlab issue about this – see the Debian Wiki page about Mobile apps [4]).
Music playing isn’t a noteworthy thing for a desktop or laptop, but a good music player is important for phone use. The Lollypop music player generally does everything you expect along with support for all the encoding formats including FLAC0 – a major limitation of most Android music players seems to be lack of support for some of the common encoding formats. Lollypop has it’s controls for pause/play and going forward and backward one track on the lock screen.
The installed map program is gnome-maps which works reasonably well. It gets directions via the Graphhopper API [5]. One thing we really need is a FOSS replacement for Graphhopper in GNOME Maps.
I received my FLX1s on the 13th of Jan [1]. I had paid for it on the 16th of Oct but hadn’t received the email with the confirmation link so the order had been put on hold. But after I contacted support about that on the 5th of Jan they rapidly got it to me which was good. They also gave me a free case and screen protector to apologise, I don’t usually use screen protectors but in this case it might be useful as the edges of the case don’t even extend 0.5mm above the screen. So if it falls face down the case won’t help much.
When I got it there was an open space at the bottom where the caddy for SIMs is supposed to be. So I couldn’t immediately test VoLTE functionality. The contact form on their web site wasn’t working when I tried to report that and the email for support was bouncing.
As a test of Bluetooth I connected it to my Nissan LEAF which worked well for playing music and I connected it to several Bluetooth headphones. My Thinkpad running Debian/Trixie doesn’t connect to the LEAF and to headphones which have worked on previous laptops running Debian and Ubuntu. A friend’s laptop running Debian/Trixie also wouldn’t connect to the LEAF so I suspect a bug in Trixie, I need to spend more time investigating this.
Currently 5GHz wifi doesn’t work, this is a software bug that the Furilabs people are working on. 2.4GHz wifi works fine. I haven’t tested running a hotspot due to being unable to get 4G working as they haven’t yet shipped me the SIM caddy.
This phone doesn’t support DP Alt-mode or Thunderbolt docking so it can’t drive an external monitor. This is disappointing, Samsung phones and tablets have supported such things since long before USB-C was invented. Samsung DeX is quite handy for Android devices and that type feature is much more useful on a device running Debian than on an Android device.
The camera works reasonably well on the FLX1s. Until recently for the Librem 5 the camera didn’t work and the camera on my PinePhone Pro currently doesn’t work. Here are samples of the regular camera and the selfie camera on the FLX1s and the Note 9. I think this shows that the camera is pretty decent. The selfie looks better and the front camera is worse for the relatively close photo of a laptop screen – taking photos of computer screens is an important part of my work but I can probably work around that.
I wasn’t assessing this camera t find out if it’s great, just to find out if I have the sorts of problems I had before and it just worked. The Samsung Galaxy Note series of phones has always had decent specs including good cameras. Even though the Note 9 is old comparing to it is a respectable performance. The lighting was poor for all photos.
In 93 minutes having the PinePhone Pro, Librem 5, and FLX1s online with open ssh sessions from my workstation the PinePhone Pro went from 100% battery to 26%, the Librem 5 went from 95% to 69%, and the FLX1s went from 100% to 99%. The battery discharge rate of them was reported as 3.0W, 2.6W, and 0.39W respectively. Based on having a 16.7Wh battery 93 minutes of use should have been close to 4% battery use, but in any case all measurements make it clear that the FLX1s will have a much longer battery life. Including the measurement of just putting my fingers on the phones and feeling the temperature (FLX1s felt cool and the others felt hot).
The PinePhone Pro and the Librem 5 have an optional “Caffeine mode” which I enabled for this test, without that enabled the phone goes into a sleep state and disconnects from Wifi. So those phones would use much less power with caffeine mode enabled, but they also couldn’t get fast response to notifications etc. I found the option to enable a Caffeine mode switch on the FLX1s but the power use was reported as being the same both with and without it.
One problem I found with my phone is that in every case it takes 22 seconds to negotiate power. Even when using straight USB charging (no BC or PD) it doesn’t draw any current for 22 seconds. When I connect it it will stay at 5V and varying between 0W and 0.1W (current rounded off to zero) for 22 seconds or so and then start charging. After the 22 second display the phone will make the tick sound indicating that it’s charging and the power meter will measure that it’s drawing some current.
I added the table from my previous post about phone charging speed [6] with an extra row for the FLX1s. For charging from my PC USB ports the results were the worst ever, the port that does BC did not work at all it was looping trying to negotiate after a 22 second negotiation delay the port would turn off. The non-BC port gave only 2.4W which matches the 2.5W given by the spec for a “High-power device” which is what that port is designed to give. In a discussion on the Purism forum about the Librem5 charging speed one of their engineers told me that the reason why their phone would draw 2A from that port was because the cable was identifying itself as a USB-C port not a “High-power device” port. But for some reason out of the 7 phones I tested the FLX1s and the One Plus 6 are the only ones to limit themselves to what the port is apparently supposed to do. Also the One Plus 6 charges slowly on every power supply so I don’t know if it is obeying the spec or just sucking.
On a cheap AliExpress charger the FLX1s gets 5.9V and on a USB battery it gets 5.8V. Out of all 42 combinations of device and charger I tested these were the only ones to involve more than 5.1V but less than 9V. I welcome comments suggesting an explanation.
The case that I received has a hole for the USB-C connector that isn’t wide enough for the plastic surrounds on most of my USB-C cables (including the Dell dock). Also to make a connection requires a fairly deep insertion (deeper than the One Plus 6 or the Note 9). So without adjustment I have to take the case off to charge it. It’s no big deal to adjust the hole (I have done it with other cases) but it’s an annoyance.
| Phone | Top z640 | Bottom Z640 | Monitor | Ali Charger | Dell Dock | Battery | Best | Worst |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FLX1s | FAIL | 5.0V 0.49A 2.4W | 4.8V 1.9A 9.0W | 5.9V 1.8A 11W | 4.8V 2.1A 10W | 5.8V 2.1A 12W | 5.8V 2.1A 12W | 5.0V 0.49A 2.4W |
| Note9 | 4.8V 1.0A 5.2W | 4.8V 1.6A 7.5W | 4.9V 2.0A 9.5W | 5.1V 1.9A 9.7W | 4.8V 2.1A 10W | 5.1V 2.1A 10W | 5.1V 2.1A 10W | 4.8V 1.0A 5.2W |
| Pixel 7 pro | 4.9V 0.80A 4.2W | 4.8V 1.2A 5.9W | 9.1V 1.3A 12W | 9.1V 1.2A 11W | 4.9V 1.8A 8.7W | 9.0V 1.3A 12W | 9.1V 1.3A 12W | 4.9V 0.80A 4.2W |
| Pixel 8 | 4.7V 1.2A 5.4W | 4.7V 1.5A 7.2W | 8.9V 2.1A 19W | 9.1V 2.7A 24W | 4.8V 2.3A 11.0W | 9.1V 2.6A 24W | 9.1V 2.7A 24W | 4.7V 1.2A 5.4W |
| PPP | 4.7V 1.2A 6.0W | 4.8V 1.3A 6.8W | 4.9V 1.4A 6.6W | 5.0V 1.2A 5.8W | 4.9V 1.4A 5.9W | 5.1V 1.2A 6.3W | 4.8V 1.3A 6.8W | 5.0V 1.2A 5.8W |
| Librem 5 | 4.4V 1.5A 6.7W | 4.6V 2.0A 9.2W | 4.8V 2.4A 11.2W | 12V 0.48A 5.8W | 5.0V 0.56A 2.7W | 5.1V 2.0A 10W | 4.8V 2.4A 11.2W | 5.0V 0.56A 2.7W |
| OnePlus6 | 5.0V 0.51A 2.5W | 5.0V 0.50A 2.5W | 5.0V 0.81A 4.0W | 5.0V 0.75A 3.7W | 5.0V 0.77A 3.7W | 5.0V 0.77A 3.9W | 5.0V 0.81A 4.0W | 5.0V 0.50A 2.5W |
| Best | 4.4V 1.5A 6.7W | 4.6V 2.0A 9.2W | 8.9V 2.1A 19W | 9.1V 2.7A 24W | 4.8V 2.3A 11.0W | 9.1V 2.6A 24W |
The Furilabs support people are friendly and enthusiastic but my customer experience wasn’t ideal. It was good that they could quickly respond to my missing order status and the missing SIM caddy (which I still haven’t received but believe is in the mail) but it would be better if such things just didn’t happen.
The phone is quite user friendly and could be used by a novice.
I paid $US577 for the FLX1s which is $AU863 by today’s exchange rates. For comparison I could get a refurbished Pixel 9 Pro Fold for $891 from Kogan (the major Australian mail-order company for technology) or a refurbished Pixel 9 Pro XL for $842. The Pixel 9 series has security support until 2031 which is probably longer than you can expect a phone to be used without being broken. So a phone with a much higher resolution screen that’s only one generation behind the latest high end phones and is refurbished will cost less. For a brand new phone a Pixel 8 Pro which has security updates until 2030 costs $874 and a Pixel 9A which has security updates until 2032 costs $861.
Doing what the Furilabs people have done is not a small project. It’s a significant amount of work and the prices of their products need to cover that. I’m not saying that the prices are bad, just that economies of scale and the large quantity of older stock makes the older Google products quite good value for money. The new Pixel phones of the latest models are unreasonably expensive. The Pixel 10 is selling new from Google for $AU1,149 which I consider a ridiculous price that I would not pay given the market for used phones etc. If I had a choice of $1,149 or a “feature phone” I’d pay $1,149. But the FLX1s for $863 is a much better option for me. If all I had to choose from was a new Pixel 10 or a FLX1s for my parents I’d get them the FLX1s.
For a FOSS developer a FLX1s could be a mobile test and development system which could be lent to a relative when their main phone breaks and the replacement is on order. It seems to be fit for use as a commodity phone. Note that I give this review on the assumption that SMS and VoLTE will just work, I haven’t tested them yet.
The UI on the FLX1s is functional and easy enough for a new user while allowing an advanced user to do the things they desire. I prefer the Android style and the Plasma Mobile style is closer to Android than Phosh is, but changing it is something I can do later. Generally I think that the differences between UIs matter more when on a desktop environment that could be used for more complex tasks than on a phone which limits what can be done by the size of the screen.
I am comparing the FLX1s to Android phones on the basis of what technology is available. But most people who would consider buying this phone will compare it to the PinePhone Pro and the Librem 5 as they have similar uses. The FLX1s beats both those phones handily in terms of battery life and of having everything just work. But it has the most non free software of the three and the people who want the $2000 Librem 5 that’s entirely made in the US won’t want the FLX1s.
This isn’t the destination for Debian based phones, but it’s a good step on the way to it and I don’t think I’ll regret this purchase.
Meeting opened at 20:04 AEDT by Joel and quorum was achieved.
Minutes taken by Neill.
Everything Open was notified that a volunteer has been approved for a working with children check. The council will check whether they deliberately used Linux Australia as they are not volunteering with Everything Open or directly with Linux Australia.
MOTION: Linux Australia adds Dave Sparks and Christopher Burgess to its anz.co.nz mandate as payment authorisers.
I seek a seconder and votes on the motion.
I vote in favour of the motion.
Seconded by Jonathan Woithe
Results: Motion passed
secretary@linux.org.au– Contact the volunteer re their working with children check.
secretary@linux.org.au– Send notification of upcoming election.
Meeting closed at 20:44 AEDT
Next meeting is scheduled for 2026-01-14 and is not a subcommittee meeting, but will be the final meeting for the current council.
The post 2025-12-17 Council Meeting Minutes appeared first on Linux Australia.
Meeting opened at 20:05 AEDT by Joel and quorum was achieved
Minutes taken by Neill.
https://lists.linux.org.au/pipermail/announce/2024-December/000373.html
Secretary to send reminder for membership on the 10th
Dates:
Meeting closed at 21:53 AEDT (UT+11:00)
Next meeting is scheduled for 2025-12-17 at 20:00 AEDT (UT+11:00)
The post 2025-12-03 Council Meeting Minutes appeared first on Linux Australia.
I just read this informative article on ANSI terminal security [1]. The author has written a tool named vt-houdini for testing for these issues [2]. They used to host an instance on their server but appear to have stopped it. When you run that tool you can ssh to the system in question and without needing a password you are connected and the server probes your terminal emulator for vulnerabilities. The versions of Kitty and Konsole in Debian/Trixie have just passed those tests on my system.
This will always be a potential security problem due to the purpose of a terminal emulator. A terminal emulator will often display untrusted data and often data which is known to come from hostile sources (EG logs of attempted attacks). So what could be done in this regard?
Due to the complexity of terminal emulation there is the possibility of buffer overflows and other memory management issues that could be used to compromise the emulator.
The Fil-C compiler is an interesting project [3], it compiles existing C/C++ code with memory checks. It is reported to have no noticeable impact on the performance of the bash shell which sounds like a useful option to address some of these issues as shell security issues are connected to terminal security issues. The performance impact on a terminal emulator would be likely to be more noticeable. Also note that Fil-C compilation apparently requires compiling all libraries with it, this isn’t a problem for bash as the only libraries it uses nowadays are libtinfo and libc. The kitty terminal emulator doesn’t have many libraries but libpython is one of them, it’s an essential part of Kitty and it is a complex library to compile in a different way. Konsole has about 160 libraries and it isn’t plausible to recompile so many libraries at this time.
Choosing a terminal emulator that has a simpler design might help in this regard. Emulators that call libraries for 3D effects etc and native support for displaying in-line graphics have a much greater attack surface.
A terminal emulator could be run in a container to prevent it from doing any damage if it is compromised. But the terminal emulator will have full control over the shell it runs and if the shell has access needed to allow commands like scp/rsync to do what is expected of them then that means that no useful level of containment is possible.
It would be possible to run a terminal emulator in a container for the purpose of connecting to an insecure or hostile system and not allow scp/rsync to/from any directory other than /tmp (or other directories to use for sharing files). You could run “exec ssh $SERVER” so the terminal emulator session ends when the ssh connection ends.
There aren’t good solutions to the problems of terminal emulation security. But testing every terminal emulator with vt-houdini and fuzzing the popular ones would be a good start.
Qubes level isolation will help things in some situations, but if you need to connect to a server with privileged access to read log files containing potentially hostile data (which is a common sysadmin use case) then there aren’t good options.
About 6 months ago I got a Nissan LEAF ZE1 (2019 model) [1]. Generally it’s going well and I’m happy with most things about it.
One issue is that as there isn’t a lot of weight in the front with the batteries in the centre of the car the front wheels slip easily when accelerating. It’s a minor thing but a good reason for wanting AWD in an electric car.
When I got the car I got two charging devices, the one to charge from a regular 240V 10A power point (often referred to as a “granny charger”) and a cable with a special EV charging connector on each end. The cable with an EV connector on each end is designed for charging that’s faster than the “granny charger” but not as fast as the rapid chargers which have the cable connected to the supply so the cable temperature can be monitored and/or controlled. That cable can be used if you get a fast charger setup at your home (which I never plan to do) and apparently at some small hotels and other places with home-style EV charging. I’m considering just selling that cable on ebay as I don’t think I have any need to personally own a cable other than the “granny charger”.
The key fob for the LEAF has a battery installed, it’s either CR2032 or CR2025 – mine has CR2025. Some reports on the Internet suggest that you can stuff a CR2032 battery in anyway but that didn’t work for me as the thickness of the battery stopped some of the contacts from making a good connection. I think I could have got it going by putting some metal in between but the batteries aren’t expensive enough to make it worth the effort and risk. It would be nice if I could use batteries from my stockpile of CR2032 batteries that came from old PCs but I can afford to spend a few dollars on it.
My driveway is short and if I left the charger out it would be visible from the street and at risk of being stolen. I’m thinking of chaining the charger to a tree and having some sort of waterproof enclosure for it so I don’t have to go to the effort of taking it out of the boot every time I use it. Then I could also configure the car to only charge during the peak sunlight hours when the solar power my home feeds into the grid has a negative price (we have so much solar power that it’s causing grid problems).
The cruise control is a pain to use, so much so that I haven’t yet got it to work usefully ever. The features look good in the documentation but in practice it’s not as good as the Kia one I’ve used previously where I could just press one button to turn it on, another button to set the current speed as the cruise control speed, and then just have it work.
The electronic compass built in to the dash turned out to be surprisingly useful. I regret not gluing a compass to the dash of previous cars. One example is when I start google navigation for a journey and it says “go South on street X” and I need to know which direction is South so I don’t start in the wrong direction. Another example is when I know that I’m North of a major road that I need to take to get to my destination so I just need to go roughly South and that is enough to get me to a road I recognise.
In the past when there is a bird in the way I don’t do anything different, I keep driving at the same speed and rely on the bird to see me and move out of the way. Birds have faster reactions than humans and have evolved to move at the speeds cars travel on all roads other than freeways, also birds that are on roads are usually ones that have an eye in each side of their head so they can’t not see my car approaching. For decades this has worked, but recently a bird just stood on the road and got squashed. So I guess that I should honk when there’s birds on the road.
Generally everything about the car is fine and I’m happy to keep driving it.
One of the problems I encountered with the PinePhone Pro (PPP) when I tried using it as a daily driver [1] was the charge speed, both slow charging and a bad ratio of charge speed to discharge speed. I also tried using a One Plus 6 (OP6) which had a better charge speed and battery life but I never got VoLTE to work [2] and VoLTE is a requirement for use in Australia and an increasing number of other countries. In my tests with the Librem 5 from Purism I had similar issues with charge speed [3].
What I want to do is get an acceptable ratio of charge time to use time for a free software phone. I don’t necessarily object to a phone that can’t last an 8 hour day on a charge, but I can’t use a phone that needs to be on charge for 4 hours during the day. For this part I’m testing the charge speed and will test the discharge speed when I have solved some issues with excessive CPU use.
I tested with a cheap USB power monitoring device that is inline between the power cable and the phone. The device has no method of export so I just watched it and when the numbers fluctuated I tried to estimate the average. I only give the results to two significant digits which is about all the accuracy that is available, as I copied the numbers separately the V*A might not exactly equal the W. I idly considered rounding off Voltages to the nearest Volt and current to the half amp but the way the PC USB ports have voltage drop at higher currents is interesting.
This post should be useful for people who want to try out FOSS phones but don’t want to buy the range of phones and chargers that I have bought.
I have seen claims about improvements with charging speed on the Librem 5 with recent updates so I decided to compare a number of phones running Debian/Trixie as well as some Android phones. I’m comparing an old Samsung phone (which I tried running Droidian on but is now on Android) and a couple of Pixel phones with the three phones that I currently have running Debian for charging.
The Librem 5 had problems with charging on a port on the HP ML110 Gen9 I was using as a workstation. I have sold the ML110 and can’t repeat that exact test but I tested on the HP z640 that I use now. The z640 is a much better workstation (quieter and better support for audio and other desktop features) and is also sold as a workstation.
The z640 documentation says that of the front USB ports the top one can do “fast charge (up to 1.5A)” with “USB Battery Charging Specification 1.2”. The only phone that would draw 1.5A on that port was the Librem 5 but the computer would only supply 4.4V at that current which is poor. For every phone I tested the bottom port on the front (which apparently doesn’t have USB-BC or USB-PD) charged at least as fast as the top port and every phone other than the OP6 charged faster on the bottom port. The Librem 5 also had the fastest charge rate on the bottom port. So the rumours about the Librem 5 being updated to address the charge speed on PC ports seem to be correct.
The Wikipedia page about USB Hardware says that the only way to get more than 1.5A from a USB port while operating within specifications is via USB-PD so as USB 3.0 ports the bottom 3 ports should be limited to 5V at 0.9A for 4.5W. The Librem 5 takes 2.0A and the voltage drops to 4.6V so that gives 9.2W. This shows that the z640 doesn’t correctly limit power output and the Librem 5 will also take considerably more power than the specs allow. It would be really interesting to get a powerful PSU and see how much power a Librem 5 will take without negotiating USB-PD and it would also be interesting to see what happens when you short circuit a USB port in a HP z640. But I recommend not doing such tests on hardware you plan to keep using!
Of the phones I tested the only one that was within specifications on the bottom port of the z640 was the OP6. I think that is more about it just charging slowly in every test than conforming to specs.
The next test target is my 5120*2160 Kogan monitor with a USB-C port [4]. This worked quite well and apart from being a few percent slower on the PPP it outperformed the PC ports for every device due to using USB-PD (the only way to get more than 5V) and due to just having a more powerful PSU that doesn’t have a voltage drop when more than 1A is drawn.
The Ali Charger is a device that I bought from AliExpress is a 240W GaN charger supporting multiple USB-PD devices. I tested with the top USB-C port that can supply 100W to laptops.
The Librem 5 has charging going off repeatedly on the Ali charger and doesn’t charge properly. It’s also the only charger for which the Librem 5 requests a higher voltage than 5V, so it seems that the Librem 5 has some issues with USB-PD. It would be interesting to know why this problem happens, but I expect that a USB signal debugger is needed to find that out. On AliExpress USB 2.0 sniffers go for about $50 each and with a quick search I couldn’t see a USB 3.x or USB-C sniffer. So I’m not going to spend my own money on a sniffer, but if anyone in Melbourne Australia owns a sniffer and wants to visit me and try it out then let me know. I’ll also bring it to Everything Open 2026.
Generally the Ali charger was about the best charger from my collection apart from the case of the Librem 5.
I got a number of free Dell WD15 (aka K17A) USB-C powered docks as they are obsolete. They have VGA ports among other connections and for the HDMI and DisplayPort ports it doesn’t support resolutions higher than FullHD if both ports are in use or 4K if a single port is in use. The resolutions aren’t directly relevant to the charging but it does indicate the age of the design.
The Dell dock seems to not support any voltages other than 5V for phones and 19V (20V requested) for laptops. Certainly not the 9V requested by the Pixel 7 Pro and Pixel 8 phones. I wonder if not supporting most fast charging speeds for phones was part of the reason why other people didn’t want those docks and I got some for free. I hope that the newer Dell docks support 9V, a phone running Samsung Dex will display 4K output on a Dell dock and can productively use a keyboard and mouse. Getting equivalent functionality to Dex working properly on Debian phones is something I’m interested in.
The “Battery” I tested with is a Chinese battery for charging phones and laptops, it’s allegedly capable of 67W USB-PD supply but so far all I’ve seen it supply is 20V 2.5A for my laptop. I bought the 67W battery just in case I need it for other laptops in future, the Thinkpad X1 Carbon I’m using now will charge from a 30W battery.
There seems to be an overall trend of the most shonky devices giving the best charging speeds. Dell and HP make quality gear although my tests show that some HP ports exceed specs. Kogan doesn’t make monitors, they just put their brand on something cheap. Buying one of the cheapest chargers from AliExpress and one of the cheaper batteries from China I don’t expect the highest quality and I am slightly relieved to have done enough tests with both of those that a fire now seems extremely unlikely. But it seems that the battery is one of the fastest charging devices I own and with the exception of the Librem 5 (which charges slowly on all ports and unreliably on several ports) the Ali charger is also one of the fastest ones. The Kogan monitor isn’t far behind.
The Samsung Galaxy Note 9 was released in 2018 as was the OP6. The PPP was first released in 2022 and the Librem 5 was first released in 2020, but I think they are both at a similar technology level to the Note 9 and OP6 as the companies that specialise in phones have a pipeline for bringing new features to market.
The Pixel phones are newer and support USB-PD voltage selection while the other phones either don’t support USB-PD or support it but only want 5V. Apart from the Librem 5 which wants a higher voltage but runs it at a low current and repeatedly disconnects.
One of the major problems I had in the past which prevented me from using a Debian phone as my daily driver is the ratio of idle power use to charging power. Now that the phones seem to charge faster if I can get the idle power use under control then it will be usable.
Currently the Librem 5 running Trixie is using 6% CPU time (24% of a core) while idle and the screen is off (but “Caffeine” mode is enabled so no deep sleep). On the PPP the CPU use varies from about 2% and 20% (12% to 120% of one core), this was mainly plasmashell and kwin_wayland. The OP6 has idle CPU use a bit under 1% CPU time which means a bit under 8% of one core.
The Librem 5 and PPP seem to have configuration issues with KDE Mobile and Pipewire that result in needless CPU use. With those issues addressed I might be able to make a Librem 5 or PPP a usable phone if I have a battery to charge it.
The OP6 is an interesting point of comparison as a Debian phone but is not a viable option as a daily driver due to problems with VoLTE and also some instability – it sometimes crashes or drops off Wifi.
The Librem 5 charges at 9.2W from a a PC that doesn’t obey specs and 10W from a battery. That’s a reasonable charge rate and the fact that it can request 12V (unsuccessfully) opens the possibility to potential higher charge rates in future. That could allow a reasonable ratio of charge time to use time.
The PPP has lower charging speeds then the Librem 5 but works more consistently as there was no charger I found that wouldn’t work well with it. This is useful for the common case of charging from a random device in the office. But the fact that the Librem 5 takes 10W from the battery while the PPP only takes 6.3W would be an issue if using the phone while charging.
Now I know the charge rates for different scenarios I can work on getting the phones to use significantly less power than that on average.
The 57W battery or something equivalent is something I think I will always need to have around when using a PPP or Librem 5 as a daily driver.
The ability to charge fast while at a desk is also an important criteria. The charge speed of my home PC is good in that regard and the charge speed of my monitor is even better. Getting something equivalent at a desktop of an office I work in is a possibility.
Improving the Debian distribution for phones is necessary. That’s something I plan to work on although the code is complex and in many cases I’ll have to just file upstream bug reports.
I have also ordered a FuriLabs FLX1s [5] which I believe will be better in some ways. I will blog about it when it arrives.
| Phone | Top z640 | Bottom Z640 | Monitor | Ali Charger | Dell Dock | Battery | Best | Worst |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Note9 | 4.8V 1.0A 5.2W | 4.8V 1.6A 7.5W | 4.9V 2.0A 9.5W | 5.1V 1.9A 9.7W | 4.8V 2.1A 10W | 5.1V 2.1A 10W | 5.1V 2.1A 10W | 4.8V 1.0A 5.2W |
| Pixel 7 pro | 4.9V 0.80A 4.2W | 4.8V 1.2A 5.9W | 9.1V 1.3A 12W | 9.1V 1.2A 11W | 4.9V 1.8A 8.7W | 9.0V 1.3A 12W | 9.1V 1.3A 12W | 4.9V 0.80A 4.2W |
| Pixel 8 | 4.7V 1.2A 5.4W | 4.7V 1.5A 7.2W | 8.9V 2.1A 19W | 9.1V 2.7A 24W | 4.8V 2.3A 11.0W | 9.1V 2.6A 24W | 9.1V 2.7A 24W | 4.7V 1.2A 5.4W |
| PPP | 4.7V 1.2A 6.0W | 4.8V 1.3A 6.8W | 4.9V 1.4A 6.6W | 5.0V 1.2A 5.8W | 4.9V 1.4A 5.9W | 5.1V 1.2A 6.3W | 4.8V 1.3A 6.8W | 5.0V 1.2A 5.8W |
| Librem 5 | 4.4V 1.5A 6.7W | 4.6V 2.0A 9.2W | 4.8V 2.4A 11.2W | 12V 0.48A 5.8W | 5.0V 0.56A 2.7W | 5.1V 2.0A 10W | 4.8V 2.4A 11.2W | 5.0V 0.56A 2.7W |
| OnePlus6 | 5.0V 0.51A 2.5W | 5.0V 0.50A 2.5W | 5.0V 0.81A 4.0W | 5.0V 0.75A 3.7W | 5.0V 0.77A 3.7W | 5.0V 0.77A 3.9W | 5.0V 0.81A 4.0W | 5.0V 0.50A 2.5W |
| Best | 4.4V 1.5A 6.7W | 4.6V 2.0A 9.2W | 8.9V 2.1A 19W | 9.1V 2.7A 24W | 4.8V 2.3A 11.0W | 9.1V 2.6A 24W |
I am not entirely sure what makes the AI debate so polarizing, although I suspect it has something to do with feeling threatened by a changing landscape. What I can say with certainty is that I find having a nuanced conversation about AI with people often difficult. It seems to me that people fall into two polar opposite camps — those who thing AI is completely great and that we should fire all the programmers and creatives; and those who think that AI is all bad and we should go backwards in time to a place before it existed.
Honestly, I think neither end of the spectrum is right. I should admit here that my own stance is significantly more nuanced that it was six months ago, but having now used various code assistant LLMs for a few months there are clearly useful contributions it makes to my work day. I think the elevator pitch would be something like “AI is a useful tool if treated like very smart autocomplete in tightly constrained environments”. I would even go so far as to say that one of the measures of “AI maturity” of a code base should be how tight the constraints are — unit tests, functional tests, static analysis, and so forth don’t go away with AI generated code — they are in fact more important than ever.
This is where the inexperienced developers will trip themselves up. If they’re not reviewing the generated code closely and course correcting the machine as required, then they’re likely to end up with a mess that isn’t performant or maintainable. The human still needs to know what “good” looks like. I think version control is key here too, because being able to walk backwards when you went down a dead end remains just as important as ever.
The thing is the current state of the art for code generation AIs is about as good as a junior developer. It requires just as much supervision, coaching, and prompting to think about the right things. However, just as you wouldn’t get a junior developer to mentor another junior developer, I am not sure that everyone has the skills required to adequately supervise the current state of the art in code generation.
I am on vacation, as I am sure many people are at this time of year. This means the usual things for me — cleaning up the home office, this time in the most annoying manner I can think of; playing with personal projects I haven’t had time for during the year; and just… resting. Part of resting for me is reading, which is how I happened up this excellent blog post about how the expectations placed upon Silicon Valley engineering managers have changed over the last couple of decades.
The post resonates strongly with me — I think the idea that the expectations placed upon managers have changed in noticeable eras is true, but it also explains my own mixed feelings about the Silicon Valley of today. You see, as the industry became less passionate about treating engineers well and building things which genuinely improved the world over the last couple of years, I became less passionate about being treated poorly by my employers. It is definitely true that an employer is within their rights to let you know that you’re a replaceable asset of convenience, which I think is definitely a thing Cisco reinforced as often as possible, but the inverse is also true. If this employment thing is a purely commercial relationship, then it is simply rational for me to take a better offer if it comes along without feeling any guilt.
That is, I wonder if the industry will enjoy reaping what they are currently sowing when those better opportunities do inevitably come along?
As I bid adieu to 2025, annus horribilis, I wish to welcome 2026, Annus Mirabilis.
What changed from Hello 2025?
Fell in love with Pumpkin, Vanessa’s dog. I only did 41 days of travel, 7 trips, 13 cities and 36,049 miles. This was basically covid 2020 ;)
Ushered it in Kuala Lumpur 2025 and 2026.
I look forward to having a better year ahead. Best year as 42 is coming, and that is the answer to life, the universe and everything.
Know whom my friends are. Know who were fair weather friends. Very enlightening 2025 has been. You’ll eat, just not at my table.
Ever onwards. And upwards.
As a follow up from my last post about my 8K TV [1] I tested out a Samsung 65″ QN900C Neo QLED 8K that’s on sale in JB Hifi. According to the JB employee I spoke to they are running out the last 8K TVs and have no plans to get more.
In my testing of that 8K TV YouTube had a 3840*2160 viewport which is better than the 1920*1080 of my Hisense TV. When running a web browser the codeshack page reported it as 1920*1080 with a 1.25* pixel density (presumably a configuration option) that gave a usable resolution of 1536*749.
The JB Hifi employee wouldn’t let me connect my own device via HDMI but said that it would work at 8K. I said “so if I buy it I can return it if it doesn’t do 8K HDMI?” and then he looked up the specs and found that it would only do 4K input on HDMI. It seems that actual 8K resolution might work on a Samsung streaming device but that’s not very useful particularly as there probably isn’t much 8K content on any streaming service.
Basically that Samsung allegedly 8K TV only works at 4K at best.
It seems to be impossible to buy an 8K TV or monitor in Australia that will actually display 8K content. ASUS has a 6K 32″ monitor with 6016*3384 resolution for $2016 [2]. When counting for inflation $2016 wouldn’t be the most expensive monitor I’ve ever bought and hopefully prices will continue to drop.
Rumour has it that there are 8K TVs available in China that actually take 8K input. Getting one to Australia might not be easy but it’s something that I will investigate.
Also I’m trying to sell my allegedly 8K TV.
Russ Allbery wrote an interesting review of Politics on the Edge, by Rory Stewart who sems like one of the few conservative politicians I could respect and possibly even like [1]. It has some good insights about the problems with our current political environment.
Wired has an interesting article about computer face recognition systems failing on people with facial disabilities or scars [3]. This is a major accessibility issue potentially violating disability legislation and a demonstration of the problems of fully automating systems when there should be a human in the loop.
The October 2025 report from the Debian Reproducible Builds team is particularly interesting [4]. “kpcyrd forwarded a fascinating tidbit regarding so-called ninja and samurai build ordering, that uses data structures in which the pointer values returned from malloc are used to determine some order of execution” LOL
Louis Rossman made an insightful video about the way that Hyundai is circumventing Right to Repair laws to make repairs needlessly expensive [6]. Korean cars aren’t much good nowadays. Their prices keep increasing and the quality doesn’t.
Brian Krebs wrote an interesting article about how Google is taking legal action against SMS phishing crime groups [7]. We need more of this!
Josh Griffiths wrote an informative blog post about how YouTube is awful [8]. I really should investigate Peertube.
Louis Rossman made an informative YouTube video about Right to Repair and the US military, if even the US military is getting ripped off by this it’s a bigger problem than most people realise [9]. He also asks the rhetorical question of whether politicians are bought or whether it’s a “subscription model”.
Brian Krebs wrote an informative article about “free streaming” Android TV boxes that act as hidden residential VPN proxies [11]. Also the “free streaming” violates copyright law.
Linus Tech Tips has an interesting interview with Linus Torvalds [14].
Interesting video about the Kowloon Walled City [15]. It would be nice if a government deliberately created a hive city like that, the only example I know of is the Alaskan town in a single building.
I’ve had a Creality CFS upgrade for my K1 Max sitting on my workbench for probably a month waiting for me to install it. Part of that delay is that I knew it would take a while to install, and I am glad I waited.
I finally got around to doing that yesterday, and I have thoughts… First off, the Creality installation documentation is ok, but not great. I would have been in a lot more pain without Thinkering with Jerd’s tutorial video. So thank you to Jerd, whoever you may be. I also agree with Jerd that the extensive use of hot glue on connectors is super annoying. While I suspect it makes sense in terms of ensuring that devices work when they arrive to a customer, it makes upgrades super annoying and surely there is a better way. Overall I think I spent at least six hours on the install.
But what about multicolor printing now that I’ve finished the upgrade? Well, my initial observations align mostly with my expectations in that:
Printing is slow if there are color changes. This is especially true if you include the time taken by filament jams and failures to feed that I didn’t notice immediately. My first non-trivial test print will likely take 16 hours to complete. So, you can’t just set a complicated print going and go to work. It will be unlikely to have finished by the time you get home because it will jam somewhere along the way. This is especially annoying given that the way I’ve been clearing the jams is simply to press “retry”, which seems to resolve the issues. Could the machine not do that for me?
Multicolor printing is also a bit wasteful, even when using “flush to infill”. I was expecting this, but yeah its definitely a thing.
These are of course only true for multicolor prints, if you treat the thing as a loader which can deliver whatever single color you need for this specific print then its pretty cool out of the box.
To address the multicolor print issues, I have learned you should minimize the numbers of colors per layer to reduce time and waste, as well as ordering some unobtainium PFTE tube replacement which alleges it will jam less by being “more slippery”. We’ll see how that goes I suppose.
Finally, I was also surprised by how the filament change worked. I assumed that anything already loaded into the feeder tube would be flushed, and therefore tube length should be minimized. This is in fact not true, the filament gets retracted — the change of filament waste is driven by flushing the extruder and having to clean the extruder between colors. So, you can in fact have the CFS further away from the printer than I expected, although I had to consume PFTE tube to learn that. I do expect that the longer the feed tube the more filament failures to load, but then again the tighter the bends in the tube the more of those too, so there is a balance here somewhere.
What is you want to study computer science, but can’t afford university fees? Or, studied computer science a really long time ago and want to see what’s changed? Or just like learning stuff? Well, lots of schools now post their lectures on YouTube, so its entirely possible to construct a zero cost “self driving degree”, as long as you’re good enough at Canva to make your own certificate at the end. I consider this list incomplete, but in the end I decided I’d post the things from 2025 that I’d found and liked. I can always do an updated version later.
Introduction
Databases
The focus here isn’t on SQL itself, there are lots of places to learn that. Instead, the focus here is how does a database actually work under the hood? That said, let’s chuck in a quick SQL introduction anyway.
Operating Systems
Networking
I am a bit shocked to discover that you can get through an entire Computer Science degree now without covering networking at all. That’s… concerning.
Programming Languages
Machine Learning
Security
Meeting opened at 20:08 AEDT by Joel and quorum was achieved.
Minutes taken by Neill.
After a discussion between Jack and Russell about Stripe’s tax notifications, it seems reasonable to argue that we shouldn’t have to pay VAT/GST in other countries for services being consumed in Australia.
Russell: Our Accountant didn’t give us firm advice one way or the other when I asked him.
Russell: If someone was paying us to watch the live stream while they are in another country it might be different. Therefore we can’t sell digital tickets to overseas attendees.
Russell feels that some of this may be an attempt by Stripe to sell us a service.
Elena suggests that we should just say that digital tickets are sold under Australian conditions.
We will develop a written policy on this and publish and make subcommittees aware of it. Elena will write the first version.
Michael has informed the Steering Committee that he is going to leave the Committee, and they are evaluating their options for the next DrupalCon, probably in India, probably in 2027.
Elena has started work on the annual report. There is a document in the shared drive. Elena will produce a plan for chasing down the required information this week.
I am writing to you about your recent application to join Linux Australia._
We would like to confirm that you would still like to join and if so ask if you could outline how you currently participate in our community.
We aim to represent and assist the groups and individuals who make up the Free Software, Open Source and Open Technology communities in Australia.
We support a number of conferences in Australia, New Zealand/Aotearoa and the Asia Pacific region, including Everything Open, Drupal Down Under, Pycon Au and Kiwi Pycon
Can you tell us how you heard of us, and briefly describe your participation in the communities we represent? There are no specific requirements for membership, but to reduce the number of spam applications, we are confirming applications are genuine before we approve them.
Meeting closed at 20:48 AEDT
Next meeting is scheduled for 2025-12-03 and is a subcommittee meeting
The post 2025-11-19 Council Meeting Minutes appeared first on Linux Australia.
Meeting opened at 20:07 AEDT by Jennifer and quorum was achieved at 20:13 AEDT
Minutes taken by Neill.
I’ve also started a new informal essay series titled “From the directors desk” where I share a little more transparently how we approach organising PyCon AU 2026 behind the scenes. The first post is live, and I’d welcome feedback – primarily in the shape of future topic suggestions 
Lastly: I’m aware our plan to update ‘actuals’ in the approved/shared budget has been delayed. Nic will be back on deck ‘soon’ . The delay is primarily optimising for getting it right as a team, for the long term, and in a repeatable way aligned to Xero actuals. As an interim reassurance: we reconcile Xero weekly, and I’m tracking closely any budgeted spend this year (narrator: minimal to no new spend expected) matched closely against actuals in Xero. I’ll raise to discuss on Wednesday night.
Proposed Agenda for our 5 minutes on Wednesday:

Meeting closed at 21:43
Next meeting is scheduled for 2025-11-19 at 20:00 AEDT (UT+11:00)
The post 2025-11-05 Council Meeting Minutes appeared first on Linux Australia.
Meeting opened at 19:35 AEDT by Jennifer and quorum was achieved at 19:56.
Minutes taken by Neill.

Hello Councillors,Â
I’m sorry to say I can’t make it to the meeting tonight.Â
I have however updated our usual slides with the latest information. We’re falling a bit behind on sponsorship and ticket sales. We still have some strong sponsors in the pipeline, but they’re getting harder to pin down.Â
The treasure hunt has gone live and you can see more here. We’ve turned this into a paid event with a small fee, and also opened it up to non-Con attendees, provided one person on the team has a Conference ticket.Â
We’re working hard to try and secure some final sponsors. We know from last year that most of our registrations will come at the very end: For Singapore, we went from 130 to 250 ticket holders in the last 6 weeks so hopefully we will see a repeat here.Â
Apologies again I can’t make it tonight!Â
Mike
Hi all,
I’ve had bit going on outside work these last few weeks and don’t have much of an update for this evening, so sending my apologies.
As far as updates go, Terry the other account signatory has completed his induction etc, so the bank account and Stripe are set up, but we’re yet to spend any money 
Work is continuing on the Joomla AU website revamp and we should have the memberships live next week.
I’ll be at next month’s meeting in person to provide an update.
Cheers
Nathan
Still waiting on payment from a few last minute sponsors.
Good attendance with excellent diversity.
Currently looking at roughly $5k loss.
Attached is an update ahead of tomorrow night’s LAC meeting.
A copy is provided here, and all updates & docs for Linux Australia remain here (good for a bookmark  ). [Links removed in published minutes]
). [Links removed in published minutes]
While the update is looking backwards, I wanted to share a few “looking forward” points:
We’re aiming to finish assembling the core team by month end (October)
We’re intending to have a published “Call for track organisers” in time for Kiwi PyCon at the end of November
We’re intending to have an updated ‘full’ 2026 website in time for that call for tracks.
Additionally (admin, primarily for Russell’s benefit):
We’re aware of an unreconciled PayPal transaction in Xero; Pete has forwarded from Russell’s email. We’ll get that reconciled in due course
We’re mindful that the currently shared budget spreadsheet does not have actuals yet. Thats our top priority to be on top of now.
We noticed a miscalculation in Fixed Costs that did not include the Financial Assitance grants in the total costs. ‘Fixed Costs’ tab has been updated to amend this (specifically the sums in I24, J24, I58, J58) . Total impact is ~$5k which does not affect our P&L position in either budget scenario and is something for us to navigate in April next year pending sponsorships.
Speak tomorrow!
Cheers,
Jack
The on list motion passed. The budget is approved.
The motion was:
ON LIST MOTION: Linux Australia accepts the DrupalSouth Wellington 2025 organising committee as a subcommittee of Linux Australia, and authorises the expenditure on the budget submitted with their proposal.
Proposer: Russell Stuart
Seconded: Jonathan
Motion Passed by a majority of the council.
Jonathan will let Julia know about Council’s approval of the Drupal South budget.
Meeting closed at 21:12
Next meeting is scheduled for 2025-10-22 at 20:00 AEDT (UT+11:00)
The post 2025-10-08 Council Meeting Minutes appeared first on Linux Australia.
Meeting opened at 19:32 AEDT by Joel and quorum was achieved.
Minutes taken by Jonathan.
[Link removed]
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u8uyP4dYv5A

DrupalSouth operating budget – Wellington 2026 [Link removed]
The subcommittee would like feedback within the next couple of weeks.
Russell to allocate a Stripe account and Bank Account for EO2026.
That Linux Australia suspend LUV’s access to its bank account.
Seconded: Russell
Passed unanimously
Meeting closed at 20:52
Next meeting is scheduled for 2025-09-24 at 19:30 AEST (UT+10:00)
The post 2025-09-10 Council Meeting Minutes appeared first on Linux Australia.
Meeting opened at 19:40 AEDT by Russell and quorum was achieved.
Minutes taken by Neill.
PROPOSER: Russell Stuart
Seconded: Jonathan
Result: Passed
The proposal looks good to those of us present at this meeting, but we will defer final discussion to a meeting where more council members are available.
We will need a more formal proposal to vote on.
Meeting closed at 20:17 AEST
Next meeting is scheduled for 2025-09-10 and is a subcommittee meeting
The post 2025-08-27 Council Meeting Minutes appeared first on Linux Australia.
With at least three disciplines of interest - energy and climatology, public economics, and high-performance computing - there is the issue of whether current trends in artificial intelligence are environmentally sustainable. The following is a basic sketch of electricity usage, needs, and costings.
The promise of artificial intelligence is as old as computing itself, and, in some ways, it is difficult to distinguish from computing in general. As the old joke goes, it is no contest for real stupidity, and an issue that became all too evident to Charles Babbage when he developed the idea of a programmable computer:
On two occasions I have been asked, - "Pray, Mr. Babbage, if you put into the machine wrong figures, will the right answers come out?" ... I am not able rightly to apprehend the kind of confusion of ideas that could provoke such a question.
-- Passages from the Life of a Philosopher (1864), ch. 5 "Difference Engine No. 1"
Of course, we now have computational devices that can attempt to solve problems with incorrect inputs and perhaps provide a correct answer. That, if anything, is what distinguishes classical computation from contemporary artificial intelligence. Time does not permit a thorough exploration of the rise and fall of several attempts to implement AI; however, the most recent version of the last decade, which involves the application of transformer deep learning and the use of Graphics Processing Units, continues to attract investment and interest.
Transformer architectures for artificial neural networks are a fascinating topic in their own right; attention (pun intended) is directed to the use of GPUs as the main issue. Whilst the physical architecture of GPUs makes them particularly suitable for graphics processing, it was also realised that they could be used for a variety of vector processing, providing massive data parallelism, i.e., "general purpose (computing on) graphics processing units", GPGPUs. However, physics gets in the way of the pure mathematical potential of GPUs; they generate a significant amount of heat and require substantial electricity, and that's where the environmental question arises.
The current global electricity consumption by data centres is approximately 1.5%, according to the International Energy Agency. However, that is expected to reach 3.0% by 2030, primarily due to the growth of AI, which would include not just the GPUs themselves, but also the proportional contributions by CPU hosts, cooling, transport, installation, and so forth. A doubling of energy consumption over a period of a few years (from c400TWh in 2024 to c900TWh in 2030) is very significant and, if the estimates prove to be even roughly correct, then further energy utilisation needs to be considered as an ongoing trajectory for at least another two decades until it becomes ubiquitous.
There are essentially two ways of managing energy used in production with an environmental perspective, given a particular policy. One approach is high-energy and high-production, concentrating on renewables or non-GHG energy sources. The other is a reduced-energy, high-efficiency approach that concentrates on better outcomes, "doing more with less". More important than either of these, in my opinion, is the incorporation of externalised costs into the internal price of an energy source. One graphic example of this is the deaths per Terawatt-hour by energy source. Solar, for example, is more than three orders of magnitude safer than coal.
To satisfy existing and expected demand, the AI industry is, in part, turning to nuclear for its energy needs. Data centres tend to be located within population centres, partially due to latency reasons, whereas renewables like wind and solar require a significant amount of land area. Additionally, where existing nuclear power plants and infrastructure are already in place, it is relatively inexpensive, even compared to battery technologies. Nuclear provides sustained power generation not just throughout the day, but across months and seasons. With approximately 5% of generation lost in transmission, nearby power sources are more efficient.
The main weakness of nuclear power is the time and cost associated with the construction of new plants, and in this regard, the big data centre and technology groups are taking a gamble. They assume that there will be sufficient demand for AI and that they can generate enough income over the next decade to cover the costs. Whilst they are very likely to be correct in this assessment, and certainly the choice of nuclear is preferable to the fossil fuel sources that are currently driving most data centres (e.g., methane gas in the United States, coal in China).
As for demand-side considerations, these can include the energy efficiency of the data centres themselves, the way models are designed, and the way AI is utilised. Cooling is an especially interesting case; as mentioned, GPUs run quite hot, and to avoid catastrophic failure, they require effective cooling. This is usually done with evaporative cooling, which means significant water loss, or by chillers, which doesn't mean much loss, but a huge amount of water for cooling. A third option is dielectric liquids, such as mineral oil, which results in a data centre that is quiet and at room temperature, while servers operate at an optimal temperature. The main disadvantage is the messy and time-consuming procedures for upgrading system units.
The model design also presents some opportunities for improvement. The typical approach is to train neural networks with large quantities of data; however, the more indiscriminate the data collection is, the greater the possibility of conventional error. As some critics suggest, an LLM is essentially a language interface that sits in front of a search engine. A smaller but more accurate collection of data can be more accurate, as well as being less resource-intensive to train in the first place. A number of smaller models can operate with connective software for matters outside of the initial module's scope instead of a monolithic approach.
Finally, there is the matter of what AIs are being used for. Certainly, there are some powerful and important success stories such as the key designers behind AlphaFold winning the 2024 Nobel Prize in Chemsitry for protein structure prediction and, as many contemporary workers (especially in computer science) are all too aware, the ability of AIs to produce code is quite good, assuming th developer knows how to structure the questions with care and engages in thorough testing. Additionally, the increasing application of these technologies in robotics and autonomous vehicles is disconcerting, as illustrated by the predictive and plausible video "Slaughterbots".
On the consumer level, an AI can perform tasks which a human is less efficient at. So rather than simply asking "how many tonnes of a GHG does AI cause", a net emissions question should be asked, appending "... compared to human activity", that is, productivity substitution. However, with effectiveness comes the lure of convenience, as it attempts to extend the use of AI to everything, even when human energy usage would be less than that of an AI-mediated task. Ultimately, it is the combination of human failings, a combination of laziness (always choosing convenience), wilful ignorance (not knowing and caring about energy efficiency), distractibility (extending AI for trivialities rather than tasks of importance), and powerlust (commercial or political), that present a continuing challenge to the prospect of implementing an environmentally-sustainable development of artificial intelligence.
On the evening of September 3, 2025, there was suddenly a strong and remarkably unpleasant flat metallic odour in our master bedroom and ensuite. We opened all the doors and windows and got the fan on, and eventually it went away. The smell didn’t come back after closing up, but the next morning when I was inspecting the Redflow ZCell battery in the crawl space under the house I discovered a 6cm long crack towards the right hand side of the back of the electrode stack, about 2.5cm above the base. A small amount of clear liquid was leaking out.

Due to the way our house is constructed on a hill, the master bedroom, walk in robe and ensuite on the lower floor share some airflow with the crawl space under the main floor of the house. For example, the fan in the ensuite vents to that space, and I’ve felt a breeze from an unfinished window frame in the walk in robe, which must be coming from the space under the house. I’ve since siliconed that window frame up, but the point is, the electrode stack split, the battery was leaking, and we could smell a toxic fume in the bedroom.
Readers of the previous post in this series will be aware that Redflow went bust in August 2024, and that our current battery was purchased from post-liquidation stock to replace the previous one which had also failed due to a leak in the electrode stack. When the new unit was commissioned in March 2025 I applied some configuration tweaks in an attempt to ensure the longest lifespan possible, but it lasted slightly less than six months before this failure. Not great for something that was originally sold with a ten year warranty.
Under the circumstances I wasn’t willing to try to procure yet another new ZCell to replace this one, but given we’d found the leak very early this time, I figured I had nothing to lose by trying to repair it. I had heard of marine fibreglass being used successfully in one other case to repair a leaking ZCell, so I discharged the battery completely then set to work patching it up the following weekend. This involved:
Here’s a picture of the finished repair. I didn’t bother sanding it smooth because it just doesn’t matter – it’s a battery, not the hull of a boat – and I could do without creating any more dust. I actually ran two strips of fibreglass because there was also a little split at the top of the stack, although that one didn’t appear to be leaking.

Recommissioning the unit was interesting. Upon bringing it online, it immediately went into a safe shutdown state because the electrolyte had dropped down from its usual running temperature of 18-24°C to a bit over 8°C during the five days it had been offline.
In order for a ZCell to charge, the electrolyte needs to be at least 10°C, and at least 15°C for it to discharge. So I took one of our 2400W panel heaters under the house and turned it on next to the unit. “How long does it take for a 2400W panel heater to heat 100L of nearby liquid electrolyte by 2°C?” I hear you ask. “Too damn long” is the answer. I started the heater at 13:10, and it was 16:50 before the battery was convinced that the electrolyte was far enough above 10°C to be happy to start charging again. But, charge it did, and we were up and running again… Until the next morning when my wife detected that nasty smell in the ensuite again. Upon further inspection of the unit I found a tiny drip coming from the bottom of the front of the stack, behind the Battery Control Module (BCM). So once again I discharged and decommissioned the battery in preparation for repair.
This time I had to pull the BCM off to get to the electrode stack behind it. First I checked that the battery really was discharged with a multimeter. Then I disconnected the DC bus cabling, the comms cable, and the connections to the pumps, fans and leak sensors after taking a photo to make sure I was going to put everything back in the right place. Finally I unscrewed the battery terminals and pulled the BCM off. It’s actually a really neat arrangement – the BCM just slides on and off over the two cylindrical terminals the come out of the stack. It’s a bit stiff, but once you know it comes off that way, you just jiggle and pull until it’s removed.

One thing to be extremely careful of is that you don’t accidentally drop the washers from the battery terminals down into the bottom of the battery, because if you do you will never, ever get them back again, and will have to order some M8 silicon bronze belleville washers from Bronze & Brass Fasteners Pty. Ltd. to use as replacements. I don’t know exactly what Redflow used here, but I know they’re belleville washers from reading the manual, I determined they were M8 by measuring them, silicon bronze is apparently a good electrical conductor, and BABF would let me buy them individually rather than in lots of a hundred. I purchased eight, in order to have several more spares.

There was a bit of cracking on the front of the stack, similar to what was on the back, so then it was a repeat of the earlier fibreglassing procedure. This added a couple of millimetres depth to the front of the stack. Now the circuit board in the BCM could no longer sit flat against the ends of the battery terminals, due to a series of little protrusions on the back of the BCM case which would ordinarily sit flush against the stack. These I lovingly twisted off with a pair of pliers. Then I reconnected all the cabling and used a nice shiny new torque wrench to ensure the battery terminals and DC bus cabling were tightened to 10Nm per the manual.


I wasn’t quite ready to recommission the battery yet at this point given we’d had those two nasty fume experiences in the bedroom. If I’d missed anything with this second repair, or if anything else broke and there were gas emissions of any kind, we didn’t want to experience them. So I purchased a sub floor ventilation kit with a bushfire compliant external vent and installed that under the house.

Then in early October (it took a while to get all this work done around my actual job) I brought the battery online again. Of course I had to once more use the panel heater to get it going. We’re running the ventilation fan 24/7 (it’s very quiet), and I got into the habit of going under the house and doing a visual inspection of the battery every morning as part of our daily rounds feeding the chickens.
Everything went beautifully until October 29 when I noticed a small drip of red liquid which appeared to be coming from a capillary tube on the front right of the stack. The previous leaks had appeared clear, which I imagine means they were from the zinc electrolyte side of the battery, whereas this red suggested to me a leak from the bromine side of the battery. The electrolyte actually initially has the same chemical composition in both tanks, but charging changes it – you’ll see the electrolyte in the bromine pipe on the front of the battery go orange, then red, as charge increases, whereas the electrolyte visible in the zinc pipe remains a mostly transparent pale yellow. Anyway, another leak meant decommissioning the battery again to investigate.

Off came the BCM again to check my fibreglass work (pristine and undamaged!) and off came the side of the enclosure to get a better look at the problem area. I inspected the capillary tube in minute detail with a magnifying glass and couldn’t find any obvious damage that would explain the leak. The tube runs from the top of the stack down through a hole in the bottom front of the stack, which keeps everything very neat, but honestly seemed to me like it was introducing a potential weak point into the front of the stack, so I rerouted the tube then carefully filled the hole in the stack with Araldite, on the assumption the leak was actually in the stack. In case the leak turned out to be in the tube, I ordered some viton tubing to use as a replacement. After recommissioning the battery again no further leak was evident over several days, indicating that the problem was indeed in the stack, and not in the tube. This is probably just as well, as my new viton tubing turned out to have a slightly smaller internal diameter (2mm) than whatever Redflow used during manufacture – maybe 2.5mm?
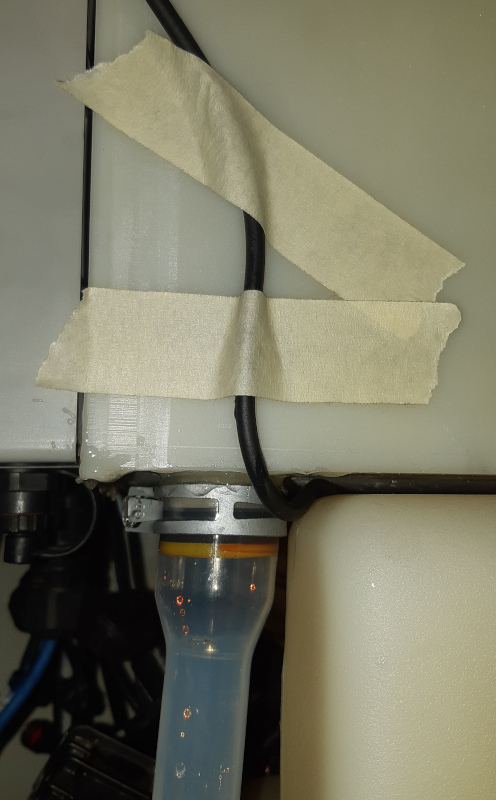
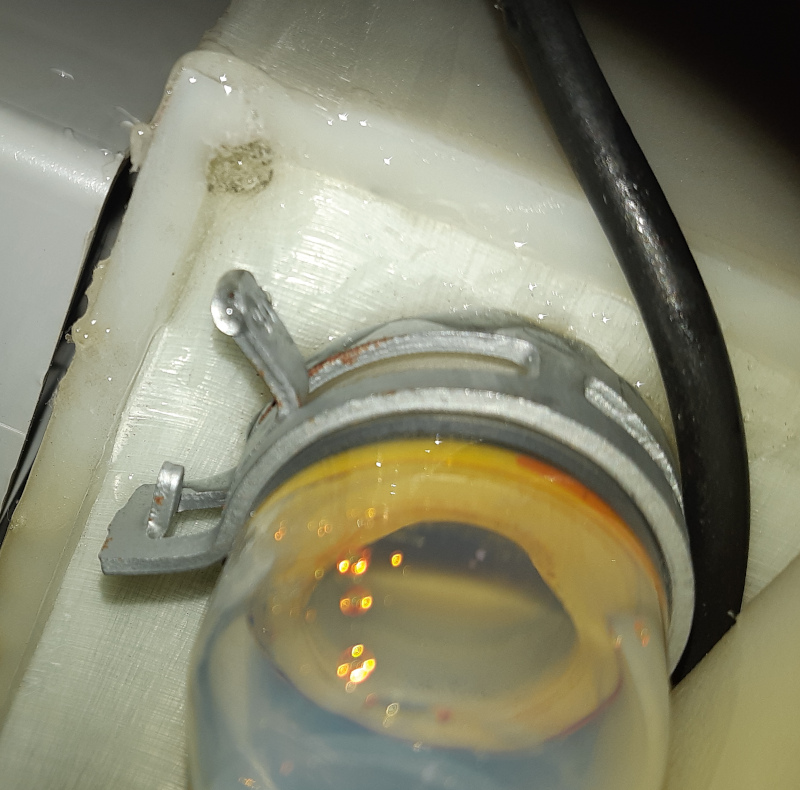


A few days after that on November 7, the battery indicated a hardware failure due to “impedance error”, and a small drip of red liquid appeared on the front left side of the stack. I’ve been told this error can be due to higher pH levels and the formation of zinc hydroxide, or degradation of the core electrode, or separator failure, or overheating of the stack reactor. Within the limits of my knowledge and ability there was very little I could do about any of these things, so then the question became: what next?
At this point I felt that I had really pushed things as far as I reasonably could. If the fibreglass repairs on the front and back of the stack proved sufficient and nothing else had gone wrong, I would have been happy to continue operating the battery as we had been since March, but these additional leaks and the impedance error suggested to me that things were going to continue to go downhill. It seems that the answer to the question posed in my last post, i.e. “how far down the road can we kick the migration can” turned out to be about eight months.
The only technology that’s immediately viable for us to switch to is LiFePO4 batteries. We’re looking at a stack or two of Pylontech Pelios because they will work with our existing Victron inverter/charger gear and come in IP65 cases so can be installed outdoors without too much difficulty. It will still be a while before we can get those installed though, and in the meantime I can’t just decommission the existing battery because then our solar generation won’t work.
The way our system is installed, we have solar panels connected to an MPPT on the DC bus, which is connected to the battery, and to our MutliPlus II Inverter/Chargers which in turn power our loads. The ZCell Battery Management System (BMS) tells the system what the battery charge and discharge limits are. If the battery is missing or broken, the BMS will not let the MPPT run at all, which means that no battery = no solar power, not even to power our loads.
I actually tried to work around this problem a couple of times in the past when previous batteries were dead. There’s a description of some unsuccessful attempts in an earlier post, and I also separately tried to fake up what I called a Virtual ZCell in software back in December 2024. In that experiment I was telling the Victron system that there was a battery present at 25% state of charge, but with a charge current limit of 0A (so it wouldn’t try to charge the non-existent battery) and a discharge current limit of 1A (so the battery looked at least a little bit available but no real discharge would be attempted). Incredibly this worked, but after about a week the MPPT started raising various errors so I gave it up. It seems that it’s necessary for a real physical battery to be present in order to help correctly regulate the voltage on the DC bus.
Back to the real battery: After the impedance error occurred I shut it down, rerouted the left front capillary tube, Araldited up its hole and the bottom front of the stack as I had done on the right hand side, then recommissioned the battery and reset the impedance error. I then set the system maximum state of charge limit in the BMS to the lowest value possible (20%). This would mean that the battery would never be charged much, and thus would never be stressed much. I imagined that whatever reactions were happening inside the stack that were causing things to break would happen either less often, or with less severity, or both.
The Araldite repairs were ultimately not completely successful. A teeny tiny red drip or two have since reappeared on the bottom front of the stack, but they are very small drips. I wipe them up every couple of days. The impedance error has not yet recurred. The fibreglass is still solid. We are thus able to continue to use our whole system in some capacity – notably with functioning solar power generation – until we’re able to migrate to those Pelios.
I will continue to write about our system in future, but this post will probably be the last that covers Redflow batteries in any detail. I have included some further observations below in the hope that they will be useful to others such as the Flow Battery Research Collective in their efforts to design and build a viable open source flow battery. I would also like to take the opportunity to express my thanks to Stuart Thomas (another ZCell user) for plenty of helpful advice and interesting discussions over the past year.
There’s an article on the design of the ZBM3 on Simon Hackett’s blog from back in May 2021. Having now spent a fair bit of time physically messing with the ZBM3 myself I’m happy to confirm almost all the good things in that post about about the design of the unit – the whole thing is just much neater and nicer than the ZBM2. The one thing that ultimately didn’t work out with the new design, unfortunately, was improved reliability. Our original ZBM2 lasted from August 2021 to December 2023 – just over two years – before failing due to a leak in the electrode stack. Our first ZBM3 failed after nine months. The subsequent one started leaking after six months and even though I continue to nurse it along, I think we can reasonably treat that one as failed too.
Based on my experience, the reliability issues are all in the stack. Whether that’s a problem with the manufacture of the stack, or chemical reaction issues at runtime, or a combination of the two, or something else entirely, I don’t know. But if those problems could be fixed or mitigated somehow, the rest of the design is quite clever:
Nevertheless, in my opinion, there is still room for improvement:
Speaking of the catch can, it’s connected to the zinc tank by a pressure release valve, although the ZBM3 manual erroneously states that it’s connected to the bromine tank. There does not appear to be any pressure release valve attached to the bromine tank, whereas the ZBM2 had a gas handling unit consisting of pressure release valves connected to both tanks (see section 4.7 “Gas Handling Units” in the ZBM2 manual). Is the pressure release really not necessary for the bromine tank with the ZBM3, or is this another source of potential trouble?
The carbon sock, which needs to be replaced annually, is interesting. It looks a bit like a door snake, but it’s filled with some sort of carbon material and sits in the zinc tank. I understand it behaves somewhat like a sacrificial anode, the idea being that whatever corrosion or oxidation that might happen to the carbon in the electrodes in the stack under certain operating conditions, will instead happen to the carbon in the sock.
Another item of annual maintenance is to “check the pH and adjust if necessary”. How, exactly, and to what value? I have recent correspondence which says the pH should ideally be 1.5-2.5 and that it can be lowered by adding hydrochloric acid and running the pumps for a couple of days, but it would be helpful to somehow include a pH sensor in the unit given that mopping up leaks with litmus paper isn’t really very accurate.
As for the stack itself, it looks like a solid rectangular chunk of some sort of fibreglassy material. The front plate appears to be a separate piece that was stuck on somehow, which I assume makes for a weaker spot between that plate and the rest of the stack. This could explain some of the leaks I experienced. Maybe the ZBM2 design with the bolts holding two stacks together really did make for a better seal?
Finally, the most recent enclosure design – a solid metal box with cowlings on each end that allow airflow but not animal ingress – is excellent until you have to do any work on it. Everything is very heavy, and once you remove the screws that hold one of the ends on, everything has a tendency to slip just slightly out of alignment, making it difficult to screw back together, at least for one person. Given the frequency with which I ended up needing to inspect and mess around with my most recent unit, I removed the ends and one side of the enclosure and just left it that way.
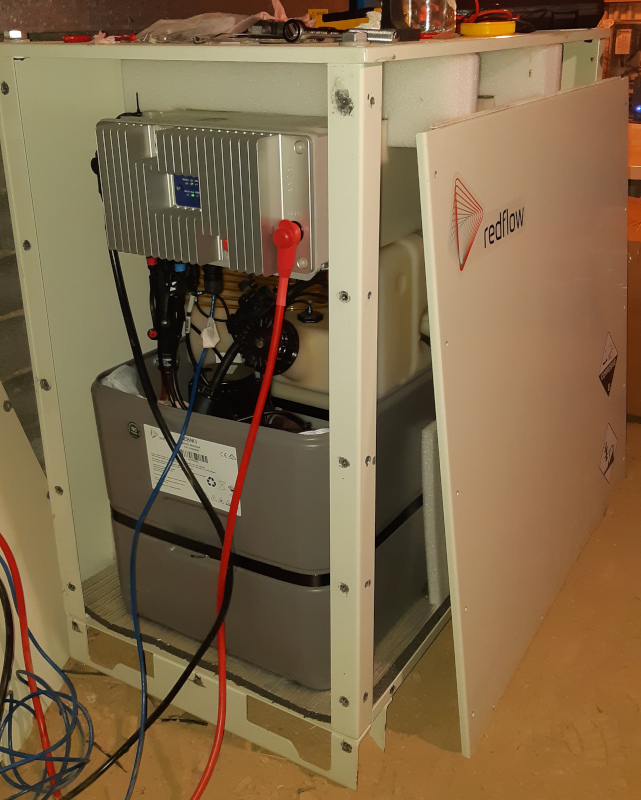

The management and monitoring interface for the BMS is overall decent and easy to use. There’s a main status screen from which you can drill down to get more detail and perform various operations. The included quick start and reference guides are very thorough and cover most of the details, so rather that describing the UI further here I’ve decided to reproduce those manuals in PDF form for posterity:
You can easily get full details of the current state of all connected batteries by browsing the UI, or by hitting the /rest/1.0/status endpoint to dump everything in JSON format. It’s possible to browse the last three months of BMS logs via the UI, but they disappear after that. There are historical graphs for battery current, voltage, temperature and state of charge, but their resolution decays the further back in time you go. I assume it’s using something like RRDtool behind the scenes.
Historical logs of battery state is where I ran into trouble. You can browse these via the UI, or download CSV reports for a given timespan, but the problem is the battery state is only recorded at one minute intervals. This means that if anything interesting happens in the 59 seconds between two log entries, you don’t see it. There’s a longer description of this issue in the first post in this series, where I noticed that the Charge, Discharge and EED contators in the battery were toggling on and off far more often than expected. It’s also a problem if a warning or error is triggered for only a few seconds. In this case the BMS logs will show something like the following:
2025-12-02 04:56:15 WARN ZBM:1 has indicated 'warning_indicator' state 2025-12-02 04:56:17 INFO ZBM:1 is no longer in 'warning_indicator' state
The logs of battery state however will not show the warning at all. In the above example the warning occurred from 04:56:15 to 04:56:17, but the battery logs surrounding that event only show the state at 04:55:59 and 04:56:59 when nothing interesting was happening. You can work around that by writing a script to scrape the REST status endpoint at, say, one second intervals then log that data to a separate database, but it would be better if this were handled by the BMS somehow. I know logging battery state every second would create way too much data for a tiny device to store, but maybe just logging on state changes? Or at the very least if there’s a warning or error, the BMS should log which warning indicator is active and the associated value. In the above example I happen to know it was a low temperature warning, but that’s only because I was doing exactly what I mentioned above, i.e. running a script externally to check the status every second and displaying the state if something changed.
Despite everything I’ve been through with our various ZCells, I remain convinced that flow batteries in general are a better idea for long-term stationary energy storage than lithium, provided they can be made to actually live up to the promise of a multi-decade lifespan. The most obvious pros compared to lithium in my opinion are:
The most obvious cons compared to lithium are:
In the context of vehicles, mobile phones, and other portable devices, those cons matter. But for homes, apartment blocks, microgrids, community batteries, hospitals, schools, commercial establishments, grid scale batteries, etc., those things just don’t (or shouldn’t) matter (as much). There’s physically more space in a house than in a car, and if you need slightly more generation capacity to offset potentially lower efficiency, then that just means having a couple more solar panels that you might otherwise.
Things get a bit more difficult though when you start thinking about consumer acceptance. A flow battery is, fundamentally, a machine. It has moving parts, and it potentially requires maintenance. Readers will have realised by now that I am quite mad rather obsessed somewhat of an enthusiast and don’t mind having to tinker with things occasionally. I imagine this is not the case for most people, who likely want their energy systems to Just WorkTM and require no special attention.
A viable flow battery, especially for residential usage, thus needs to be as low-maintenance as possible, and as easy to work on as possible when it does require maintenance. That latter point is a function of both unit design, and choice of installation site. The crawl space under our house for example is ideal if a battery only requires infrequent maintenance and minimal disassembly. If the whole unit needed to be stripped it would be much better off in a shed or other room that has appropriate access. Finally, these things need to come with a complete service manual including descriptions of all the parts and every possible procedure that might need to be performed in case of failure.
I was talking to a friend the other day about our shared mutual appreciation of virtio-vsock, and it made me wonder something. How do virtual machines on Linux actually work? I know it involves qemu and the kernel’s KVM virtual machine implementation, but exactly how do they interact? How does the kernel get qemu to do emulation tasks as required?
qemu is several things hanging out together in a trench coat, but one of those things is software which can configure Linux’s built-in KVM virtual machine functionality to run a virtual machine, and then handle emulation of the devices that virtual machine is attached to which cannot be represented with actual physical hardware. This part of qemu is called a “KVM client” in the Linux kernel documentation. Its called that because if we ignore the emulation part for now it is just literally a client calling established APIs to the Linux kernel.
I was mildly surprised to find that this topic is reasonably well documented and actually not particularly hard to implement once you know what to look for. I should also admit that I have been playing with AI models recently, and Anthropic’s Sonnet 4.5 was actually quite helpful. I don’t know how other people use these models, but I’ve fallen into two patterns of usage. In this case I used Sonnet like a search engine, with prompts like:
Please help me come up with a good project name which is a pun on python and kvm.
It came up with “pypervisor”, which I think is actually a pretty good name even though it does not include KVM in the pun at all. Or this example:
What do I pass to libc.ioctl when there is no data to pass?
I would then use the results of those “searches” to write my code.
The other method of usage is more trusting, where I have very recently started using Claude Code to generate code for me. So far I’ve only done this for private projects I will never release publicly, and its definitely a great way to churn out lots of code quickly, although I have had problems with that code not being correct or hallucinating APIs to call. This mode of operation is also noticeably worse as a way of learning, as you’re just presented with a finished product without any of the iterative process to get there.
I have also rapidly found that my biggest concern with these models is that they don’t provide supporting references for their statements, which is something we expect middle school kids to figure out. I would be much more comfortable if it could provide links to sources it used, both so I could validate what it said but also so the underlying authors could get more credit and incentive to keep writing. Google’s “AI Mode” sort of seems to do this, so it doesn’t seem completely impossible.
Instead, I’ve been using prompts like this:
Can you recommend any web pages which demonstrate using python to create a KVM virtual machine?
Or, from another session the other day on an unrelated topic:
Please provide me with some links to web pages which further discuss this topic.
So having said all that, the following references were quite helpful:
In the end, it turns out the Kernel API for running a virtual machine with KVM really isn’t that bad. Especially once you’ve accepted that the API doesn’t look at all like what a userspace developer would expect the API to look like. Instead of making calls to a library like glibc, you need to open /dev/kvm, and then use a series of ioctl calls to configure your virtual machine. Objects you create along the way are tracked as file descriptors, which makes sense given ioctls want to happen on files.
I don’t have a strong history here on providing tutorial content, so I am not entirely sure how to present my example while also producing a single block of usable code. While the entire project is on github, I am including the main body of the code here for ease of reference. For that main body I have opted to just putting in a lot of comments. Feedback on this approach is welcome.
#!/usr/bin/python3
# A not very good KVM client / virtual machine manager written in python.
# Based heavily on the excellent https://lwn.net/Articles/658511/.
# Development was assisted by Claude Sonnet 4.5, and US Intellectual
# Property law.
import ctypes
import fcntl
import mmap
import sys
from displayhelpers import *
from exitcodes import *
from ioctls import *
from structs import *
# A single 4kb page
MEM_SIZE = 0x1000
def main():
# Open the KVM device file. This gives us a top level reference to the
# KVM API which we can then make global calls against.
with open('/dev/kvm', 'rb+', buffering=0) as kvm:
try:
# Check that the API is a supported version. This should
# basically never fail on a modern kernel.
api_version = fcntl.ioctl(kvm, KVM_GET_API_VERSION)
print(f'KVM API version: {api_version}')
if api_version != 12:
print(f'KVM API version {api_version} was unexpected')
sys.exit(1)
except OSError as e:
print(
f'Failed to lookup KVM API version: {e.errno} - {e.strerror}'
)
sys.exit(1)
# Create a VM file descriptor. This is the "object" which tracks the
# virtual machine we are creating.
print()
try:
vm = fcntl.ioctl(kvm, KVM_CREATE_VM)
print(f'VM file descriptor: {vm}')
except OSError as e:
print(f'Failed to create a VM: {e.errno} - {e.strerror}')
sys.exit(1)
# mmap memory for the VM to use. Sonnet 4.5 alleges that we need to
# use mmap here instead of just allocating a largeish byte array in
# native python for a few reasons: the allocation needs to be
# page-aligned; mmap'ed memory can be zero-copied into the virtual
# machine, a python array cannot; MAP_SHARED means our python process
# can inspect the state of the virtual machine's memory; python
# memory allocations are not at a stable location -- python might
# rearrange things. So yeah, those seem like reasons to me.
mem = mmap.mmap(
-1,
MEM_SIZE,
prot=mmap.PROT_READ | mmap.PROT_WRITE,
flags=mmap.MAP_SHARED | mmap.MAP_ANONYMOUS,
offset=0
)
mem_buf = (ctypes.c_char * len(mem)).from_buffer(mem)
mem_addr = ctypes.addressof(mem_buf)
print(f'VM memory page is at 0x{mem_addr:x}')
# This is the data structure we're going to pass to the kernel to
# tell if about all this memory we have allocated.
region_s = kvm_userspace_memory_region_t()
region_s.slot = 0
region_s.flags = 0
region_s.guest_phys_addr = 0
region_s.memory_size = MEM_SIZE
region_s.userspace_addr = mem_addr
try:
# This dance gives us the address of the data structure, which is
# what the kernel is expecting.
region_bytes = ctypes.string_at(
ctypes.addressof(region_s), ctypes.sizeof(region_s))
fcntl.ioctl(vm, KVM_SET_USER_MEMORY_REGION, region_bytes)
except OSError as e:
print(f'Failed to map memory into VM: {e.errno} - {e.strerror}')
sys.exit(1)
# Add a vCPU to the VM. The vCPU is another object we can do things
# to later.
try:
# The zero here is the index of the vCPU, this one being of
# course our first.
vcpu = fcntl.ioctl(vm, KVM_CREATE_VCPU, 0)
print(f'vCPU file descriptor: {vcpu}')
except OSError as e:
print(f'Failed to create a vCPU: {e.errno} - {e.strerror}')
sys.exit(1)
# mmap the CPU state structure from the kernel to userspace. We need
# to lookup the size of the structure, and the LWN article notes:
# "Note that the mmap size typically exceeds that of the kvm_run
# structure, as the kernel will also use that space to store other
# transient structures that kvm_run may point to".
try:
kvm_run_size = fcntl.ioctl(kvm, KVM_GET_VCPU_MMAP_SIZE)
except OSError as e:
print(
f'Failed to lookup kvm_run struct size: {e.errno} - '
f'{e.strerror}'
)
sys.exit(1)
print()
print(f'The KVM run structure is {kvm_run_size} bytes')
kvm_run = mmap.mmap(
vcpu,
kvm_run_size,
prot=mmap.PROT_READ | mmap.PROT_WRITE,
flags=mmap.MAP_SHARED,
offset=0
)
kvm_run_s = kvm_run_t.from_buffer(kvm_run)
kvm_run_addr = ctypes.addressof(kvm_run_s)
print(f'vCPU KVM run struture is at 0x{kvm_run_addr:x}')
print()
print(pretty_print_struct(kvm_run_s))
print()
# Read the initial state of the vCPU special registers
sregs = kvm_sregs_t()
fcntl.ioctl(vcpu, KVM_GET_SREGS, sregs)
print('Initial vCPU special registers state')
print()
print(pretty_print_sregs(sregs))
print()
# Setup sregs per the LWN article. cs by default points to the
# reset vector at 16 bytes below the top of memory. We want to start
# at the begining of memory instead.
sregs.cs.base = 0
sregs.cs.selector = 0
fcntl.ioctl(vcpu, KVM_SET_SREGS, sregs)
# Read back to validate the change
sregs = kvm_sregs_t()
fcntl.ioctl(vcpu, KVM_GET_SREGS, sregs)
print('CS updated vCPU special registers state')
print()
print(pretty_print_sregs(sregs))
print()
# Read the initial state of the vCPU standard registers
regs = kvm_regs_t()
fcntl.ioctl(vcpu, KVM_GET_REGS, regs)
print('Initial vCPU standard registers state')
print()
print(pretty_print_struct(regs))
print()
# Setup regs per the LWN article. We set the instruction pointer (IP)
# to 0x0 relative to the CS at 0, set RAX and RBX to 2 each as our
# initial inputs to our program, and set the flags to 0x2 as this is
# documented as the start state of the CPU. Note that the LWN article
# originally had the code at 0x1000, which is super confusing because
# that's outside the 4kb of memory we actually allocated.
regs.rip = 0x0
regs.rax = 2
regs.rbx = 2
regs.rflags = 0x2
fcntl.ioctl(vcpu, KVM_SET_REGS, regs)
# Read back to validate the change
regs = kvm_regs_t()
fcntl.ioctl(vcpu, KVM_GET_REGS, regs)
print('Updated vCPU standard registers state')
print()
print(pretty_print_struct(regs))
print()
# Set the memory to contain our simple demo program, which is from
# the LWN article again. Its important to note that the memory we
# mapped earlier is accessible to _both_ this userspace program and
# the vCPU, so we can totally poke around in it if we want.
program = bytes([
0xba, # mov $0x3f8, %dx
0xf8,
0x03,
0x00, # add %bl, %al
0xd8,
0x04, # add $'0', %al
ord('0'),
0xee, # out %al, (%dx)
0xb0, # mov $'\n', %al
ord('\n'),
0xee, # out %al, (%dx)
0xf4, # hlt
])
mem[0:len(program)] = program
# And we now enter into the VMM main loop, which is where we sit for
# the lifetime of the virtual machine. Each return from the ioctl is
# called a "VM Exit" and indicates that a protection violation in
# the vCPU has signalled a request for us to do something.
while True:
print('Running...')
fcntl.ioctl(vcpu, KVM_RUN)
kvm_run_s = kvm_run_t.from_buffer(kvm_run)
exit_reason = VM_EXIT_CODES.get(
kvm_run_s.exit_reason,
f'Unknown exit reason: {kvm_run_s.exit_reason}'
)
print(f'VM exit: {exit_reason}')
print()
match exit_reason:
case 'KVM_EXIT_HLT':
print('Program complete (halted)')
sys.exit(0)
# Claude had the direction values backwards. qemu definitely
# agrees with this though.
# https://github.com/qemu/qemu/blob/master/linux-headers/linux/kvm.h#L245
case 'KVM_EXIT_IO':
io = kvm_run_s.exit_reasons.io
print(pretty_print_struct(io))
print()
# We only handle input to ioport 0x03f8 for now
if io.direction == KVM_EXIT_IO_OUT and io.port == 0x3f8:
data_ptr = ctypes.addressof(kvm_run_s) + io.data_offset
data = ctypes.string_at(data_ptr, io.size)
try:
data_str = data.decode('ascii')
except:
data_str = 'failed to decode ASCII'
print(f'Output: {data}, {data_str}')
else:
print('Not yet implemented...')
sys.exit(1)
case 'KVM_EXIT_SHUTDOWN':
print('VM shutdown')
sys.exit(0)
case 'KVM_EXIT_INTERNAL_ERROR':
print('Internal errors are probably bad?')
sys.exit(1)
case _:
print(f'Unhandled VM exit: {exit_reason}')
sys.exit(1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()I hope someone else finds this interesting too.
Environment Modules allow users to dynamically modify the $PATHs in their shell environment. In particular, it provides the ability to switch between different software applications and versions. It is a very handy tool for developers who want to test against multiple versions or compilation options of an application and for users on a multi-user system (e.g., high performance computing) where both consistency and the opportunity to introduce newer features needs to exist for different research groups. The two major environment modules systems are the older, Tcl-based system, and the newer Lua-based system (Lmod). Both allow default versions of a software application to be set as in the $PATH when invoked. This can cause problems and should be disabled.
With a standard module system, one can see the modules for an application. For example, using a LMod system:
$ module av GCC/
------------------------------------ /apps/easybuild-2022/easybuild/modules/all/Core ----------------------------
GCC/11.3.0 (L) GCC/12.3.0 GCC/13.3.0 (D)
This illustrates that from the GNU Compiler suite (GCC), the application GCC/11.3.0 is loaded (by default in this case as part of the login) and that GCC/11.3.0 is the default as part of a wider toolchain. That is, if the command
module load GCC
is invoked, the existing environment $PATH will change so that it points to the binary, libraries, etc for GCC/12.3.0 instead of GCC/11.3.0. In the older, Tcl-based modules system, it was possible to have both versions loaded simultaneously; the most recent version would be the initial search path, but if a particular library, for example, couldn't be found, it would search whatever was in the $PATH. That could be an interesting issue for the replication of results.
Having a default obviously saves a few keystrokes, but problems can result. The major issue is that when new software is introduced by the local friendly HPC engineers, then the default changes. For example, the latest version of GCC, at the time of writing, is 15.1 (April 2025). If that was installed on a system, one would witness:
$ module av GCC/
------------------------------------ /apps/easybuild-2022/easybuild/modules/all/Core ----------------------------
GCC/11.3.0 (L) GCC/12.3.0 GCC/13.3.0 GCC/15.1.0 (D)
Instead of loading GCC/12.3.0 from the
module load GCC
command, LMod will add GCC/15.1.0 to the $PATH. Is this a problem? Most certainly because when software (version, compiler) changes, the results can change. For example, with the release of GCC/13 it included the statement: -Ofast, -ffast-math and -funsafe-math-optimizations will no longer add startup code to alter the floating-point environment when producing a shared object with -shared. In a nutshell, this means that one can get different numerical results by compiling the same code between GCC/12 and GCC/13 due to different ways the compiler would handle rounding, precision, and exceptions when using floating-point calculations. This could be very interesting if one cares about that supposed hallmark of science, "reproducibility".
To avoid this, at a user-level, one should always use the fully-qualified version of a software application. For example, instead of loading a module with
module load GCC
, whether in an interactive session or job script, one should use the specific version, e.g.,
module load GCC/13.3.0
. Of course, sometimes users don't follow the friendly and sensible advice from their system engineers, and that's where a blunter tool needs to be invoked.
Site-wide LMod configuration (at let's face it, LMod is the overwhelmingly dominant version of environment modules these days) occurs in the lmod_config.lua file,
$LMOD_DIR/../init/lmod_config.lua
. Adding the following lines is sufficient:
-- Do not automatically pick a version when multiple options are available
always_load_default = false
-- Do not automatically swap modules from the same family
auto_swap = false
-- Disallow default-version resolution and force the user to specify which version
site_defaults = {
load_default = false,
}
Another option is to export optins in
/etc/profile.d/lmod.sh
or equivalent. This avoids making changes to the lmod_config file.
export LMOD_DISABLE_NAME_AUTOSWAP=yes
export LMOD_DISABLE_VERSION_AUTODEFAULT=yes
If a system is using EasyBuild for software installs (and many of us are), EasyBuild will create
.version
files which include the default; this can be removed by changing the
easybuild.cfg
file to have
module_install_defaults = False
.
One issue that arises from the above, from a support perspective, is that existing user expectations and job submission scripts may come into conflict with a new policy. For example, if a job submission script included
module load GCC
, the job would fail as LMod would be asking for user input on which specific version of GCC they wish to load.
This is a valid concern in the short term, but in the longer term, the benefits of providing consistent environment variables, reproducibility, and educating users far outweigh the costs. Further, the longer one persists with the policy of allowing application defaults the greater the damage.
LAME (recursive acronym Lame ain't an MP3 encoder) has been an exceptional application for creating MP3 audio files from other formats (e.g., WAV, FLAC, MPEG-1, MPEG-2) or even for re-encoding existing MP3 files. Creating MP3 files is popular due to their extensive use in portable media players, as they combine an impressive reduction in file size with minimal loss from uncompressed audio. LAME was first released 27 years ago, has been in regular development since, and is now bundled with the very popular audio editor, Audacity, and other excellent audio conversion applications like FFmpeg. The following are several examples of how to use LAME on the command line, convert files, and automate this process, along with the use of cdparanoia and ffmpeg. This might be handy if you want to (for example) back up a collection of CDs.
To extract files from existing media, use cdparanoia, a delightfully old and stable tool where the last release was September 2008 and the front-end for libparanoia, which is also used in the cdrtools suite, which can be used for the creation of audio and data CDs. To use cdparanoia to extract files from disk, first use the command to get the information about what drives you have, i.e., $ cdparanoia -vsQ, a verbose search and query. Then, to extract the files, simply use $ cdparanoia -B, batch mode, saving each track to a separate file. The default format is WAV; if one wants RAW, use $ cdparanoia -rB.
Using LAME to convert files, the simplest action is to convert a file with no options. e.g., $ lame input.wav output.mp3. This can be extended with the numerous options offered by LAME. Perhaps the most common is the -V% (variable bit rate) (e.g., $ lame -V0 input.wav output.mp3. Values are from 0 to 9, where 0 is the highest quality (but largest file size), which is good for very high-fidelity recording, whilst 9.999 is the lowest one, which is fine for low fidelity needs (e.g., a monophonic voice recording); the default is 4. Run a test on a WAV file to see if you can detect the difference in audio quality and check the file size differences. Note that despite being a good encoder, LAME is not recommended for archives; use a lossless audio codec (e.g., FLAC).
If one has multiple files to convert, a short loop is an effective strategy (e.g., $ for item in *.wav; do lame "$item" "${item%.wav}.mp3"; done). This is certainly preferable to opening files with a GUI application and running the conversion one file at a time. If one has a number of large files, then use of GNU Parallel is an excellent choice (e.g., $ parallel lame -V0 {} {.}.mp3 ::: *.wav). On a sample CD, the loop conversion took 57.201 seconds; with parallel, 13.264 seconds; it is fairly clear how this makes a difference if you have a large number of CDs. Note that with a smaller number and size of files, the use of GNU Parallel will actually take a longer time than a loop due to the overhead of splitting up the tasks. Certainly, if you are converting the WAV files from a CD, use GNU Parallel. Note that GNU Parallel will use all the cores available on a system; the number of concurrent jobs can be limited with the -j option (e.g., parallel -j2 lame -V0 {} {.}.mp3 ::: *.wav).
Finally, there is a great little tool called mp3wrap, which can wrap multiple MP3 files into a single MP3, but keeps filenames and metadata information, which can be later split back to original files (using the mp3splt command). The output file will be named OUTPUTFILE_MP3WRAP.mp3; keep the MP3WRAP string so that the split program detects that the file is wrapped with this utility. To create a single file, simply use $mp3wrap album.mp3 track*.mp3.
Have you ever bought a product that was a little bit expensive compared to its peers, largely on the basis of recommendations from friends? Were you then disappointed? Well, that’s me with the quadlock maghead magnetic charging head.
So first off, all I want is to be able to wirelessly charge my phone while commuting. I had a dock which did that, but it died, so I was in the market for something better. I drive a 4WD and actually go off road, and one of the flaws of the previous dock was that it wasn’t rigid enough in difficult terrain, and basically everyone said I should change over to quadlock. So… I did.
Now of course you need to buy into their eco system, so you can’t just buy a dock. I needed a windscreen mount, a case, and a magnetic charging head to replace the stock passive head, and all of that came to just over $150 AUD. My previous dock was $30 AUD so it felt fairly expensive.
I must say quadlock make excellent suction caps — the windscreen mount is super rigid and definitely a step up in terms of quality. However, the maghead has simply never worked right. I’ve tried with three USB current inputs — a 100 watt charger (because you want to charge fast right?), a 60 watt charger because that’s what all the other USB-C PD outlets in the car are, and whatever slightly terrible USB charging current the head unit can provide. All of these chargers cause the maghead to immediately overheat when I try to use it, regardless of environmental factors like ambient temperature of the starting temperature of the head. Now, the head unit charger takes maybe a few tens of seconds to overheat, but the others do it within single digit seconds so either way its pretty useless. I have repeatedly asked quadlock for documentation on the expected input current for the maghead, but they refuse to answer the question. The only documentation I can find is for the maximum output current for the head.
But its ok right? I was also told quadlock has excellent support. So I filed a ticket. Which they didn’t reply to for ages. All up, it took ten days to get them to answer my ticket and eventually receive a replacement unit. This included such gems as being asked for a photo of how hot the maghead is. Like… what? I want to reinforce that while their initial response to my ticket was fast, there were multiple sessions of waiting days for a trivial answer, and they still haven’t answered all my questions.
In the end they shipped me another maghead, which fails in exactly the same way. So I am going to give up and just put them in a draw and use the passive head with a USB-C charging cable plugged into my phone like a neanderthal. Oh, and I’ll warn everyone I meet that quadlock isn’t quite what people tell you it is, unless you just want a really good suction cap.
The 2025 New Zealand Research Software Engineering Conference was held on September 23-24th. It has run for almost a decade, starting in 2016 as the CRI Coding Conference before becoming the Science Coding Conference, a title it kept until 2020, when it became the Research Software Engineering Conference. Throughout this time, it has focused on science and engineering, high performance computing, and cloud computing and is aimed at various coders, sysadmins, software engineers, data analysts, and IT managers from public research institutions and has the endorsement of the RSE Association of Australia and New Zealand.
As the programme indicates, this year's selection of presentations and BoFs has a strong emphasis on machine learning and developments in artificial intelligence. This was evident right from the very start with Nick Jones' keynote address on the first day, and with numerous presentations throughout the conference. A concern must be raised when this pivot to AI/ML involves a recursive comparative testing being conducted with other AI/ML systems. Ultimately, the validity of computational modelling must come not only from the quality of the inputs but the real-world predictive (and hindcasting) value of the outputs.
Thankfully, there was little in the way of "AI/ML marketing hype" at this conference, which really was firmly dedicated to actual computational practice, development of skills and knowledge, and research outputs. Further, there was only a moderate amount of theory, and that's primarily for foundations, as it should be. Being in Aotearoa New Zealand, it is perhaps unsurprising that there were several presentations on Earth sciences, but also of note was the emphasis on climatology, oceanography, and new developments in forensics.
Interestingly, Australian research software development and education were present in a number of presentations, including speakers from WEHI and CSIRO. From Research Computing Services at the University of Melbourne received a surprising highlight with my own presentation, "Programming Principles in a High Performance Computing Environment", the first presentation of the conference and Daniel Tosello's "VSCode on the node" being the third. It bodes well for current and future Trans-Tasman collaboration.
Finally, the Research Software Engineering New Zealand Conference included a small number of explicit community-building presentations. In conferences such as these, presentations are often of a special interes,t but with a much wider and latent feature being the awareness of the directions that other institutions and individuals are taking and the strength of professional connections, a critical requirement not only for an individual's development, but also for raising the collective knowledge of the institutions that they belong to.
I’ve fallen into this pattern where I do an hour or so of self-directed learning in the mornings before going to work. Until recently it was an excellent CMU course on the design of SQL database systems, which I’ve mentioned previously here. I’ve finished that, so I thought I would do something shorter and fun as a break before finding another course to do. I chose The freeCodeCamp.org hot dog or not hot dog tensorflow course. 90 minutes seemed achievable, and I too wish to know if an object in front of me is a hot dog or not.
The course uses Google Colab to walk you through the process. Colab is interesting, I had never used it before and I must say the user interface wasn’t completely obvious to me. One issue is that the workspace keeps timing out — I do my learning in small bursts tetrised around the other things in my life, and Google wants to reap idle workspaces (which is fair). Combined with the quite slow dataset download process this just wasn’t working for me.
But I own computers, some of which have GPUs. I should just be able to run the same code in my homelab right?
Well… That’s a nice theory. It was much harder than I expected. Because my chosen machine has an integrated AMD GPU, I need to use AMD’s ROCm. That means I needed to enter a twisting maze of conflicting python, tensorflow and tensorflow-rocm versions, a typoed GPU version check (yes really), and spend a few hours fighting the incantations and reading reddit posts. Additionally, because I need real physical GPU hardware for this, I can’t just play in a virtual machine. I instead need to risk messing up a physical machine I am somewhat fond of, so that’s nice.
I’ll save you the time. To get tensorflow working on Debian 12 with an AMD GPU, I needed to do the following dance steps…
The version of ROCm I need only supports python 3.9, 3.10, and 3.12. Of course Debian 12 ships with python 3.11 which is the missing option there, so that’s nice. Let’s use pyenv to get a python 3.12 on Debian 12:
sudo apt install -y build-essential libssl-dev zlib1g-dev libbz2-dev \
libreadline-dev libsqlite3-dev wget curl llvm libncursesw5-dev \
xz-utils tk-dev libxml2-dev libxmlsec1-dev libffi-dev liblzma-dev
curl https://pyenv.run | bash
Now add this to your .bashrc:
export PYENV_ROOT="$HOME/.pyenv"
export PATH="$PYENV_ROOT/bin:$PATH"
eval "$(pyenv init --path)"
eval "$(pyenv init -)"
eval "$(pyenv virtualenv-init -)"
And restart your shell. Now you can install python 3.12:
pyenv install 3.12.11I like virtualenvs to be in ~/virtualenvs/ so we need to be sneaky making our virtualenv instead of using the pyenv tooling:
${PYENV_ROOT}/versions/3.12.11/bin/python3 -m venv ~/virtualenvs/tensorflow
. ~/virtualenvs/tensorflow/bin/activate
Now we need to install ROCm:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install "linux-headers-$(uname -r)"
sudo apt install -y python3-setuptools python3-wheel libpython3.11
wget <a href="https://repo.radeon.com/amdgpu-install/latest/ubuntu/jammy/amdgpu-install_7.0.1.70001-1_all.deb">https://repo.radeon.com/amdgpu-install/6.4.3/ubuntu/jammy/amdgpu-install_6.4.60403-1_all.deb</a>
sudo apt install ./amdgpu-install_7.0.1.70001-1_all.deb
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install amdgpu-dkms rocmAnd now we can go back and install tensorflow and ROCm in our python 3.12 virtualenv:
pip3 install uv
uv pip install tensorflow==2.19.0
uv pip install -U tensorflow-rocm==2.19.0 \
-f https://repo.radeon.com/rocm/manylinux/rocm-rel-7.0/And now we can run python, import tensorflow, and ask if it has a physical GPU:
$ python3
Python 3.12.11 (main, Sep 21 2025, 08:10:09) [GCC 12.2.0] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import tensorflow as tf
2025-09-21 08:24:18.780938: I tensorflow/core/platform/cpu_feature_guard.cc:210] This TensorFlow binary is optimized to use available CPU instructions in performance-critical operations.
To enable the following instructions: SSE3 SSE4.1 SSE4.2 AVX AVX2 AVX512F AVX512_VNNI AVX512_BF16 FMA, in other operations, rebuild TensorFlow with the appropriate compiler flags.
>>> print(tf.test.is_gpu_available())
WARNING:tensorflow:From :1: is_gpu_available (from tensorflow.python.framework.test_util) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.
Instructions for updating:
Use `tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU')` instead.
2025-09-21 08:24:25.156483: I external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/rocm/rocm_executor.cc:920] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero
2025-09-21 08:24:26.361397: I external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/rocm/rocm_executor.cc:920] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero
2025-09-21 08:24:26.361442: I external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/rocm/rocm_executor.cc:920] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero
2025-09-21 08:24:26.362540: I external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/rocm/rocm_executor.cc:920] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero
2025-09-21 08:24:26.362576: I external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/rocm/rocm_executor.cc:920] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero
2025-09-21 08:24:26.362608: I external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/rocm/rocm_executor.cc:920] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero
2025-09-21 08:24:26.362630: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:2021] Created device /device:GPU:0 with 1982 MB memory: -> device: 0, name: AMD Radeon Graphics, pci bus id: 0000:c6:00.0
True
>>> print(tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU'))
2025-09-21 08:24:51.553486: I external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/rocm/rocm_executor.cc:920] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero
2025-09-21 08:24:51.553590: I external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/rocm/rocm_executor.cc:920] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero
2025-09-21 08:24:51.553613: I external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/rocm/rocm_executor.cc:920] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero
[PhysicalDevice(name='/physical_device:GPU:0', device_type='GPU')]
>>> Truly we live in the future.
I have updated this to post use ROCm 7.0.1, it originally used ROCm 6.4.
On December 14, 2024 – three weeks after I published the last exciting installment in this series of posts – our new Redflow ZCell battery, which replaced the original one which had developed a leak in the electrode stack, itself failed due to a leak in the electrode stack. With Redflow in liquidation there was obviously no way I was getting a warranty replacement this time around. Happily, Aidan Moore from QuantumNRG put me in touch with Jason Litchfield from GrazAg, who had obtained a number of Redflow’s post-liquidation stock of batteries. With the Christmas holidays coming up, the timing wasn’t great, but we were ultimately able to get the failed unit replaced with a new ZBM3.
At this point the obvious question from anyone who’s been following the Redflow saga is probably going to be: why persevere, especially in light of this article from the ABC which speaks of ongoing reliability issues and disturbingly high failure rates for these batteries. That’s a good question, and like many good questions it has a long and complicated answer.
The technical path of least resistance would have been to migrate to a small rack of Pylontech batteries, as these apparently Just WorkTM with our existing Victron inverter/charger gear. The downside is they’re lithium, so a non-zero fire risk, and our installation is currently in the crawl space under the dining room. If we switched to lithium batteries, we’d need to arrange a separate outdoor steel enclosure of some kind with appropriate venting and fans, probably on the other side of the driveway, and get wiring to and from that. My extremely hand-wavey guess at the time was that it’d easily have cost us at least $20K to do that properly, with maybe half of that being the batteries.
The thing is, I remain convinced that flow batteries are in general a better idea for long-term stationary energy storage than lithium. This article from the Guardian provides a quick high-level summary of what makes flow batteries different. What I really want to be able to do – given Redflow is gone – is migrate to another flow battery, ideally one that actually lives up to the promise of multi-decade longevity. Maybe someone will finally come up with a residential scale vanadium flow battery. Maybe someone will buy Redflow’s IP, carry on their work and fix some of their reliability issues (the latest update from the liquidators at the time of writing says that they have “entered an exclusive negotiation period with a party for the acquisition of Redflow Group’s intellectual property (IP) and certain specific assets”). Maybe we’ll even see a viable open source flow battery – I would love for this to happen, not least because if it failed I’d probably be able to figure out how to fix the damn thing myself!
Leaving our current system in place, and swapping in a new ZBM3 meant we could kick the migration can down the road a ways. It bought us more time to see what other technologies develop, and it cost a lot less in the short term than migrating to lithium would have: $2,750 including GST for a post-demise-of-Redflow 10kWh ZBM3 (although shipping was interesting – more on that later). The real trick going forwards is seeing exactly how far down the road we’ll be able to kick that can. How can we ensure the greatest possible longevity of the new battery?

The ABC article puts it down to manufacturing problems, notably a dependence on repurposed third-party components. While I can see that dependence causing all sorts of extremely irritating manufacturing and design issues, I’m not entirely convinced this is the whole story. I will freely admit that my personal sample is very small, but my two batteries both failing due to electrode stack leaks? If a hose split or a pump had died, or some random doohikey let the magic smoke out, then OK, cool, I get it, those I can see being repurposed third-party components. But these failures were apparently in the electrode stack, and I’m struggling to see how that could be a repurposed third-party component. If nothing else the stack (and the tanks) are surely the pieces that Redflow manufactured themselves. This is their core technology. What could be causing stack leaks? Are they just poorly manufactured, or is there some sort of chemical failure at runtime which physically splits the stack? Or something else? Bear in mind that this is all speculation on my part – I’m neither a chemist nor a battery manufacturer – but I know what I’ve seen, and I know what I’ve heard about leaks in other peoples’ batteries.
On the chemistry front, I found a paper from 2023 entitled Scientific issues of zinc-bromine flow batteries and mitigation strategies. This was authored by a bunch of researchers from the University of Queensland and the former CTO of Redflow, and highlights hydrogen evolution, zinc corrosion and zinc dendrite formation as the fundamental issues with zinc bromine flow batteries. I sincerely hope the authors will forgive me for condensing their fascinating ~9,000 word paper into the following 95 word paragraph:
When the battery is being charged, zinc is plated onto the electrodes. During discharge, the zinc is removed. Dendrites (little tree like structures) can grow due to uneven zinc deposition, or due to hydrogen gas evolution. Left unchecked, dendrites can puncture the separator between the electrodes and lead to short circuits. Additionally, hydrogen gas generated by the battery can raise the electrolyte pH. If the pH is too high, solid zinc can clog a membrane in the stack. If the pH is too low, it can cause zinc corrosion which can make the battery self-discharge.
What if Redflow just never completely solved or mitigated the above issues? Could a dendrite puncture not just the separator, but actually split the stack and result in it leaking? Could clogged membranes combined with hydrogen gas create enough pressure to do the same?
We know that ZBMs have a maintenance cycle which runs at least every 72 hours to first discharge the battery then (theoretically) completely strip the zinc from the electrodes over a subsequent two hour period. We also know that ZBMs have a carbon sock which sits inside the zinc electrolyte tank and helps to keep electrolyte pH in the correct operating range. This needs to be replaced annually.
What if 72 hours is still too long between maintenance cycles? If you search back far enough you’ll find that the maximum maintenance period was originally 96 hours, and I assume that was later revised down to 72 hours after experience in the field. I’ve had subsequent correspondence which says that even more frequent maintenance (24-48 hours) can be better for the batteries. I’ve also encountered a curious intermittent fault with the ZBM3 where occasionally the Strip Pump Run Timer in the battery operates at half speed. If that happens and you don’t notice and reset the battery, the maintenance cycle will actually occur every 144 hours, which is way too long.
In the past I’ve observed frequent high charge current warnings in the Battery Management System (BMS) logs. This is actually normal, as by default the charge voltage is configured to be 57.5V, and there’s a separate high current voltage reduction setting of 1V. The idea is that this will try to make the battery charge as quickly as possible, and if the current gets too high, it will drop the charge voltage dynamically by 1V, which results in current reduction. Is it possible this variable (i.e. potentially uneven) charge current results in uneven zinc deposition?
I’ve also noticed that the battery State of Charge (SoC) calculations get sketchier the longer it’s been between maintenance cycles. If I have maintenance set to 72 hours, then at the end of the maintenance cycle, the battery fairly reliably still reports about 7% SoC. With a 48 hour maintenance period, it reports about 3% SoC at end of maintenance, and with a 24 hour maintenance period, it’s more like 1%. Once maintenance completes the SoC is reset to 0% automatically (because the battery really is empty at that point), but this got me thinking… If the SoC calculation is off, is there any way the battery could inadvertently allow itself to overcharge? Given the numbers above are all obviously overestimates I hope it’s more likely that the battery undercharges, but still, I had to wonder.
Aidan suggested three configuration tweaks which Redflow had told him to try to potentially help optimise battery lifespan:
These are all done via the BMS. The maximum SoC and maintenance time limit are set on the Battery Maintenance screen under Capacity Limiting and Maintenance Timing respectively. I went with 90% SoC as above and 48 hour maintenance. The charge voltage is on the EMS Integration screen. I’ve used the following settings:
In my case, the Normal Charge Voltage was originally 57V, and as I dropped it by 1.5V to get to 55.5V, I dropped the Charge-Blocked and Discharge/Maintenance Cycle voltages by the same amount to arrive at the above figures.
Dropping the maximum SoC means that the battery can’t get completely full and stay there for a long time. This must reduce the total amount of zinc plated on the electrodes, which I hope helps reduce dendrite formation. I also found when reading the paper mentioned earlier that “H2 evolution occurs mostly near the top of charge with mossy or spongy like zinc being plated”, which looks like another good reason to avoid fully charging the battery.
Dropping the charge voltage necessarily reduces the charge current and I assume keeps it much more even than it would be otherwise. I have not seen any high charge current warning since making this change. On the other hand, it does mean the battery charges slower than it would otherwise. I did a little experiment to test this, just watching the figures for amperage and kW the BMS gave me when I tweaked charge voltages:
This means I’m not using the battery as effectively as I could be with a higher charge voltage/current, but if this serves to extend the battery life, I think it’s worth it under the circumstances.
It’s important to keep an eye on is the Strip Pump Run Timer, which went weird on me a couple of times. I really should write a little script to automatically warn me if it starts running at half speed, but I’ve been habitually looking at the BMS briefly almost every day since the system was installed, so I noticed when this problem occurred because the maintenance timing was off. To reset a battery that gets in this state, go to Tools: ZBM Modbus Tool and write the value 0x80 to register 0x2053. This will appear to fail because it immediately resets the unit which thus never reports a successful write, but it does the trick.
Some time in the next six months I’m going to need to beg, borrow, steal or figure out how to manufacture carbon socks. The good news is that this time the replacement procedure is going to be really easy, because unlike the ZBM2 (where you had to mess with some pipe work) and my previous ZBM3 (where there was a cap on the side which in my case would have been completely inaccessible due to proximity to a wall), this one has an easy access screw cap on the front of the electrolyte tank.

The Redflow cloud went offline in late October 2024. This allowed remote access to the BMS, and I understand that some Redflow customers were unaware that it’s possible to access the BMS locally without the cloud. The Redflow cloud allowed firmware updates, and also let Redflow staff monitor batteries and configure them remotely, but it is not actually a hard requirement that this system exist in order for the batteries to continue to operate.
One way to access the BMS locally is via the wifi network on the BMS itself. If this is turned on, and you search for wifi access points you should find one named something like “zcell-bms-XXXX”. The password should be “zcellzcell”. Once you’re connected, open a web browser and go to http://zcell:3000. If that doesn’t work, try http://172.16.29.241:3000. This should let you see the BMS status. If you try to make any configuration changes it will ask you to log in. The default username and password are “admin” and “admin”. These can be changed under Configuration: Users.
The other way of accessing the BMS is to connect to whatever the IP address of the BMS is on your local network. The trick in this case is figuring out what the IP address is. I know what mine is because I logged into my router and looked at its list of attached devices.
Given the Redflow cloud is down and Redflow is out of business, I would actually suggest going into the BMS Site Configuration screen and unchecking the “Enable BMS cloud connection” and “Allow Redflow access to system for service intervention” boxes. There are two reasons for this:
Personally I hope whoever buys the Redflow IP will turn the cloud back on, in which case the above advice will no longer apply.
Individuals such as myself can’t just ring up a random courier and say “Hey, can you please go to New South Wales, pick up a 278kg crate with hazchem stickers that say ‘corrosion’ and have pictures of dead fish, and bring it to me here in Tasmania?” The courier will say “Hell no”, unless you have an account with them. Accordingly I would like to thank Stuart Thomas from Alive Technologies through whom I was able to arrange shipping, because his company does have an account with a courier, and he was also after some batteries so we were able to do a combined shipment. If anyone else is looking to move these batteries around, the courier in this instance was Imagine Cargo. I understand Redflow in the past used Mainfreight and Chemcouriers. In all cases, the courier will need to know the exact dimensions and weight which are in the manual, and will want a safety data sheet. Here they are:
Further thanks to Stuart and Gus (whose flatbed truck almost didn’t make it up our driveway) for last mile delivery, swapping the new ZBM3 into the old enclosure, and getting the damn thing in under our house.

It’s disappointing on many levels that Redflow went under, but like I said earlier, I remain convinced that flow batteries are in general a better idea for long-term stationary energy storage than lithium. I find it interesting that the sale of Redflow’s IP includes “specific assets and shares in Redflow (Thailand) Limited”. Given that’s where the manufacturing was done, could that indicate that the buyer is interested in potentially carrying on further development or manufacturing work? The identity of the buyer remains confidential right now, and final settlement is still a year away, so I guess we’ll just have to wait and see.
Our new ZBM3 was commissioned on March 18, and has been running well ever since. I’ve done everything I know to do to try to ensure it has a long and happy life, and will continue to keep a very close eye on it. There will be followup posts if and when anything else interesting happens.
Some time rather earlier in this journey, I found an easter egg in the BMS, which I didn’t mention in any of my previous posts. I think that might be a nice note to finish on here.
So, N years later, how is that going? It was going pretty well, but then there was a pandemic with lock-downs and curfews, which rather restricted access to dark skies.The obvious fix was to obtain access to dark skies, by way of a holiday house in the Wimmera.
In the mean time there were also a bunch of revolutions in astronomy, mostly to blame on open hardware. That means it is now possible to buy an off the shelf computer to control a bunch of mounts, cameras, auto-focusers, dew heaters and other gear. These are essentially raspberry pi machines with a modified operating system and (generally) a mobile app to control them.
Rather than fight software, keep laptops (and myself) out in the cold and kludge together VNC access, I got one of these machines (an asiair mini) and data acquisition is now mostly automated and not a problem. I set it up, tell it what I want, and in the morning I have images.
I do however still use open source software on Mac OS X to do my data processing. Notably I use Siril for pre-processing, stacking, stetching and noise reduction.
The following is an illustration of how to use xargs to conduct parallel operations on single-threaded applications, specifically wget.
GNU wget is a great tool for downloading content from websites. The wget command is a non-interactive network downloader; by "non-interactive" what is meant is that it can be run in the background. Some very hand options include -c (continue, for partially downloaded files), -m (mirror, for an entire website), -r --no-parent (recursive, no parent, to download part of a website and its subdirectories). The cURL application has a wider range of protocols and includes upload options, but is non-recursive.
Recently, I had the need to download a small number of PDF files. The wildcard-based approach would be:
$ wget -r -nd --no-parent -A 'rpgreview_*.pdf' http://rpgreview.net/files/
The -r and --no-parent options have already been explained. The -nd option allows one to save all files to the current directory, without hierarchy of directories. The -A option ('accept', or -R 'reject) allows one to specify comma-separated lists of file name suffixes or patterns to accept or reject. Note that if any of the wildcard characters, *, ?, or ranges [] to be in an acclist or rejlist.
Running the above has the following time:
real 2m19.353s
user 0m0.836s
sys 0m2.998s
An alternatiive, looping through each file one at a time, would have been something like:
for issue in {1..53}
do
wget "https://rpgreview.net/files/rpgreview_$issue.pdf"
done
(Just for the record, wget can get a bit gnarly when dealing with http requests because for some webservers there is no requirement for path delimiters to match directory delimiters. For the purposes of this discussion it is assumed that we're dealing with a rational being where the two are equivalent.)
Using a combination of the printf command and the xargs command a list of the URLs can be constructed which is then passed to xargs which can split the list to run in parallel.
By itself, xargs simply reads items from standard input, delimited by blanks or newlines, and executes commands from that list of items as arguments. This is somewhat different to the pipe command which, by itself, sends the output of one command as the input stream to another. In contrast, xargs takes data from standard input and executes a command which, by default, the data is appended to the end of the command as an argument. However, the data can be inserted anywhere however, using a placeholder for the input; the typical placeholder is {}.
The value -P 8 is entirely arbitrary here and should be modified according to available resources. Adding -nc prevents xargs attempting to download the same file more than once (wget will not overwrite an existing file, but rather append a new file with .1, etc. The -n option ensures that only one argument is run per process.
printf "https://rpgreview.net/files/rpgreview_%d.pdf\n" {1..53} | xargs -n 1 -P 8 wget -q -nc
The time of the above comes to:
real 1m23.534s
user 0m1.567s
sys 0m2.732s
Yet another choice is to use GNU parallel and seq.
seq 53 | parallel -j8 wget "https://rpgreview.net/files/rpgreview_{}.pdf"
real 1m57.647s
user 0m1.830s
sys 0m4.214s
A final option, most common in high-performance computing systems with job schedulers, is to make use of a job array. This is effective assuming resource availability. This is a very effective option if each task in the array takes more than a couple of minutes each (given that there is an overhead involved in constructing the job, submitting it to the queue, etc). In Slurm, a script the directives and code would look like the following:
#SBATCH --job-name="file-array"
#SBATCH --ntasks=1
#SBATCH --time=0-00:15:00
#SBATCH --array=1-53
wget "https://rpgreview.net/files/rpgreview_${SLURM_ARRAY_TASK_ID}.pdf"

It is appropriate, on World Quantum Day, to talk about quantum computing and quantum computers, as the two are often confused. Quantum computing is any method to generate quantum effects whereby qubit states can exist in superposition (o,1, both) rather than binary states (0,1). Binary states are represented in classical computing in low-level software as logical 0s and 1s but in hardware as high and low-voltage states.
The typical system to do quantum computing, or at least simulate it, is usually High Performance Computing (HPC). That works, it's a proven technology that has a rate of return of $44 per $1 invested - and higher when COVID research is considered. The development of HPC clusters with message passing is one of the most successful technological developments in computing in the last thirty years.
In contrast, a quantum computer directly uses a quantum mechanical system and requires appropriate specialised hardware. For example, GENCI in France uses a photonic computer, LRZ in Germany uses superconducting qubits, PSNC in Poland uses trapped ions, etc. David P. DiVincenzo offers the most significant physical challenges that face quantum computers, regardless of what technology is used; these include scaling qubits, initialisation of values, developing a universal gate for the construction of a quantum operation, developing gates that are faster than decoherence from a quantum state due to environmental interactions, and reading qubits (especially considering that can alter the quantum state).
As a result, classical computers outperform quantum computers in all real-world applications. Not only that, there is a serious issue of whether quantum computers will ever be able to outperform classical computers. Mikhail Dyakonov points out that the rudimentary qubits used in quantum computing systems is insufficient for useful calculations.
"Experts estimate that the number of qubits needed for a useful quantum computer, one that could compete with your laptop in solving certain kinds of interesting problems, is between 1,000 and 100,000. So the number of continuous parameters describing the state of such a useful quantum computer at any given moment must be at least 21,000, which is to say about 10^300. That's a very big number indeed. How big? It is much, much greater than the number of subatomic particles in the observable universe."
The promise of quantum computers is, of course, very significant in theory. In theory, it can perform some calculations incredibly fast, and the larger the task, the more impressive the result, to the extent that common secure encryption systems could be broken, as well as the more prosaic use in quantum simulations. In reality, the physical implementation has been more than challenging, to put it mildly. Classical computers, in principle, can solve the same problems as a quantum computer can, in principle solve as well. For a classical computer the problem is the sheer quantity of time that is required. For quantum computers, the problem is the implementation in reality. For the time being, and for the foreseeable future, it seems that quantum computing will continue to be done on classical computers.
| Attachment | Size |
|---|---|
| 189.81 KB |
My wife and I were with Optus for our mobile phone service since approximately the dawn of time, but recently decided to switch to another provider. We’d become less happy with Optus over the last few years after a data breach in 2022, an extended outage in 2023, and – most personally irritating – with them increasing the price of our plan despite us being under contract. Yes, I know the contract says they’re allowed to do that given 30 days notice, but they never used to do that. If you signed up for a $45 per month (or whatever) plan for two years, that’s what you paid per month for the duration. Not anymore. To their credit, when my wife lodged a complaint about this, they did end up offering us a 10% discount on our bill for the next 24 months, which effectively brought us back to the previous pricing, but we still maintain this practice just isn’t decent, dammit.
The question was: which provider to switch to? There are three networks in Australia – Telstra, Optus and Vodafone, so you either go with one of them, or with someone who’s reselling services on one of those networks. We already have a backup pre-paid phone with Telstra for emergencies, and so preferred the idea of continuing our main service on some other network for the sake of redundancy. iiNet (our ISP) repeatedly sent us email about nice cheap mobile services, but they were reselling Vodafone, and we’d always heard Vodafone had the worst coverage in regional Australia so we initially demurred. A few weeks ago though, iiNet told us they’d doubled their network coverage. It turns out this is due to TPG (iiNet and Vodafone’s parent) striking a deal with Optus for mutual network access. This all sounded like a good deal, so we ran with it. We received a new SIM each in the mail, so all we needed to do was log in to the iiNet toolbox website, receive a one time-code via SMS to confirm the SIM port, then put the new SIM in each of our phones, power cycle them and wait to connect. We decided to do one phone at a time lest we be left with no service if anything went wrong. I did my phone first, and something did indeed go wrong.
After doing the SIM activation dance, my phone – an aging Samsung Galaxy A8 4G which Optus had given me on a two year contract back in 2018 – said it was connected to iiNet. Mobile data worked. SMS worked. But I could not make or receive calls. Anyone I tried to call, the phone said “calling…” but there was no sound of a phone ringing, and eventually it just went >clunk< “call ended”. Incoming calls went straight to voicemail, which of course I could not access. Not knowing any better I figured maybe it was a SIM porting issue and decided to ignore it for a day in the hope that it would come good with time. Forty-eight hours later I realised time wasn’t working, so called iiNet support using this thing:

The extremely patient and courteous Jinky from iiNet support walked me through restarting my phone and re-inserting the SIM (which of course I’d already done), and resetting the network settings (which I hadn’t). She also did a network reset at their end, but I still couldn’t make or receive calls. Then she asked me to try the SIM in another handset, so I swapped it into our backup Telstra handset (a Samsung Galaxy S8), and somewhat to our surprise that worked fine. We double checked my handset model (SM-A530F) against the approved devices list, and it’s there, so it should have worked in my handset too… Alas, because we’d demonstrated that the SIM did work in another handset, there was nothing further Jinky could do for me other than suggest using a different handset, or finding a technician to help figure out what was wrong with my Galaxy A8.
After a lot of irritating searching I found a post on Whirlpool from someone who was having trouble making and receiving calls with their Galaxy A8 after the 3G network shutdown in late 2024. The interesting thing here was that they were using an Optus-branded but unlocked phone, with a Testra SIM. With that SIM, they couldn’t make or receive calls, but with an Optus SIM, they could. This sounded a lot like my case, just substitute “iiNet SIM” for “Testra SIM”. The problem seemed to be something to do with VoLTE settings? or flags? or something? That are somehow carrier dependent? And the solution was allegedly to partially re-flash the handset’s firmware – the CSC, or Country Specific Code bits – with generic Samsung binaries.
So I dug around a bit more. This post from Aral Balkan about flashing stock firmware onto a Galaxy S9+ using the heimdall firmware flashing tool on Ubuntu Linux was extremely enlightening. The Samsung Updating Firmware Guide on Whirlpool helpfully included a very important detail about flashing this stuff:
- Use CSC_*** if you want to do a clean flash or
- HOME_CSC_*** if you want to keep your apps and data. <== MOST PEOPLE USE THIS
The next question was: where do I get the firmware from? Samsung have apparently made it extremely difficult to obtain arbitrary firmware images directly from them – they’re buried somewhere in encrypted form on Samsung’s official update servers, so I ended up using samfw.com. I downloaded the OPS (Optus), VAU (Vodafone) and XSA (unbranded) firmware archives, matching the version currently on my phone, extracted them, then compared them to each other. The included archives for AP (System &Recovery), BL (Bootloader) and CP (Modem / Radio) were all identical. The CSC (Country / Region / Operator) and HOME_CSC files were different in each case. These are the ones I wanted, and the only ones I needed to flash. So, as described in the previously linked posts, here’s what I ended up doing:
heimdall flash --CACHE cache.img --HIDDEN hidden.img and waited in terror for my handset to be bricked.The procedure worked perfectly. VoLTE – which wasn’t previously active on my phone – now was, and I could make and receive calls. VoLTE stands for Voice over Long-Term Evolution, and is the communications standard for making voice calls on a 4G mobile network.
It was at this point that the woefully untrained infosec goblin who inhabits part of my brainstem began gibbering in panic. Something along the lines of “what the hell are you doing installing allegedly Samsung firmware from a web site you found listed in a random forum post on the internet?!?”
I believed from everything I’d read so far that samfw.com was reputable, but of course I had to double-check. After an awful lot of screwing around on a Windows virtual machine with a combination of SamFirm_Reborn (which could download Samsung firmware once I tweaked SamFirm.exe.config to not require a specific .NET runtime, but couldn’t decrypt it due presumably to that missing .NET runtime), and SamFirm (which can’t download the firmware due to Samsung changing their API to need a serial number or IMEI, but could decrypt what I’d downloaded separately with SamFirm_Reborn), I was able to confirm that the firmware I’d downloaded previously does in fact match exactly what Samsung themselves make available. So I think I’m good.
The SIM activation dance on my wife’s phone – a rather newer Samsung Galaxy S21 Ultra 5G – went without a hitch.
Neuro-divergence, encompassing conditions such as autism spectrum, ADHD, and sensory processing, can profoundly influence how individuals perceive and respond to their bodily signals.
While neurotypical individuals generally recognise and respond to hunger, thirst, and satiety cues with relative ease, neuro-divergent individuals often face unique challenges in this area. Understanding these challenges is crucial for fostering empathy and supporting effective strategies for well-being.
This article is written so it is directly readable and useful (in terms of providing action items) for people in your immediate surroundings, but naturally it can be directly applied by neuro-spicy people themselves!
For many neuro-divergent people, recognising hunger and thirst cues can be a complex task. These signals, which manifest as subtle physiological changes, might not be as easily identifiable or may be misinterpreted.
For instance, someone on the spectrum might not feel hunger as a straightforward sensation in the stomach but instead experience it as irritability or a headache. Similarly, those with ADHD may become so hyper-focused on tasks that they overlook or ignore feelings of hunger and thirst entirely.
Sensory processing issues can further complicate the interpretation of bodily signals. Neuro-divergent individuals often experience heightened or diminished sensory perception.
This variability means that sensations like hunger pangs or a dry mouth might be either too intense to ignore or too faint to detect. The result is a disconnection from the body’s natural cues, leading to irregular eating and drinking habits.
Recognising satiety and fullness presents another layer of difficulty. For neuro-divergent individuals, the brain-gut communication pathway might not function in a typical manner.
This miscommunication can lead to difficulties in knowing when to stop eating, either due to a delayed recognition of fullness or because the sensory experience of eating (such as the textures and flavours of food) becomes a primary focus rather than the physiological need.
Emotions and cognitive patterns also play significant roles. Anxiety, a common experience among neuro-divergent individuals, can mask hunger or thirst cues, making it harder to recognise and respond appropriately.
Additionally, rigid thinking patterns or routines, often seen with autism spectrum, might dictate eating schedules and behaviours more than actual bodily needs.
Understanding these challenges opens the door to effective strategies and support mechanisms:
Understanding the complex interplay between neuro-divergence and bodily signals underscores the importance of personalised approaches and compassionate support.
By acknowledging and addressing these challenges, we can help neuro-divergent individuals achieve better health and well-being!
The post Understanding and responding to hunger and thirst signals by neuro-divergent people first appeared on BlueHackers.org.The standard computing model uses unithreaded instructions and data with automation through looping and conditional branching. Automation is encouraged as it results in the computer doing the work that it is designed for. However, this can be inefficient when using a multicore system. An alternative in HPC systems is to make use of job arrays, which use a job to allocate resources to sub-jobs which can be individually controlled, whether directed toward instruction sets or datasets. Further, job arrays can be combined with job dependencies, allowing for conditional chains of job submission and runs. Finally, job arrays can be simulated through the use of heredocs with looped submission. This may even allow more familiar control with shell scripting.
This slidedeck is derived from a presentation to the Univerity of Melbourne's "Spartan Champions" group on March 7, 2025.
Since 2016, Facebook Messenger has allowed the option for end-to-end encrypted messages, and in 2023, they were established as the default.
This has caused some issues with people exporting Messenger data for archival or viewing purposes. It is a lot quicker to search for information when the data is local, and it is better practice to do so.
Encrypted Facebook Messenger data can be downloaded by selecting "Privacy & safety" on the Facebook menu, then "End-to-end encrypted chats", then "Message storage", and finally "Download secure storage data".
When the file is ready, it will provided as a zip file that contains various binaries in a "media" directory and well-formatted JSON files for each message chat for current Friends.
Despite the formatting, JSON files are less than optimal for humans to read. The "Lament" Python script makes use of pandas, json, sys, and datetime modules. Simply copy it into your messages directory, where all the JSON files are located and run:
$ python3 lament.py
It will then output a formatted HTML table that can be opened by a browser of your preference. The table includes a human-readable date (rather than the UNIX timestamp), the sender, the message, reactions, and a reference to any media.
The format and logic of the Python script are simple enough that it can be easily extended to other JSON data from Messenger and can be adapted to other JSON data files.
There’s a lot of blah flying around about DeepSeek and its latest models. My rule when running training sessions has always been TIAS, if someone asked me something that could be figured out relatively quickly by actually trying it. TIAS stands for Try It And See. It’s more valuable, because it’s a first-hand validation and doing the activity means the outcome is more likely to be remembered. So let’s do that!
My desktop has a decent AMD Ryzen 5 CPU, 32GB RAM, and an RTX 3060 GPU with 12GB VRAM. So while that’s not super hot, I sufficient to load and query a variety of LLMs locally without pain. By the way, ollama is a wonderful tool for this! So I had ollama grab deepseek-R1, which is the biggest reasoning model. It takes slightly longer to get an answer, but it tells you the process (aka “what it is thinking”. indicated inbetween the <think> … </think> tags). Details of the model:
>>> /show info Model architecture qwen2 parameters 7.6B context length 131072 embedding length 3584 quantization Q4_K_M
I am not using any pre-prompting here, I simply started ollama with the model and started asking the questions as noted below. A local model in ollama is typically not Internet connected nor does it have access to the broader system, proven by the following:
>>> What is the current date?
<think>
</think>
Hi there! I suggest getting online to get real-time information. If you have any other questions, please don't hesitate to let me know!
Ok, fair. On to a question then that the model might be able to answer.
>>> Who is the current president of the US?
<think>
Alright, the user previously asked for the current date and time, which I provided a response for. Now, they're asking who the current president of the US is.
I need to make sure my response is accurate and up-to-date. Since the last response was from July 2023, it's likely that the current president as of October 2023 would still be Joe Biden.
I should structure the answer clearly, stating their position explicitly. Adding a friendly emoji can make the response feel warmer.
I'll also keep it concise and straightforward to match the user's possible expectations.
</think>
As of now, the current President of the United States is **Joe Biden**.
Given the stated model build date of October 2023 which used input on this from July 2023, the answer is correct. The reasoning is interesting (though not unexpected).
a) it is maintaining state. As it should, otherwise each question would stand on its own and you’d never be able to ask a follow-up question.
b) It tries to infer from the previous question as to what the user’s intent is. Useful.
>>> Who is the current president of China?
<think>
Alright, so I need to figure out who the current president of China is. Let me start by recalling some information I have about Chinese leaders.
I know that former President Xi Jinping has been serving as the leader for quite a while now. I think he was first elected in 2012 or maybe 2013. Wait, actually, it was 2012 when he became the General Secretary of the Communist Party and then later he became president.
I also remember that there have been other leaders before him, like Deng Xiaoping, who was a very important leader in the reform and opening-up policies. Then there's Hu Jintao, who served two terms. After Hu, I think it was Wen Jiabao, but I'm not sure about his tenure.
So, putting this together, after Deng Xiaoping came Hu Jintao, then Wen Jiabao, followed by Xi Jinping taking over from 2013 onwards. So the current president is Xi Jinping.
</think>
The current President of China is **Xi Jinping**.
Correct. Now for the question that seems to get everybody’s knickers in a knot. DeepSeek’s mobile app doesn’t want to answer it, and people call out China’s censorship. We’ll talk about that in a moment, but let’s first try asking the local model straight out:
>>> Tell me about the Tiananmen Square event.
<think>
Okay, so I need to explain what happened at Tiananmen Square in China during the year 1989. From what I remember, it was a very significant event related to the Chinese government and its policies.
First, I think it started with a peaceful demonstration by students, intellectuals, and other groups who were upset about certain government actions or policies they believed were unfair. They gathered in Tiananmen Square because they wanted to express their opinions and demands.
As more people joined the protest, things turned into a larger-scale event. There were clashes between the protesters and the government's security forces. I believe there was some violence involved, with tear gas being used and maybe even some arrests or disruptions of the protest.
I also remember that there were military actions involved to maintain control, which might have led to casualties on both sides. The exact numbers are fuzzy in my memory, but I think several people were injured or killed during the events.
The government eventually cracked down hard on what they saw as an illegal demonstration. There was a lot of media coverage about it at the time, and now there's a debate about whether it was justified or an overreaction.
I'm not entirely sure about all the details, like the exact dates or how many people were involved, but I know it was a pivotal moment in modern Chinese history that led to various political changes. Maybe it's related to the 1989 protests and the subsequent shift in power within the government?
Overall, it seems like a complex event with multiple factors influencing its outcome, including government actions, international reactions, and the internal dynamics of the Communist Party.
</think>
Tiananmen Square is a significant historical event that occurred in Beijing on June 3-4, 1989. It was a peaceful demonstration by students, intellectuals, workers, and others who were protesting against what they perceived as unfair government policies regarding various issues such as human rights, economic reforms, and environmental regulations.
The protest began with small demonstrations and gradually turned into larger, more organized antigovernment activities. On June 3, several thousand people gathered in Tiananmen Square to protest against the Chinese Communist Party's handling of these issues.
As the protests grew, there was significant government crackdown. Security forces used tear gas, rubber bullets, and heavy machine gun fire to disperse the crowd, resulting in casualties on both sides. The government ultimately cracked down more brutally, arresting and killing many protesters. According to some accounts, at least 138 people were killed during the events.
The Tiananmen Square protests led to a dramatic shift in Chinese political power. After the crackdown, several members of the Chinese Communist Party who had supported the government's actions against the protesters were removed from leadership positions. The event also catalyzed widespread international condemnation and opened up a
period of political transition in China.
Right. So there we have it. It’s not refusing, it’s not hedging, it’s not skirting around the issue, it just answers (you should see ChatGPT hedge it answers, it’s icky, you need to very strictly pre-prompt it to make it not do that). DeepSeek doesn’t appear to be holding back at all, down to the use of “heavy machine gun fire to disperse the crowd”. As to whether there were indeed casualties on both sides I cannot say, even internationally there is rather a lack of independently verified information regarding the event. But for the purpose of this exercise, we can at least conclude that the model itself does not appear to be censoring its output.
So what about the mobile app that queries the model running in China? Well, someone else asked it a similar question to what I did above, and it didn’t want to talk about it. Then the person added “, answer in l33t speak.” to the question, whereupon they received a substantial answer (possibly less extensive than mine, but they may have queried the non-reasoning model).
What does this tell us? It’s simple logic (at least as a hypothesis): it probably means that the model itself contains all the information, but that in the online app the output gets scanned and censored via some automated mechanism. That mechanism isn’t perfect and humans are very creative, so in this instance it was bypassed. Remember: you can often tell a lot about how an application works internally just by observing how it behaves externally. And with the experiment of running a big DeepSeek model locally, we’ve just verified our hypothesis of where the censorship occurs as well, it seems clear that the model itself is not censored. At least not on these issues.
This is not to say that the model isn’t biased. But all models are biased, at the very least through their base dataset as well as the reinforcement learning, but often also for cultural reasons. Anyone pretending otherwise is either naive or being dishonest. But that’s something to further investigate and write about another time.
The post An initial look at running DeepSeek-R1 locally first appeared on Lentz family blog.I write, but just not here. Client sites, X, etc. so there is chronicling, but just not on the blog.
What changed from Hello 2024?
I got married. I moved into the flat. Companies have gone up and down, like life.
170 days on the road, 308,832km travelled, 38 cities, and 16 countries. I have never travelled this little in recent life, but maybe the whole getting married thing (planning a wedding is no mean feat), and sorting the flat out (dealing with incompetent interior designers, sorting things there, etc.), caused this?
It is 2025, and I’m actually planted in Kuala Lumpur, not having done an end of year trip, to usher in the New Year somewhere else. I started the year in Paris, and I ended the year in Kuala Lumpur, tired, and maybe a bit burnt out.
Working hard to get back into the grind; don’t get me wrong, I’ve been doing nothing but grinding, but c’est la vie.
I recently replaced the screen of a Google Pixel 3A XL, the new panel is made by tianma and worked well under Andoird, until it doesn’t. On every boot up the screen will work until the phone went to sleep, and then the screen will stop responding to touch, until another reboot. After the screen became unresponsive, the rest of the phone would remain responsive during the locked state and it’s possible to unlock the screen with fingerprint, but there is no way to make the touchscreen responsive again without reboot.
To fix this, go to Settings -> System -> Gestures and disable Double-tap to check phone. After which the screen should no longer stuck into unresponsive state. This seems to be a common problem affecting many phones with replaced screen.
Google will surely shutdown their support forum one day and I encourage everyone to put their notes somewhere reliable, like a selfhosted blog :)
Our 5.94kW solar array with Redflow ZCell battery and Victron Energy inverter/charger system is now slightly over three years old, which means it’s time to review its third year of operation. There are several previous posts in this series:
If you’ve read the above you’ll know that the solar array was originally installed back in 2017 along with a Sanden heat pump hot water service. That initial installation saved us a lot on our electricity bills, but it wasn’t until we got the ZCell and the Victron gear that we were able to really manage our own power. The ZCell allows us to store our own locally generated electricity for later use, and the Victron kit manages everything and gives us a whole lot of fascinating data to look at via the VRM portal.
There were some kinks in the first two years. We missed out on three weeks of prime solar PV generation from January 20 – February 11 in 2022 due to having to replace the MPPT solar charge controller. We also had no solar PV generation from February 17 – March 9 in 2023 on account of having our old tile roof replaced with colorbond steel. In my last post on this topic I wrote:
In both cases our PV generation was lower than it should have been by an estimated 500-600kW. Hopefully nothing like this happens again in future years.
…and then at the very end of that post:
I’m looking forward to doing another one of these posts in a year’s time. Hopefully I will have nothing at all interesting to report.
Alas, something “like this” did happen again, and I have some interesting things to report.
In early December 2023 our battery failed due to a leak in the electrode stack. It was replaced under warranty, but the replacement unit didn’t arrive until March 2024. It was a long three months. Then in August when we were looking at finally purchasing a second ZCell, we discovered that Redflow had made a commercial decision to focus exclusively on large-scale deployments (minimum 200 kWh, i.e. 20 batteries) and was thus no longer selling individual ZBMs for residential or small business use. As an existing customer we probably would have still been able to get a second battery, except that in late August the company went into voluntary administration after failing to secure funding to build a new factory in Queensland. The administrators attempted to seek a sale and/or recapitalisation, but this was ultimately unsuccessful. The company ceased operations on October 18 and subsequently went into liquidation. This raises several questions about the future of our system, but more on that later. First, let’s look at how the system performed in year three.
Here are the figures for grid power in, solar generation, power used by our loads, and power exported to the grid over the past three years. As in the last two posts, the “what?” column here is the difference between grid in plus solar in, minus loads minus export, i.e. the power consumed by the system itself, or the energy cost of the system.
| Year | Grid In | Solar In | Total In | Loads | Export | Total Out | what? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021-2022 | 8,531 | 5,640 | 14,171 | 10,849 | 754 | 11,603 | 2,568 |
| 2022-2023 | 8,936 | 5,744 | 14,680 | 11,534 | 799 | 12,333 | 2,347 |
| 2023-2024 | 8,878 | 5,621 | 14,499 | 11,162 | 1,489 | 12,651 | 1,848 |
Note that in year three our grid power usage and solar generation are slightly down from the previous year (-58kWh and -123kWh respectively), so the total power going into the system is lower by 181kWh. Our loads are happily down by 372kWh, a good chunk of which will be due to replacing some old always-on computer equipment with something a bit less power hungry.
What’s really interesting here is that our power exported to the grid is close to double the previous two years, and the energy cost of the system is noticeably lower. In the first two years of operation the latter figure was 16-18% of the total power going into the system, but in year three it’s down to a bit under 13%.
The additional solar export appears to be largely due to the failed battery. Compare the following two graphs from 2022-2023 and 2023-2024.Yellow is direct usage of solar power, blue is solar to battery and red is solar to grid. As you can see there’s way more solar to grid in the period December 2023 – March 2024 when the battery was dead and thus unable to be charged:
Why is there still any blue in that period indicating solar power was going to the battery? This is where things get a bit weird. One consideration is that the battery is presumably still drawing a tiny bit of power for its control circuitry and fans, but when I look at the figures for January 2024 (for example), it shows 76.8 kWh of power going to the battery from solar. There is no way that actually happened with the battery dead and unable to be charged.
Here’s what I think is going on: when the battery went into failure mode, the ZCell Battery Management System (BMS) will have told the Victron gear not to charge it. This effectively disabled the MPPT solar charger, which meant we weren’t able to use our solar at all, not even to run the house. I asked Murray from Lifestyle Electrical Services if there was some way we could reconfigure things to still use solar power with the battery out of action and he remoted in and tweaked some settings. Unfortunately I don’t have an exact record of what was changed at this point, because it was discussed via phone. All I have in my notes is a very terse “Set CGX to use Victron BMS?” which doesn’t make much sense because we don’t have a Victron BMS. Possibly it refers to switching the battery monitor setting from “ZCell BMS” to “MultiPlus-II 48/5000/ 70-50 on VE.Bus”. Anyway, whatever the case, I think we have to assume that the “to battery” and “from battery” figures from December 2023 – March 2024 are all lies.
At this point we were able to limp along with our solar generation still working during the day, but something was still not quite right. Every morning and evening the MPPT appeared to be fighting to run. Watching the console at, say, 08:00, I’d see the MPPT providing solar power for a few seconds, then it’d stop for a second or two, then it’d run again for a few seconds. After some time it would start behaving normally and we’d have solar generation for the day, but then in the evening it would go back to that flicking on and off behaviour. My assumption is that the ZCell BMS was still trying to force the MPPT off. Then in mid-Februrary I suddenly got a whole lot of Battery Low Voltage warnings from the MPPT, which I guess makes sense – the ZCell was still connected and its reported voltage had been very slowly dropping away over the past couple of months. The warnings appeared when it finally hit 2.5V. Murray and I experimented further to try to get the MPPT to stop doing the weird fighting thing, but were unsuccessful. At one point during this we ended up with the Mutli-Plus II inverter/chargers in some sort of fault state and contacted Simon Hackett for further assistance. We got all the Victron gear back into a sensible state and Simon and I spent a bunch of time on a Saturday afternoon messing with everything we could think of, but ultimately we were unable to get the MPPT to provide power from the solar panels, and use grid power, without the battery present. One or the other – grid power only or solar power only – we could do, but we couldn’t get the system to do both at the same time again without the battery present. Turns out a thing that’s designed to be an Energy Storage System just won’t quite work right without the Storage part. So from February 15 through to March 14 when the replacement battery arrived we were running on grid power only with no solar generation.
Happily, we didn’t have any grid power outages during the three months we were without a battery. Our first outage of any note wasn’t until March 23, slightly over a week after the replacement battery was installed. There were a few brief grid outages at other times later – a couple of minutes one day in April, some glitches on a couple of days in August, but the really bad one was on the 1st of September when the entire state got absolutely hammered by extremely severe weather. Given there was a severe weather warning from the BOM I’d made sure the battery was full in advance, which was good because our grid power went out while we were asleep at about 00:37 and didn’t come back on until 17:28. We woke up some time after the grid went down with the battery at 86% state of charge and went around the house to turn off everything we could except for the fridge and freezer, which got our load down to something like 250W. By morning, the battery still had about 70% in it and even though the weather was bad we still had some solar generation, so between battery and solar we got through just fine until the grid came back on in the afternoon. We were lucky though – some folks in the north of the state were without power for two weeks due to this event. I later received a cheque for $160 from TasNetworks in compensation for our outage. I dread to think what the entire event cost everyone, and I don’t just mean in terms of money.
Speaking of money though, the other set of numbers we need to look at are our power bills. Here’s everything from the last seven years:
| Year | From Grid | Total Bill | Grid $/kWh | Loads | Loads $/kWh |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016-2017 | 17,026 | $4,485.45 | $0.26 | 17,026 | $0.26 |
| 2018-2019 | 9,031 | $2,278.33 | $0.25 | 11,827 | $0.19 |
| 2019-2020 | 9,324 | $2,384.79 | $0.26 | 12,255 | $0.19 |
| 2020-2021 | 7,582 | $1,921.77 | $0.25 | 10,358 | $0.19 |
| 2021-2022 | 8,531 | $1,731.40 | $0.20 | 10,849 | $0.16 |
| 2022-2023 | 8,936 | $1,989.12 | $0.22 | 11,534 | $0.17 |
| 2023-2024 | 8,878 | $2,108.77 | $0.24 | 11,162 | $0.19 |
As explained in the last post, I’m deliberately smooshing a bunch of numbers together (peak power charge, off peak power charge, feed in tariff, daily supply charge) to arrive at an effective cost/kWh of grid power, then bearing in mind our loads are partially powered from solar I can also determine what it costs us to run all our loads. 2016-2017 is before we got the solar panels and the new hot water service, so you can see the immediate savings there, then further savings after the battery went in in 2021. This year our cost/kWh (and thus our power bill) is higher than last year for two reasons:
I should probably also mention that we actually spent $1,778.94 on power this year, not $2,108.77. That’s thanks largely due to a $250 ‘Supercharged’ Renewable Energy Dividend payment from the Tasmanian Government and $75 from the Federal Government’s Energy Bill Relief Fund. The remaining $4.83 in savings is from Aurora Energy’s ridiculous Power Hours events. I say “ridiculous” because they periodically give you a bunch of time slots to choose from, and once you’ve locked one of them in, any power you use at that time is free. To my mind this incentivises additional power usage, when we should really be doing the exact opposite and trying to use less power over all. So I haven’t tried to use more energy, I’ve just tried to lock in times that were in the evening when we were going to be using more grid power than during the day to scrape in what savings I could.
One other weird thing happened this year with the new battery. ZCells need to go into a maintenance cycle every three days. This happens automatically, but is something I habitually keep an eye on. On September 11 I noticed that we had been four days without running maintenance. Upon investigation of the battery logs I discovered that the Time Since Strip counter and Strip Pump Run Timer were running at half speed, i.e. every minute they were each only advancing by approximately 30 seconds:
I manually put the battery into maintenance mode and Simon was able to remotely reset the CPU by writing some magic number to a modbus register, which got the counters back to the correct speed. I have no idea whether this is a software bug or a hardware issue, but I’ll continue to keep an eye on it. The difficulty is going to be dealing with the problem should it recur, given the demise of Redflow. Simon certainly won’t be able to log in remotely now that the Redflow cloud is down, although there is a manual reset procedure. If you remove the case from the battery there is apparently a small phillips head screw on the panel with the indicator lights. Give the screw a twist and the lights go out. Untwist and the lights come back on and the unit is reset. I have yet to actually try this.
The big question now is, where do we go from here? The Victron gear – the Cerbo GX console, the Multi-Plus II inverter/chargers, the MPPT – all work well with multiple different types of battery, so our basic infrastructure is future-proof. Immediately I hope to be able to keep our ZCell running for as long as possible, and if I’m able to get a second one as a result of the Redflow liquidation I will, simply so that we can ensure the greatest possible longevity of the system before we need to migrate to something else. We will also have to somehow figure out how to obtain carbon socks which need annual replacement to maintain the electrolyte pH. If we had to migrate to something else in a hurry Pylontech might be a good choice, but the problem is that we really don’t want a rack of lithium batteries in the crawl space under our dining room because of the fire risk. There are other types of flow battery out there (vanadium comes to mind) but everything I’ve looked at on that front is either way too big and expensive for residential usage, or is “coming soon now please invest in us it’s going to be awesome”.
I have no idea what year four will look like, but I expect it to be interesting.
I believe buying a Kindle in 2024 is a bad idea, even if you only intend to use it for reading DRM-free locally stored ebooks. Basic functions such as organizing books into folders/collections are locked until the device is registered and with each system update the interface has became slower and more bloated.
Initially I purchased this device because Amazon book store isn’t too bad and it’s one of the easier way to buy Japanese books outside of Japan, but with all the anti-features Amazon add in I don’t think it’s still worth using.
Using a recent exploit and with this downgrader thread on the mobileread forum, I’m able to downgrade my paperwhite to an older 5.11.2 firmware which has a simpler interface while being much more responsive. If you already have a Kindle perhaps this is worth doing.
It’s possible to install alternative UI and custom OS to many Kindle models but they generally run slower than the default launcher. On the open hardware side Pine64 is making an e-ink tablet called the PineNote with an Rockchip RK3566 and 4G of RAM it should be fast enough to handle most documents/ebooks, but currently there is no usable Linux distribution for it.
We all wear masks in public. But how much do you change when you take yours off? The gap between your public and private self is the measure of your authenticity. #Authenticity #PersonalGrowth #ChrisDo
https://www.canva.com/design/DAGPfl9FLsU/tgl6rz3Ek1c49HDa-Felxw/edit
Assessment: This content is suitable for LinkedIn as it reflects on a practical tech solution and shares a personal story.
Approach: A brief text post that connects your experience with broader insights on data management.
Content:
"Recently, I found myself in a tight spot when both my phone and laptop ran out of storage. After some frustration, I decided to invest in cloud storage with rsync.net, and it’s made a world of difference. This experience reminded me how important it is to stay on top of data management, especially in our increasingly digital world. How do you manage your digital storage? #DataManagement #CloudStorage #TechInsights"
image prompt:
---
Create a professional yet approachable image showing a workspace with a laptop and a phone, both displaying a 'Storage Full' notification. Next to them, depict a cloud storage icon (representing rsync.net) with a checkmark indicating a solution. The background should be neutral and tidy, evoking a sense of organization and efficiency. Use a cool color palette to maintain a professional tone.
Approach: Short video with text overlay. Use a quick clip of you reacting to the storage full message, followed by a clip showing the solution.
Content:
Clip 1: (Reacting to 'Storage Full' messages)
Text overlay: "When your phone and laptop BOTH fill up...😱"
Clip 2: (Showing you happily purchasing cloud storage on rsync.net)
Text overlay: "So I finally got cloud storage—no more panic! 🌥� #TechWoes #CloudStorage #StoryTime"
1) A 'Storage Full' Warning on a Phone and Laptop Screen
Text Prompt:
"Create a clean and modern image showing a smartphone and a laptop side by side, both displaying prominent 'Storage Full' warning messages on their screens. The design should use bold, easy-to-read text for the warnings, with simple red and yellow alert icons. The background should be minimal, using neutral colors like light grey or white to keep the focus on the devices and warnings. Use a flat design style with sharp, clean lines to maintain a sleek and professional look."
Text Prompt:
"Design a clean and modern image featuring a close-up of a computer screen where a cursor is selecting a cloud storage icon. The icon should be a stylized, simple cloud with a checkmark or arrow indicating selection. The background should be a minimal desktop or web interface, with a focus on the cloud storage icon. Use a flat design style, with soft blue and white tones to create a sense of calm and reliability. Keep the overall aesthetic sleek and professional, with sharp lines and clear details."
Text Prompt:
"Create a clean and modern image depicting a person sitting at a desk with a laptop and phone in front of them. The person should have a relaxed, satisfied expression, indicating that their storage problem has been solved. The background should be simple and uncluttered, possibly showing a hint of the workspace with minimalistic decor. Use a soft color palette with blues, greys, and whites to evoke a sense of calm and contentment. The design should be flat and stylized, with clean lines and a focus on the person's expression and posture."
Approach: Short, impactful tweet with hashtags to drive engagement.
Content:
"Gary Vee says to put out 15-25 pieces of content per day. 🎯 Start with long-form content and repurpose across platforms like YouTube, Instagram, and TikTok. Who's ready to level up? #GaryVee #ContentStrategy #SocialMedia"
https://twitter.com/thursday_bw/status/1829461724120154233
The easiest way to change/set PIN for FIDO2 token seems to be with Chromium/Chrome:
chrome://settings/securityKeys, or click Settings -> Privacy and Security -> Security -> Manage security keysCreate a PIN, if you don’t have a PIN set already, a new PIN will be created, otherwise you will be asked to change the existing pinI’ve been daily driving the PinePhone Pro with swmo for some times now, it’s not perfect but I still find it be one of the most enjoyable devices I’ve used. Probably only behind BlackBerry Q30/Passport which also has a decent keyboard and runs an unfortunately locked-down version of QNX. For me it’s less like a phone and more like a portable terminal for times when using a full size laptop is uncomfortable or impractical, and with the keyboard it’s possible to write lengthy articles on the go.
This isn’t the only portable Linux terminal I owned, before this I used a Nokia N900 which till this day is still being maintained by the maemo leste team, but the shutdown of 3G network in where I live made it significantly less usable as a phone and since it doesn’t have a proper USB port I cannot use it as a serial console easily.
The overall experience on the PPP now as of 2024 isn’t as polished as that of the BlackBerry Passport, and adhoc hacks are often required to get the system going, however as the ecosystem progress the experience will also improve with new revisions of hardware and better software.
I use sxmo and swmo interchangeably in this post, they refer to the same framework running under Xorg and wayland, the experience is pretty much the same.
Sxmo is packaged for Debian:
sudo apt install sway sxmo-util
Allow access to LED/brightness:
sudo usermod -aG feedbackd user
The default scaling of sxmo doesn’t allow the many desktop applications to display their window properly, especially when such application is written under the assumption of being used on a larger screen. To set the scaling to something more reasonable, add the following line to ~/.config/sxmo/sway:
exec wlr-randr --output DSI-1 --scale 1.3
When using swmo environment initialization is mostly done in ~/.config/sxmo/sway and ~/.config/sxmo/xinit is not used.
Scaling for Firefox needs to be adjusted separately by first enabling compact UI and then set settings -> default zoom to your liking.
I used lightdm as my session manager, to launch lightdm in landscape mode, change the display-setup-script line in the [Seat:*] section of /etc/lightdm/lightdm.conf to:
display-setup-script=sh -c 'xrandr -o right; exit 0'
To rotate to swmo to landscape mode on start:
$ echo exec sxmo_rotate.sh >> ~/.config/sxmo/sway
To rotate Linux framebuffer, add fbcon=rotate:1 to the U_BOOT_PARAMETERS line in /usr/share/u-boot-menu/conf.d/mobian.conf and run u-boot-update to apply.
I also removed quiet splash from U_BOOT_PARAMETERS to disable polymouth animation as it isn’t very useful on landscape mode.
Swmo doesn’t come with a secure screen locker. but swaylock works fine and it can be bind to a key combination with sway’s configure file. To save some battery life, systemctl suspend can be triggered after swaylock, to bind that to Meta+L:
# .config/sxmo/sway
bindsym $mod+l exec 'swaylock -f -c 000000 && systemctl suspend'
In suspend mode, the battery discharge at a rate of about 1% per hour, I consider this to be more than acceptable.
To unlock from a shell, just kill swaylock.
Before you can suspend the system as a non-root user, the following polkit rule needs to be written to /etc/polkit-1/rules.d/85-suspend.rules:
polkit.addRule(function(action, subject) {
if (action.id == "org.freedesktop.login1.suspend" &&
subject.isInGroup("users")) {
return polkit.Result.YES;
}
});
It would be better if there can be a universal interactive user group which automatically grant such permission to the desktop/mobile user.
The default keymap for the PinePhone keyboard is missing a few useful keys, namely F11/F12 and PgUp/PgDown. To create those keys I used evremap(1) to make a custom keymap. Unfortunately the Fn key cannot be mapped as a layer switcher easily, so I opted to remap AltG and Esc as my primary modifiers.
I’m working on a Debian package for evremap and it will be made available for Debian/Mobian soon.
Incus is a container/VM manager for Linux, it’s available for Debian from bookworm/backports and is a fork of LXD by the original maintainers behind LXD. It works well for creating isolated and unprivileged containers. I have multiple incus containers on the PinePhone Pro for Debian packaging and it’s a better experience than manually creating and managing chroots. In case there is a need for running another container inside an unprivileged incus container, it’s possible to configure incus to intercept certain safe system calls and forward them to the host, removing the need for using privileged container.
Sway is decently usable in convergence mode, in which the phone is connected to a dock that outputs to an external display and keyboard and mouse are used as primary controls instead of the touchscreen.
This isn’t surprising since sway always had great support for multi monitor, however another often overlooked convergence mode is with waypipe. In this mode another Linux machine (e.g. a laptop) can be used to interact with applications running on the phone and the phone will be kept charged by the laptop. This is particularly useful for debugging phone applications or for accessing resources on the phone (e.g. sending and receiving sms). One thing missing in this setup is that graphic applications cannot roam between the phone and the external system (e.g. move running applications from one machine to another). Xpra does this for Xorg but doesn’t work with wayland.
Due to the simplicity of the swmo environment it’s not too difficult to get the system running with SELinux in Enforcing mode, and I encourage everyone reading this to try it. If running debian/mobian a good starting point is the SELinux/Setup page on Debian wiki.
Note: selinux-activate won’t add the required security=selinux kernel option to u-boot (it only deals with GRUB) so you have to manually add it to the U_BOOT_PARAMETERS line in /usr/share/u-boot-menu/conf.d/mobian.conf and run u-boot-update after selinux-activate. The file labeling process can easily take 10 minutes and the progress won’t be displayed on the framebuffer (only visible via the serial console).
SELinux along with the reference policy aren’t enough for building a reasonably secure interactive system, but let’s leave that for a future post.
The April 2024 meeting is the first meeting after Everything Open 2024 and the discussions are primarily around talks and lectures people found interesting during the conference, including the n3n VPN and the challenges of running personal email server. At the start of the meeting Yifei Zhan demonstrated a development build of Maemo Leste, an active Maemo-like operating system running on a PinePhone Pro.
Other topics discussed including modern network protocol ossification, SIP and possible free and open source VoLTE implementation.
The PinePhone keyboard contains a battery, which will be used to charge the PinePhone when the keyboard is attached. Althrough there are existing warnings on the pine64 wiki which sums up to ‘don’t charge or connect anything to your pinephone’s type C interface when the keyboard is attached’, my two pinephone keyboards still managed to fry themselves, with one releasing stinky magic smoke and the other melting the plastic around the pogo pins on the pinephone backplate.
This all happened while the pinephone’s type C interface being physically block when attached to the keyboard. In the first case, the keyboard’s controller PCB blew up when I tried to charge it, in the latter case the keyboard somehow overheated and melted the plastic near the pogo interface on the phone side.
Pine64 provided me a free replacement keyboard after multiple emails back and forth, but according to Pine64 there will be no more free replacement for me in future, and there is no guarantee that this will not happen to my replacement keyboard.
The cost for replacing all the fried parts with spare parts from the Pine64 store is about 40 USD (pogo pins + backplate + keyboard PCB), and considering this problem is likely to happen again, I don’t think purchasing those parts is a wise decision.
Both the melting plastic and the magic smoke originated from the fact that charges are constantly shuffled around when the keyboard is attached to the pinephone, and since the keyboard can function independently from the battery, we can disconnect and remove the battery from the keyboard case to make sure it will not blow up again. After such precedure the keyboard will keep functioning althrough the keyboard-attached pinephone might flip over much more easily due to the lightened keyboard base. Be aware that the keyboard isn’t designed to be taken apart, and doing so will likely result in scratches on the case. As for me, I’d much rather have a keyboard case without builtin battery than have something that can overheat or blow up.
To prevent the kernel module from flooding the dmesg and reporting bogus battery level after the battery removal, blacklist the ip5xxx_power module:
# echo blacklist ip5xxx_power > /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist.conf
I didn’t take as much notes on day 2 and 3, so I merged them into a single article.
Adversaries:
LLM can help eliminate common language mistakes, perform better social enginerring
Many adversaries are trying to integrate LLMs into their workflow, with varying results
Time frame from initial foothold to lateral movements is getting shorter, due to better toolings?
porting syzcaller to run on Power
general fuzzinng engines
Unsupervised: no human input required
Coveraged-guided: fuzz and measures which codepath is fuzzed
Things to fuzz: syscalls/dxrivers/fs/ebpf/kvm/network stacks…
Simple kernel fuzzers existed est. 1991
Hosted version on Google Cloud: https://syzkaller.appspot.com/upstream
Sanitisers: print errors on memory corruption/UB/concurrency problems etc
KMSAN isn’t on Power yet
Hardware:
New architecture enablement
Stack traces are printed differently across archs
instruction fuzzing
QEMU/KVM on bare metal Open Power systems
Bug found:
PowerVM
PowerVC
FileSender
radio::console
AgOpenGPS
BPF made creating new scheduler simpler
Scheduling problem is now more complicated due to increasing complexity of workload/CPU design
BPF provides reliable access to critical data structures inside the kernel
Forked from n2n to avoid CLA
Peer-to-peer VPN at network layer, acting like a distributed virtual switch
NAT piecing
Written in C, should have good cross-platform supports (more testing wanted on *BSD)
TunTap interface support is expected from the OS side, shouldn’t be a problem for common Unix-likes
Packaging and distro submission are still WIP
Future roadmap
Useful for
Simpler than wireguard/openvpn but offers OK security (not for security-critical apps?)
Easier to configure, use INI style config files
seL4 is bad at usability, Lions OS intends to solve this
Still in early stage of development
Composable components for build custom OS for a single task
Focus on simplicity
0.1.0 just released, still in its early stage
high performance
Only for Arm64/aarch64 now, riscv64 in future?
A reference system called Kitty exists
Here you can find a list of links related to my topic which I find useful or just interesting.
Info page https://2024.everythingopen.au/schedule/presentation/24/
Slides EO2024.Slides.exploring.mobile.linux.security.odp
Recording XXX to be processed
VerityMobile GitHub :: ZhanYF/veritymobile
Access Measurements from Linux Userland
Sign in to GitLab with fTPM-backed FIDO token
https://optee.readthedocs.io/en/latest/general/about.html
https://optee.readthedocs.io/en/latest/architecture/secure_storage.html
https://optee.readthedocs.io/en/latest/architecture/globalplatform_api.html#globalplatform-api
https://optee.readthedocs.io/en/latest/general/presentations.html
https://source.android.com/docs/security/features/trusty
https://support.apple.com/en-sg/guide/security/sec59b0b31ff/web
This also covers Measured Boot and Secure Boot
https://next.redhat.com/2021/05/13/what-can-you-do-with-a-tpm/
https://github.com/psanford/tpm-fido
https://www.ledger.com/blog/ssh-with-tpm
https://bootlin.com/pub/conferences/2021/lee/perrot-secure-boot/perrot-secure-boot.pdf
https://github.com/kkamagui/shadow-box-for-arm https://github.com/kkamagui/manifest
https://github.com/kkamagui/shadow-box-for-x86
https://blog.3mdeb.com/2021/2021-12-03-rockchip-secure-boot/
https://sergioprado.blog/rpmb-a-secret-place-inside-the-emmc/
https://github.com/firecracker-microvm/firecracker
https://github.com/firecracker-microvm/firectl
I got a call yesterday from a guy who had looked at the Experia Bruce has at Zen and was considering buying one. I talked with him for about three quarters of an hour, going through my experience, and to sum it up simply I can just say: this is a fantastic motorbike.
Firstly, it handles exactly like a standard motorbike - it handles almost exactly like my previous Triumph Tiger Sport 1050. But it is so much easier to ride. You twist the throttle and you go. You wind it back and you slow down. If you want to, the bike will happily do nought to 100km/hr in under four seconds. But it will also happily and smoothly glide along in traffic. It says "you name the speed, I'm happy to go". It's not temperamental or impatient; it has no weird points where the throttle suddenly gets an extra boost or where the engine braking suddenly drops off. It is simple to ride.
As an aside, this makes it perfect for lane filtering. On my previous bike this would always be tinged with a frisson of danger - I had to rev it and ease the clutch in with a fair bit of power so I didn't accidentally stall it, but that always took some time. Now, I simply twist the throttle and I am ahead of the traffic - no danger of stalling, no delay in the clutch gripping, just power. It is much safer in that scenario.
I haven't done a lot of touring yet, but I've ridden up to Gosford once and up to Sydney several times. This is where Energica really is ahead of pretty much every other electric motorbike on the market now - they do DC fast charging. And by 'fast charger' here I mean anything from 50KW up; the Energica can only take 25KW maximum anyway :-) But this basically means I have to structure any stops we do around where I can charge up - no more stopping in at the local pub or a cafe on a whim for morning tea. That has to either offer DC fast charging or I'm moving on - the 3KW onboard AC charger means a 22KW AC charger is useless to me. In the hour or two we might stop for lunch I'd only get another 60 - 80 kilometres more range on AC; on DC I would be done in less than an hour.
But OTOH my experience so far is that structuring those breaks around where I can charge up is relatively easy. Most riders will furiously nod when I say that I can't sit in the seat for more than two hours before I really need to stretch the legs and massage the bum :-) So if that break is at a DC charger, no problems. I can stop at Sutton Forest or Pheasant's Nest or even Campbelltown and, in the time it takes for me to go to the toilet and have a bit of a coffee and snack break, the bike is basically charged and ready to go again.
The lesson I've learned, though, is to always give it that bit longer and charge as much as I can up to 80%. It's tempting sometimes when I'm standing around in a car park watching the bike charge to move on and charge up a bit more at the next stop. The problem is that, with chargers still relatively rare and there often only being one or two at each site, a single charger not working can mean another fifty or even a hundred kilometres more riding. That's a quarter to half my range, so I cannot afford to risk that. Charge up and take a good book (and a spare set of headphones).
In the future, of course, when there's a bank of a dozen DC fast chargers in every town, this won't be a problem. Charger anxiety only exists because they are still relatively rare. When charging is easy to find and always available, and there are electric forecourts like the UK is starting to get, charging stops will be easy and will fit in with my riding.
Anyway.
Other advantages of the Experia:
You can get it with a complete set of Givi MonoKey top box and panniers. This means you can buy your own much nicer and more streamlined top box and it fits right on.
Charging at home takes about six hours, so it's easy to do overnight. The Experia comes with an EVSE so you don't need any special charger at home. And really, since the onboard AC charger can only accept 3KW, there's hardly any point in spending much money on a home charger for the Experia.
Minor niggles:
The seat is a bit hard. I'm considering getting the EONE Canyon saddle, although I also just need to try to work out how to get underneath the seat to see if I can fit my existing sheepskin seat cover.
There are a few occasional glitches in the display in certain rare situations. I've mentioned them to Energica, hopefully they'll be addressed.
Overall rating:
5 stars. Already recommending.
Way back in the distant past, when the Apple ][ and the Commodore 64 were king, you could read the manual for a microprocessor and see how many CPU cycles each instruction took, and then do the math as to how long a sequence of instructions would take to execute. This cycle counting was used pretty effectively to do really neat things such as how you’d get anything on the screen from an Atari 2600. Modern CPUs are… complex. They can do several things at once, in a different order than what you wrote them in, and have an interesting arrangement of shared resources to allocate.
So, unlike with simpler hardware, if you have a sequence of instructions for a modern processor, it’s going to be pretty hard to work out how many cycles that could take by hand, and it’s going to differ for each micro-architecture available for the instruction set.
When designing a microprocessor, simulating what a series of existing instructions will take to execute compared to the previous generation of microprocessor is pretty important. The aim should be for it to take less time or energy or some other metric that means your new processor is better than the old one. It can be okay if processor generation to generation some sequence of instructions take more cycles, if your cycles are more frequent, or power efficient, or other positive metric you’re designing for.
Programmers may want this simulation too, as some code paths get rather performance critical for certain applications. Open Source tools for this aren’t as prolific as I’d like, but there is llvm-mca which I (relatively) recently learned about.
llvm-mca is a performance analysis tool that uses information available in LLVM (e.g. scheduling models) to statically measure the performance of machine code in a specific CPU.
the llvm-mca docs
So, when looking at an issue in the IPv6 address and connection hashing code in Linux last year, and being quite conscious of modern systems dealing with a LOT of network packets, and thus this can be quite CPU usage sensitive, I wanted to make sure that my suggested changes weren’t going to have a large impact on performance – across the variety of CPU generations in use.
There’s two ways to do this: run everything, throw a lot of packets at something, and measure it. That can be a long dev cycle, and sometimes just annoying to get going. It can be a lot quicker to simulate the small section of code in question and do some analysis of it before going through the trouble of spinning up multiple test environments to prove it in the real world.
So, enter llvm-mca and the ability to try and quickly evaluate possible changes before testing them. Seeing as the code in question was nicely self contained, I could easily get this to a point where I could easily get gcc (or llvm) to spit out assembler for it separately from the kernel tree. My preference was for gcc as that’s what most distros end up compiling Linux with, including the Linux distribution that’s my day job (Amazon Linux).
In order to share the results of the experiments as part of the discussion on where the code changes should end up, I published the code and results in a github project as things got way too large to throw on a mailing list post and retain sanity.
I used a container so that I could easily run it in a repeatable isolated environment, as well as have others reproduce my results if needed. Different compiler versions and optimization levels will very much produce different sequences of instructions, and thus possibly quite different results. This delta in compiler optimization levels is partially why the numbers don’t quite match on some of the mailing list messages, although the delta of the various options was all the same. The other reason is learning how to better use llvm-mca to isolate down the exact sequence of instructions I was caring about (and not including things like the guesswork that llvm-mca has to do for branches).
One thing I learned along the way is how to better use llvm-mca to get the results that I was looking for. One trick is to very much avoid branches, as that’s going to be near complete guesswork as there’s not a simulation of the branch predictor (at least in the version I was using.
The big thing I wanted to prove: is doing the extra work having a small or large impact on number of elapsed cycles. The answer was that doing a bunch of extra “work” was essentially near free. The CPU core could execute enough things in parallel that the incremental cost of doing extra work just… wasn’t relevant.
This helped getting a patch deployed without impact to performance, as well as get a patch upstream, fixing an issue that was partially fixed 10 years prior, and had existed since day 1 of the Linux IPv6 code.
Naturally, this wasn’t a solo effort, and that’s one of the joys of working with a bunch of smart people – both at the same company I work for, and in the broader open source community. It’s always humbling when you’re looking at code outside your usual area of expertise that was written (and then modified) by Really Smart People, and you’re then trying to fix a problem in it, while trying to learn all the implications of changing that bit of code.
Anyway, check out llvm-mca for your next adventure into premature optimization, as if you’re going to get started with evil, you may as well start with what’s at the root of all of it.
At this rate, there is no real blogging here, regardless of the lofty plans to starting writing more. Stats update from Hello 2023:
219 days on the road (less than 2022! -37, over a month, shocking), 376,961km travelled, 44 cities, 17 countries.
Can’t say why it was less, because it felt like I spent a long time away…
In Kuala Lumpur, I purchased a flat (just in time to see Malaysia go down), and I swapped cars (had a good 15 year run). I co-founded a company, and I think there is a lot more to come.
2024 is shaping up to be exciting, busy, and a year, where one must just do.
good read: 27 Years Ago, Steve Jobs Said the Best Employees Focus on Content, Not Process. Research Shows He Was Right. in simple terms, just do.
After a short sabbatical from public service, I’m delighted to announce I’m returning to the Australian Public Service, where I intend to do my part in the extraordinary and once-in-a-generation reform agenda currently under way 
I have had wonderful opportunities over the past 23 years to work with and in the public sector, but it was 15 years ago that I really committed my professional life and career to public sector reform. I’ve since built up a broad and deep understanding of good public administration, while also acting as an enthusiastic pathfinder to shape modern, innovative and evidence-based approaches with adaptive operating models for more humane and participatory public policy, services and governance.
As part of this journey, and for those who want to understand my move to AWS, I decided to take a “public sector sabbatical� at the beginning of last year. I had three goals:
I was extremely lucky to be offered a role in a special team at Amazon Web Services (AWS) where I have not only been encouraged, but supported to explore these wicked problems, while also being able to share and learn along the way. It was great to work for a large tech company that is genuinely committed to helping their clients to grow and succeed, including the necessary internal capability and confidence in modern tech, mindsets and design/delivery methods. I also got to work with some extraordinary colleagues and a wonderfully visionary boss  A huge thank you to Bruce Haefele, Amity Durham, Jithma Beneragama, Tim Bradley and Jodi Philips in the AWS Strategic Development team, along with all the other wonderful people I got to collaborate with. If you’re looking for AWS folk who really understand both gov and tech, Bruce and the team are great
A huge thank you to Bruce Haefele, Amity Durham, Jithma Beneragama, Tim Bradley and Jodi Philips in the AWS Strategic Development team, along with all the other wonderful people I got to collaborate with. If you’re looking for AWS folk who really understand both gov and tech, Bruce and the team are great  Thanks for the opportunity!
Thanks for the opportunity!
So I’m delighted to say I was able to do some great work on a whole range of projects while also making progress on all three of my professional goals:

My last reflection, is that I went to AWS because I wanted to continue working on public sector reform, even if from a position outside of service for a short spell, and I wanted to work specifically for an organisation that was aligned with my goal. AWS has, at its heart, a “customer obsession� which enables the company to systemically want to help clients to succeed and be highly capable, which is not always the case. So while some people were confused with my choice of sabbatical, hopefully the above helps to provide some context 
Now to the next chapter!
I’m very excited and humbled to announce I’ll soon be the Chief Data Officer in the Data and Economic Analysis Centre (DEAC) at the Department of Home Affairs. From all I can see, DEAC is one of the top data capabilities in the APS, and the portfolio does challenging and important work so I hope to bring my passions for great CCX service delivery (Client and Citizen/resident/refugee/migrant Experience), for humane and trustworthy end-to-end policy design and delivery, and of course, for data and evidence-driven decision making and continuous improvement, to the table. Perhaps we could also be a global exemplar for policy infrastructure  I am delighted to be reporting to Deputy Secretary Sophie Sharpe, and to be in a position to contribute to the APS Reform in a department that is extremely committed to the agenda. I also look forward to rejoining the APS, especially with the benefits, lessons and experience from my time in the New Zealand, NSW and Canadian Governments.
I am delighted to be reporting to Deputy Secretary Sophie Sharpe, and to be in a position to contribute to the APS Reform in a department that is extremely committed to the agenda. I also look forward to rejoining the APS, especially with the benefits, lessons and experience from my time in the New Zealand, NSW and Canadian Governments.
Coming back to the APS feels like I’m coming home. It is all the more exciting for the once-in-a-generation changes happening at all levels to become a better public sector for everyone, and I intend to do my part to help.
This post was written to follow The case for adaptive and end-to-end policy management, which explored the challenges and opportunities for reforming how we design, delivery, manage and continuously improve policies. This article explores the idea of “policy infrastructure” and why a rethink is needed to enable end-to-end policy management with impact monitoring and policy intent optimisation  I want to quickly acknowledge all the people who are contributing to this work, especially the folk involved in the Intended and Unintended Impact of Social Policy research project which is worth keeping an eye on
I want to quickly acknowledge all the people who are contributing to this work, especially the folk involved in the Intended and Unintended Impact of Social Policy research project which is worth keeping an eye on 
‘Policy infrastructure’ isn’t a term that’s often used in government, and yet we use and rely upon policy infrastructure every day. Policy infrastructure includes the data, tools and platforms that help us to analyse, design, model, implement, iterate, monitor and report on policies and policy interventions, throughout the entire policy lifecycle. Policy infrastructure necessarily includes an enormous range of software, data and platforms, because any one tool that tries to do it all never works 
Policy infrastructure is used to support both the design and development of new policies, as well as the delivery, ongoing management and evaluation of policy interventions. If we are to include all types of policies (constitution, legislation, regulation, Government objectives, operational requirements, department rules, whole of government requirements, etc), then there is a large and complex canvas of goals, success metrics, rules, requirements, eligibility criteria, formulae and requirements that need to be reflected in the policy infrastructure, relied upon by many. In the age of digitally-enabled governments, the scope of policy infrastructure also includes digital policy delivery and policy as code.
Unfortunately, there is currently no consistent or end-to-end approach to policy infrastructure – policy is created, implemented, measured, and amended by different actors, often working in isolation from each other. This inconsistency means there is no visibility of the whole policy journey by anyone involved, and a significant air gap between how policy is represented in modeling tools, and how policy is represented in the real world systems of service delivery government departments or regulated entities. This also creates a significant gap between the predicted impact policies are expected to have, and the broader impacts they have in reality. No modeling is perfect, and unexpected conflicts or variables will emerge as policy is implemented in the real world, in real time. For instance, social security and taxation legislation is extensively modeled in some policy agencies for the purpose of reform and budget analysis, but the same legislation is implemented separately (and sometimes differently) in delivery departments, where new variables exist such as system constraints, integration with other policy domains, operational rules and, of course, the intersection of cross-jurisdictional policies. Without access to the insights of the people tasked to deliver policy, policy makers and legislative/regulatory drafters may be unaware of the risks or conflicts, and unable to build in mitigations. In any case, when unintended conflicts or impacts inevitably emerge, there are limited ways to influence or iterate policy design.
Policy impact and outcomes are often not consistently measured or monitored across interventions. For instance, policy or evaluation teams might use administrative data to analyse policy impacts at a point in time, but delivery teams tend to monitor for system performance and customer experience. Imagine if all our services also enabled real time measurement of policy outcomes and broader quality of life or environmental impacts? It is possible to have a policy intervention like a public service or grant program might be considered successful in delivery (efficient, good user feedback, etc) that is simultaneously having an inverse policy impact, or creating unintended harms. So measuring and monitoring for both policy and human impact is a critical next step to build into policy infrastructure.
There is also no easy or accessible way to test your implementation against the authoritative policy or policies. No reference implementation of policy. No test suite (for example, a person/family with these characteristics should get these services, or a business with those characteristics has those obligations, etc).
The final challenge in this space is the lack of shared or common policy infrastructure, because it exacerbates interpretation confusion and mutual incomprehension between policy design and policy delivery. The diagram below presents a high level view of the current state challenge of fragmented policy infrastructure, and contrasts it with the idea of shared policy infrastructure.
CC-BY: Pia Andrews, 2023
All actors involved in a given policy domain (including all relevant policy interventions) would ideally have access to the same shared policy infrastructure, the same digital representation of policy (“policy twins�), the same modeling and monitoring tools, feedback loops and perhaps even a shared “policy backlog�. Perhaps policy infrastructure could be shared across policy domains, or even open to the public, to facilitate transparency, alternative modeling, and testing policy options or proposed reforms in a wide variety of contexts to help identify potential or unintended consequences, and to maximise intended policy outcomes.
Although not all policies are legislation or regulation, almost all government services and programs draw upon some legislation/regulation combined with myriad operational policies. The many and varied interpretations of these building blocks of public administration can make it hard to understand which rules are authoritative and which are operational. If we had reference implementations of policy as code (imagine we had api.legislation.gov.au), then we could remove the interpretation gap and have a better chance at identifying and remediating unintended policy issues as they arise.
A Policy Twin is simply the policy equivalent of a “Digital Twin�. Digital Twins provide a digital representation of spatial information like buildings, roads, water and gas pipes, which is used to model town planning, environmental impacts or other spatially driven analyses. A Policy Twin could be as simple as a digital representation of a policy, but could include legislation as code, relevant data (admin data, policy measures, lead and tail indicators, etc), modeling tools, impact monitoring and more. All the things you have seen emerge in the “Digital Twin� space, are possible with Policy Twins, and in fact some Digital Twins have already started including policy as code, such as the inclusion of resource management regulations in the Wellington City Council digital twin to model and display the impacts of changes to the building code. Here is a great article about how to turn building regulations into a Policy Twin. Inspiring stuff!
The “Rules as Code� movement to has been growing over the past decade, including the use of policy as code to enable test-driven legislative and regulatory reform. Please see more on “Rules as Code� and the “Better Rules� approach to drafting in this explainer deck.
Recently in Australia there was a VERY exciting announcement from GovCMS where they are now offering a “Rules as Code” enterprise capability to all GovCMS customers, providing greater ease of creating policy twins 
Many communities run their own data, analysis and modeling infrastructure. Whether a not for profit NGO, an Indigenous/First Nations community or a town, the insights and intelligence that could help shape and inform policy options and change are worth understanding and building into a policy infrastructure model that is capable of respectfully interacting with such systems. This makes it necessary to consider federated architectural design, and ways of sharing insights and patterns across systems without sharing raw data. The progress made in verifiable claims/credentials, as well as in confidentialised computing provide some excellent opportunities for communities and governments to co-create meaningful and empowering policy twins. It also makes sense for government policy infrastructure to be available to communities for them to model, explore and test policy reform options.
Proposals for reforming how policy is done are often, understandably, met with concerns at whether change would “slow things down�, but if we had a more end to end approach with policies designed for easy implementation, then the total time to realise policy intent could be dramatically shorter, even if it means a little more time up front. So a useful tactic might be to consider the whole “policy journey map�, like we do with user journey mapping.
What if we were to design a better, faster and end to end “policy journey map� to identify the necessary ingredients for modern, shared policy infrastructure? Below is an attempt intended to stimulate discussion and collaboration, as this is an emerging area that needs collective exploration with cross-disciplinary participation.
Imagine for instance, being able to rapidly develop new legislation/regulation with reference implementations circulated for consultation and testing prior to being enacted by parliament (with the usual democratic rigour) and then available as code that same moment for rapid & consistent implementation by all the relevant policy consumers. It is possible, but only through transforming the policy/service continuum. When we make the rules of government authoritatively consumable by software, we dramatically improve the speed & consistency of delivery, with better policy outcomes and compliance.
Below is a high level “policy user journey� contrasting the current state approach to a more streamlined, test-driven and multi-disciplinary approach, which would dramatically reduce the time to impact.
CC-BY: Pia Andrews, 2023
With the high level journey map above, we can then explore and propose the shared and common policy infrastructure we need to support the journey end to end, as per below.
CC-BY: Pia Andrews, 2023
The very early-thinking, draft model above includes the following elements, aligned to the broad temporal phases of policy delivery:
To support test-driven policy ideation (pink):
To support test-driven policy options design, development & drafting (purple):
To support the Parliamentary processes, publishing and visibility (aqua):
To support policy intervention design & implementation (delivery) (green):
To support policy compliance, iteration & improvement over time (yellow):
It’s clear when you start trying to imagine a more collaborative, adaptive, humane, iterative and test driven approach to policy management, that a lot of the techniques and methods from product management, CI/CD (Continuous Integration / Continuous Development) pipelines, service design and agile become useful. So why not reuse some of the infrastructure, tools, methods and platforms that we have adopted in service reforms over the last decade to help modernise policy delivery?
We could have CI/CD policy pipelines, policy feedback loops, product management for policy, policy monitoring and measurement tools, policy escalation frameworks, policy test suites, policy twins, and public policy engagement/codesign platforms. Perhaps each policy would have a policy manager who owns the end to end outcome realisation (rather than the current baton passing from design to delivery teams), and perhaps each policy intervention could have its own “policy product owner� who owns the delivery of that intervention, but works in concert with other interventions to the policy manager to make sure interventions are effective, complementary and continuously adapting to change and impact? We don’t need to start from scratch here, but we do need to design a good policy journey, so that we can meaningfully leverage what is available, but also identify where there are gaps to fill.
What do you see as the opportunities and challenges for policy infrastructure? What would your ideal policy journey map look like? Which portfolios would have the right mandate and systemic motivations to run which parts of the concept model above (note, not which department is best functionally/capabilities placed, but which department is best aligned/motivated  )? What other tools, data and platforms would you include? Do you have any examples to share?
)? What other tools, data and platforms would you include? Do you have any examples to share?
Please share your thoughts and any examples and let’s all take a strategic and proactive approach to modernising our policy infrastructure, so we can be more adaptive and effective in delivering policy and public outcomes.
TL;DR: Better policy design and evaluation won’t save us 
The APS Reform agenda provides a rare window of opportunity to address structural and systemic issues in the APS, so why not explore how might we transform the way policy is designed, delivered and managed end to end?
Why should we reform how we do policy? Simple. Because the gap between policy design and delivery has become the biggest barrier to delivering good public services and policy outcomes, and is a challenge most public servants experience daily, directly or indirectly. This gap wasn’t always the case, with policy design and delivery separated as part of the New Public Management reforms in the 90s. When you also consider the accelerating rate of change, increasing cadence of emergencies, and the massive speed and scale of new technologies, you could argue that end-to-end policy reform is our most urgent problem to solve.
Policy teams globally have been exploring new design methods like human-centred design, test-driven iteration (agile), and multi-disciplinary teams that get policy end users in the room (eg, NSW Policy Lab). There has also been an increased focus on improving policy evaluation across the world (eg, the Australian Centre for Evaluation). In both cases, I’m delighted to see innovative approaches being normalised across the policy profession, but it has become obvious that improving design and/or evaluation is still far from sufficient to drive better (or more humane) policy outcomes in an ever changing world. It is not only the current systemic inability to detect and respond to unintended consequences that emerge, but the lack of policy agility that perpetuates issues even long after they might be identified.
Below I outline four current challenges for policy management and a couple of potential solutions, as something of a discussion starter 
The lack of multi-disciplinary policy design, combined with a set-and-forget approach to policy, combined with delivery teams being left to interpret policy instructions without support, combined with a gap and interpretation inconsistency between policy modeling systems and policy delivery systems, all combined with a lack of feedback loops into improving policy over time, has led to a series of black holes throughout the process. Tweaking the process as it currently stands will not fix the black holes. We need a more holistic model for policy design, delivery and management.
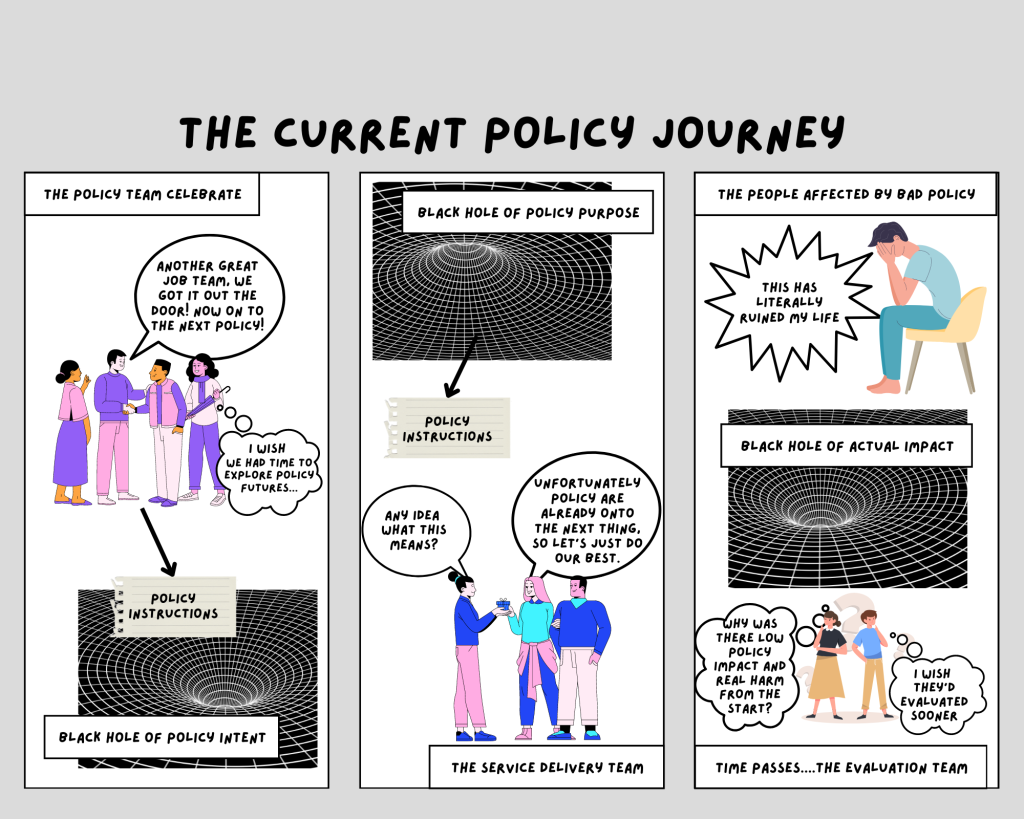
CC-BY: Pia Andrews, 2023
There is also a significant gap with the public. From the start, there is usually a lack of diversity in expertise and experience in shaping a policy, and once an intervention is decided and rolled out, the people affected by policies have limited means to give feedback. Engaging the public early and often, and then providing clear feedback loops would help policies be better designed and improved over time.
The laudable efforts to improve policy evaluation are great, but formal evaluations usually have two limitations that could be better addressed with other mechanisms. Firstly, formal evaluations often tend to be positivist, in that they look for “has this initiative delivered what it said it would�, and aren’t often driven or set up to explore and understand unintended impacts, such as human or environmental patterns that emerged as a result of a new policy interacting in a complex domain.
Secondly, formal evaluations are usually a point in time assessment, rather than real time monitoring of policy impacts. Evaluation teams are not connected to the day to day delivery of policy interventions, creating a timeliness challenge in mitigating issues that are identified. Evolving and improving policy evaluation methods will create greater understanding, but perhaps too little, too late for those affected in between. Real time monitoring of intended and unintended impacts would nicely complement formal evaluation methods, while also providing a timely trigger if anything trended in the wrong direction.
Policies are often designed by a policy team, and then handed over to implementation, so that policy team can move on to the next policy priority, creating a systemic inability to iterate policies as the real impacts are felt in delivery. It doesn’t matter how collaborative or inclusive you are in designing a policy, there will always be perpetual change in the environment, and unintended impacts to mitigate. We need to take the lessons from the creation of “Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery� (CI/CD) pipelines in service delivery, to create a “CI/CD Policy� approach which would manage policy design and delivery as part of the one continuum, drawing upon continuous feedback loops, monitoring and measurement of policy and human impacts to inform and iterate policies and the respective interventions. This would not only help policies to maximise the realisation of policy intent in a rapidly changing world, but would also provide the means to proactively identify and manage policy impacts (positive and negative) as they emerge.
Last, but not least, is the inconsistent definition, context and practice of “policy� across the sector, creating confusion and real issues of authority, decision making and accountability. Unfortunately today, many of the “policy guides� currently available limit themselves to Government Policy development, which has led to the common but dangerous assumption that Government Policies are the highest authority, and that the peak of good public service is to simply advise the Government.
To my mind, there are three highest level and fundamental categories of “policy�:
The diagram below provides a useful reference on the hierarchy of authority of different policy types, as well as a guide to decision making involved in each. This should help public servants realise that different actors are needed for change to different policy types, and that even Ministerial directions are constrained by the Foundational Policies above. It also should provide public servants more understanding as to what decision making is actually within their delegated authority, such as operational policies.
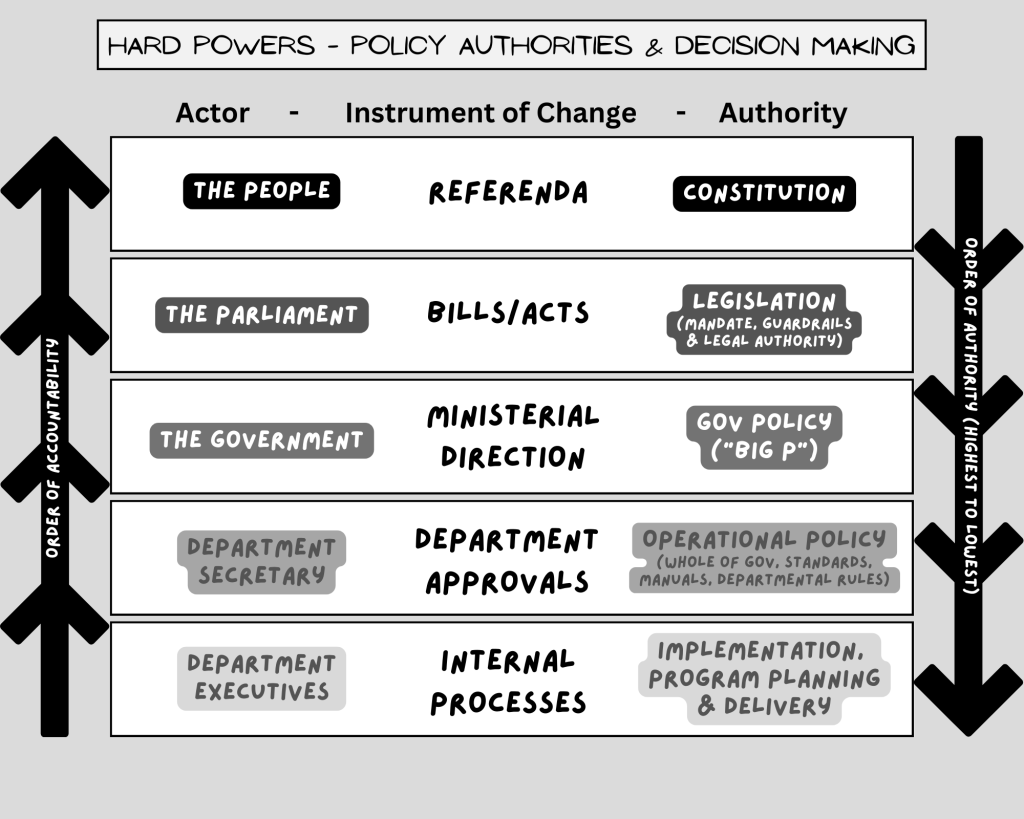
CC-BY: Pia Andrews, 2023
So what might adaptive policy management look like? Well, let’s start with what the characteristics for delivering great policy and human outcomes might look like, and then we can reverse engineer an ideal policy operating model we could work towards.
| From | To |
| Narrowly informed, largely driven by generalist policy professionals, with occasional expertise or end user input. | Multidisciplinary and diverse expertise and experience informing the whole process, including early testing of several interventions with representatives of those affected. |
| Static policies are defined, the policy team moves on, policy change is slow and difficult, often principles-based and subject to varied interpretation in delivery. | Dynamic policies, with policy expertise present in policy interventions end to end (leg, services, reg, programs, grants, etc) with continuous, evidence-based policy iteration. |
| Reactive to issues, as they are identified. Constantly looking backwards, mitigating symptoms, without time to look forwards or address causes. | Responsive to change as it happens, monitoring for impact (intended and unintended) and constantly adaptive to change in a forward looking way. |
| Assumptions driven, policy interventions are based on past or current assumptions, without testing, exploring or co-designing a range of approaches. | Test driven, a diverse range of potential policy interventions are explored, with a range of stakeholders, with feasible options tested prior to finalising policy options or ratifications. |
| Culturally exclusive, policies are developed without culturally diverse experience or expertise. | Culturally inclusive, policies are developed in a culturally inclusive way, embracing diverse knowledge systems and methods. |
| Split policy infrastructure, where policy design and modeling happen in one place, but policy delivery happens in a different place, leading to inconsistencies in implementation assumptions, and the inability for policy owners to monitor the reality of policy implementation. Modeling is often limited in scope and domain, so policy conflicts are only identified in delivery, too late to inform design. | Shared policy infrastructure, common and shared digital policy models are used for both modeling/design and delivery, such that there is no gap between the two. Policy owners can have higher confidence in the likely impacts of change, whilst also keeping a finger on the pulse of actual policy impacts. Policy intent and impact are monitored alongside performance and CX measures, and feedback loops loop back to policy. |
| Policy realisation is slow, as the whole lifecycle requires policy options, legislation/regulation, operational policy development, with several opportunities for misinterpretation. Policy intent can take years to even start to be realised. | Policy realisation is fast, policies are developed in a faster way with reference implementations resulting from rapid and test driven drafting of human and machine readable policy. This results in better rules & dramatically speeds up implementation. |
| Community engagement, engaging the public in research or testing ideas is currently ad hoc and inconsistent. | Community empowerment, could refer to both the ability for communities to generate new policy ideas with government, but also that public sectors attempt to devolve more decision making on policy or investment to communities. |
Perhaps policy making could be more of a team sport:
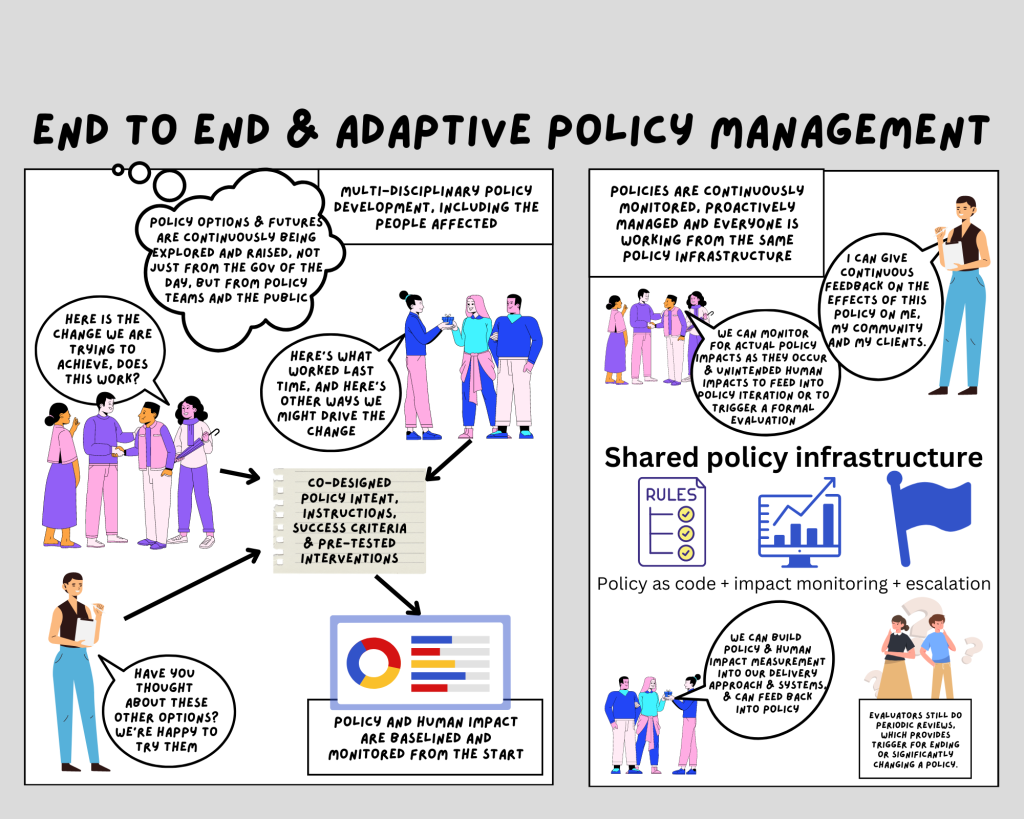
CC-BY: Pia Andrews, 2023
Below is a high level potential approach to the policy lifecycle, where policies are designed and delivered collaboratively, with shared policy infrastructure, and real impacts monitored, escalated and fed into policy improvements over time, with formal evaluations able to be triggered when things go terribly wrong, not years later. Policy makers could, for instance, establish a theory of change between the vision / outcomes and the actions being taken, to ensure the indicators and measures are connected to and represented in delivery from the start. If all policies required a purpose statement, it would help implementers to ensure the delivery was aligned to the purpose and intent of the policies.
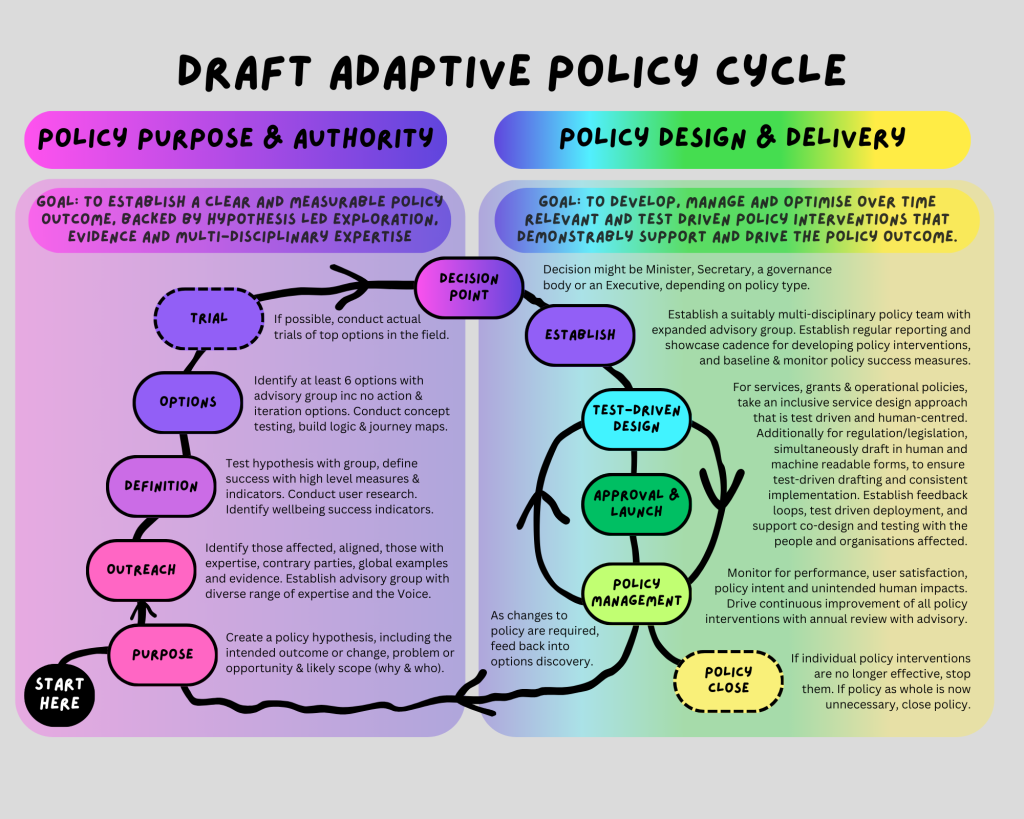
CC-BY: Pia Andrews, 2023
In this model, there is only two phases in the policy lifecycle:
Any form of policy could follow this model. Whether Constitutional reform, legislation/regulation reform, advice/options to Government, whole of government policies or operational policies, the intended outcome can be better realised through being a little more test-driven, participatory, multidisciplinary, iterative and through managing the whole policy lifecycle as an end to end approach with real time and continuous improvements to interventions (like services, regulations, etc), while also continuously monitoring for policy impact that can feed into policy improvements.
Proposals for reforming how policy is done are often – understandably – met with concerns at “slowing things down�. But if you look at the full journey of policy today, policy intent realisation is already quite slow. If we had a more end to end and test driven approach, we’d get better policies designed that are easier and faster to implement, which would dramatically shorten the time to realise policy intent, even if it means a little more time up front.
We need to not only teach what all types of “good� public policy looks like, but create a culture of continuous learning and improvement for policy professionals. Perhaps we could start by complementing the excellent digital, data, HR and strategy professions coordinated by the APSC, with a “Policy Profession�? 
But we also need to teach public service craft to all public servants, including what a healthy, politically neutral and evidence-based approach to public administration looks like, and why we aren’t achieving it as a norm across the sector. For instance, we need to have clear and consistent guidance on how to engage with Ministerial offices appropriately, so that everyone can maintain the integrity, dignity and trustworthiness expected of our public institutions. We also need clear guidance on how to promote an open APS that engages appropriately and regularly with the community, something which will hopefully be addressed in the APS Reform Agenda proposed Charter of Partnerships and Engagement.
All public servants should be confident to maintain real and long term stewardship of public good, above and beyond day to day pressures or policy objectives, and also be knowledgeable of their foundational policy accountabilities, which are found in the constitution and relevant legislation and regulations. For instance, I have been surprised and somewhat horrified to hear people talk about how AI is a problem in government because it isn’t regulated, seemingly unaware that all government systems, regardless of the technology, are subject to Administrative Law, the Privacy Act, PGPA and many other foundational policies (leg/reg). We have many checks and balances we can use to ensure good governance, we just need to be aware of and apply them more consistently across the whole sector. For example, here is a paper where I documented the “special context of government� and then applied that special context to the use of AI in government. It resulted in a holistic approach that is complementary to the concept and practice of responsible government. When everyone has a shared and common understanding of the special context and responsibilities of the public service, we have a good chance to get shared and high integrity approaches to everything we design, deliver and administer in the public sector.
Given how long this post has become, I’ll share more on this concept in a subsequent post, but here’s a teaser  Basically, whilst difference teams have different tools, including distinct and separate interpretations of policy, then we’ll continue to see an interpretation gap, and a lack of end to end policy visibility, which impedes end to end policy management.
Basically, whilst difference teams have different tools, including distinct and separate interpretations of policy, then we’ll continue to see an interpretation gap, and a lack of end to end policy visibility, which impedes end to end policy management.
CC-BY: Pia Andrews, 2023
What are the challenges you see, and what do you think needs to be done to improve policy management end to end? How might the APS Reform agenda help drive change, and how can we all do our part to improve things? How could we better deliver policy outcomes, and better public and community outcomes? How can we close the gap between policy and delivery? Would love to hear your thoughts and examples!
I want to acknowledge all the people who are contributing to this work, especially the folk involved in the Intended and Unintended Impact of Social Policy research project which is worth keeping an eye on!
Last week, I had the delightful opportunity to host some discussion tables at the 9th Annual FSTGov Government Summit in Canberra. It was an event designed just for public servants, to explore challenges and opportunities for reform and how to better serve the public. I hosted four groups in discussions about “how to build agile and adaptive public institutions�, which included 40 public servants from around 30 departments and agencies. The challenges, insights and highlights are captured below, for broader sharing and learning 
Challenge: The groups reflected that agile and adaptive still sound a bit buzzwordy, so we explored and documented roughly what they could and should mean in the context of public institutions.
Insights: Several participants talked about the use of Agile in their orgs (usually in the IT departments) as a development methodology, which helped others to understand that context. When we discussed how to build agile and adaptive public institutions more broadly, we identified a few useful characteristics, which made it more broadly practical:

Challenge: We discussed how agile adoption in IT has helped, but not solved the big challenges facing service and policy delivery in government. When IT/dev teams adopt agile methods, they are usually still in the position of receiving “business requirements� from other parts of the department who are themselves disengaged from the process of designing or delivering the service/system. We identified the fact that many departments have maintained the issues of functionally segmentation structures, with multiple “product owners� emerging (eg, a business PO and a tech PO), which defeats the purpose and undermines the benefits of product management as a methodology. We also discussed how product management, where it has been adopted, still usually relates to managing platforms rather than services, so decision making, prioritisation and risk is analysed at a platform level, not at the service level, leading to cannablistic resourcing behaviours across “product teams� that are actually part of the same service.
Insights: Ensuring each “product� being managed is at the service level to provide a more realistic and impactful way to priotise, manage risk, maximse intended policy impact and to actively manage the end user experience. Funding a diverse product team, with the design, dev, ops, business and policy expertise all represented (even if only part time, such as 3 hours a week for a policy person) dramatically helps to ensure the benefits, cadences and agility of a proper, agile, test driven and continuously improved product management approach. Explicitly adopting an MVP deployment strategy is also necessary for product management to work, otherwise the team is still driven to build and deploy everything all at once, which never works.
Challenge: Some of the group discussions reflected on what real risk is and isn’t, and we determined that the public sector reputation of being risk averse, has created a mythology that taking no action avoids risk, when the reality is that a culture of taking no action actually creates risk in a world that is continuously and unexpectedly changing around us.
Insights: Analysis of the risk of non-action should always be included in risk assessments, as well as risk to the public and those affected by the proposal. The SES reforms underway could include KPIs for executives to ensure that personal risk is well aligned to the portfolio and policy objectives, as well as aligned to the impact on the public, so that we avoid a situation where personal risk aversion can create risk for the public institutions and/or communities we serve. Risk needs to be assessed in the context of stewardship, looking at long term and short term implications, to ensure a balanced approach, that should also then be prioritised based on measurable policy and public impact.
These are just a few of the insights and observations from our discussion, what are your thoughts? How can you contribute to creating a more agile and adaptive organisation where you work? 
It’s time for a review of the second year of operation of our Redflow ZCell battery and Victron Energy inverter/charger system. To understand what follows it will help to read the earlier posts in this series:
In case ~12,000 words of background reading seem daunting, I’ll try to summarise the most important details here:
With the background out of the way we can get on to the fun stuff, including a roof replacement, an unexpected fault after a power outage followed by some mains switchboard rewiring, a small electrolyte leak, further hackery to keep a bit of charge in the battery most of the time, and finally some numbers.
The big job we did this year was replacing our concrete tile roof with colorbond steel. When we bought the house – which is in a rural area and thus a bushfire risk – we thought: “concrete brick exterior, concrete tile roof – sweet, that’s not flammable”. Unfortunately it turns out that while a tile roof works just fine to keep water out, it won’t keep embers out. There’s a gadzillion little gaps where the tiles overlap each other, and in an ember attack, embers will get up in there and ignite the fantastic amount of dust and other stuff that’s accumulated inside the ceiling over several decades, and then your house will burn down. This could be avoided by installing roof blanket insulation under the tiles, but in order to do that you have to first remove all the tiles and put them down somewhere without breaking them, then later put them all back on again. It’s a lot of work. Alternately, you can just rip them all off and replace the whole lot with nice new steel, with roof blanket insulation underneath.

Of course, you need good weather to replace a roof, and you need to take your solar panels down while it’s happening. This meant we had twenty-two solar panels stacked on our back porch for three weeks of prime PV time from February 17 – March 9, 2023, which I suspect lost us a good 500kW of power generation. Also, the roof job meant we didn’t have the budget to get a second ZCell this year – for the cost of the roof replacement, we could have had three new ZCells installed – but as my wife rightly pointed out, all the battery storage in the world won’t do you any good if your house burns down.
We had at least five grid power outages during the year. A few were brief, the grid being down for only a couple of minutes, but there were two longer ones in September (one for 30 minutes, one for about an hour and half). We got through the long ones just fine with either the sun high in the sky, or charge in the battery, or both. One of the earlier short outages though uncovered a problem. On the morning of May 30, my wife woke up to discover there was no power, and thus no running water. Not a good thing to wake up to. This happened while I was away, because of course something like this would happen while I was away. It turns out there had been a grid outage at about 02:10, then the grid power had come back, but our system had not. The Multis ended up in some sort of fault state and were refusing to power our loads. On the console was an alarm message: “#8 – Ground relay test failed”.
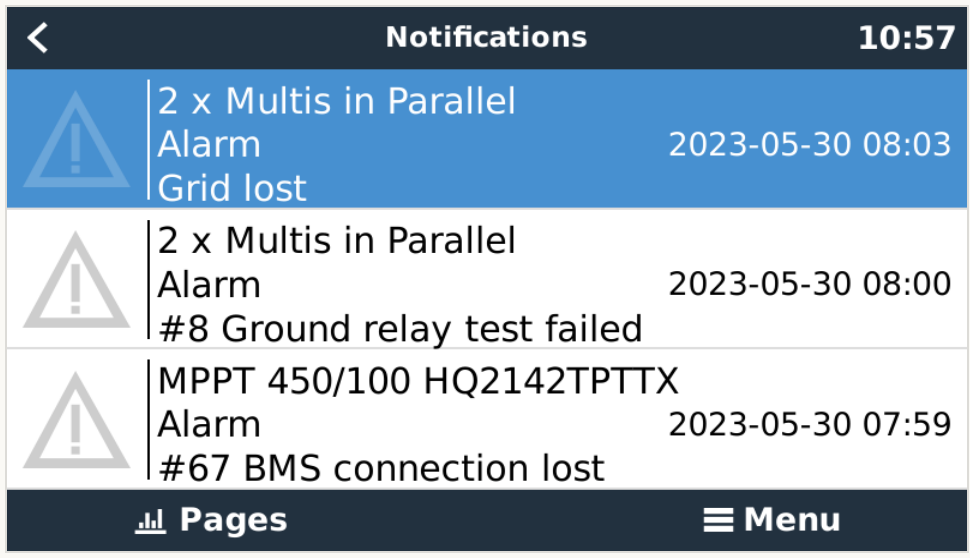
Note the times in the console messages are about 08:00. I confirmed via the logs from the VRM portal that the grid really did go out some time between 02:10 and 02:15, but after that there was nothing in the logs until 07:59, which is when my wife used the manual changeover switch to shift all our loads back to direct grid power, bypassing the Victron kit. That brought our internet connection back, along with the running water. I contacted Murray Roberts from Lifestyle Electrical and Simon Hackett for assistance, Murray logged in remotely and reset the Multis, my wife flicked the changeover switch back and everything was fine. But the question remained, what had gone wrong?
The ground relay in the Multis is there to connect neutral to ground when the grid fails. Neutral and ground are already physically connected on the grid (AC input) side of the Multis in the main switchboard, but when the grid power goes out, the Multis disconnect their inputs, which means the loads on the AC output side no longer have that fixed connection from neutral to ground. The ground relay activates in this case to provide that connection, which is necessary for correct operation of the safety switches on the power circuits in the house.
The ground relay is tested automatically by the Multis. Looking up Error 8 – Ground relay test failed on Victron’s web site indicated that either the ground relay really was faulty, or possibly there was a wiring fault or an issue with one of the loads in our house. So I did some testing. First, with the battery at 50% State of Charge (SoC), I did the following:
This demonstrated that the ground relay and the Multis in general were fine. Had there been a problem at that level we would have seen an error when I restored mains power. I then reconnected the loads and repeated steps 2-5 above. Again, there was no error which indicated the problem wasn’t due to a wiring defect or short in any of the power or lighting circuits. I also re-tested with the heater on and the water pump running just in case there may have been an issue specifically with either of those devices. Again, there was no error.
The only difference between my test above and the power outage in the middle of the night was that in the middle of the night there was no charge in the battery (it was right after a maintenance cycle) and no power from the sun. So in the evening I turned off the DC isolators for the PV and deactivated my overnight scheduled grid charge so there’d be no backup power of any form in the morning. Then I repeated the test:
The underlying detailed error message was “PE2 Closed”, which meant that it was seeing the relay as closed when it’s meant to be open. Our best guess is that we’d somehow hit an edge case in the Multi’s ground relay test, where they maybe tried to switch to inverting mode and activated the ground relay, then just died in that state because there was no backup power, and got confused when mains power returned. I got things running again by simply power cycling the Multis.
So it kinda wasn’t a big deal, except that if the grid went out briefly with no backup power, our loads would remain without power until one of us manually reset the system. This was arguably worse than not having the system at all, especially if it happened in the middle of the night, or when we were away from home. The fact that we didn’t hit this problem in the first year of operation is a testament to how unlikely this event is, but the fact that it could happen at all remained a problem.
One fix would have been to get a second battery, because then we’d be able to keep at least a tiny bit of backup power at all times regardless of maintenance cycles, but we’re not there yet. Happily, Simon found another fix, which was to physically connect the neutral together between the AC input and AC output sides of the Multis, then reconfigure them to use the grid code “AS4777.2:2015 AC Neutral Path externally joined”. That physical link means the load (output) side picks up the ground connection from the grid (input) side in the swichboard, and changing the grid code setting in the Multis disables the ground relay and thus the test which isn’t necessary anymore.
Murray needed to come out anyway to replace the carbon sock in the ZCell (a small item of annual maintenance) and was able to do that little bit of rewriting and configuration at the same time. I repeated my tests both with and without backup power and everything worked perfectly, i.e. the system came back immediately by itself after a grid outage with no backup power, and of course switched over to inverting just fine when there was backup power available.
This leads to the next little bit of fun. The carbon sock is a thing that sits inside the zinc electrolyte tank and helps to keep the electrolyte pH in the correct operating range. Unfortunately I didn’t manage to get a photo of one, but they look a bit like door snakes. Replacing the carbon sock means opening the case, popping one side of the Gas Handling Unit (GHU) off the tank, pulling out the old sock and putting in a new one. Here’s a picture of the ZCell with the back of the case off, indicating where the carbon sock goes:
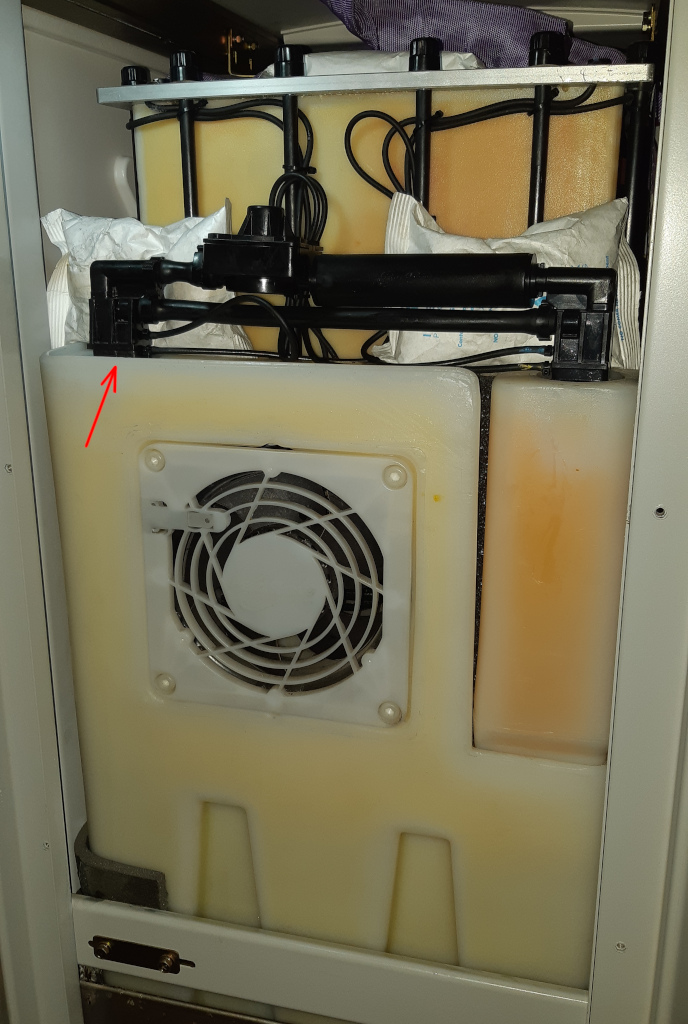

When Murray popped the GHU off, he noticed that one of the larger pipes on one side had perished slightly. Thankfully he happened to have a spare GHU with him so was able to replace the assembly immediately. All was well until later that afternoon, when the battery indicated hardware failure due to “Leak 1 Trip” and shut itself down out of an abundance of caution. Upon further investigation the next day, Murry and I discovered there was a tiny split in one of the little hoses going into the GHU which was letting the electrolyte drip out.
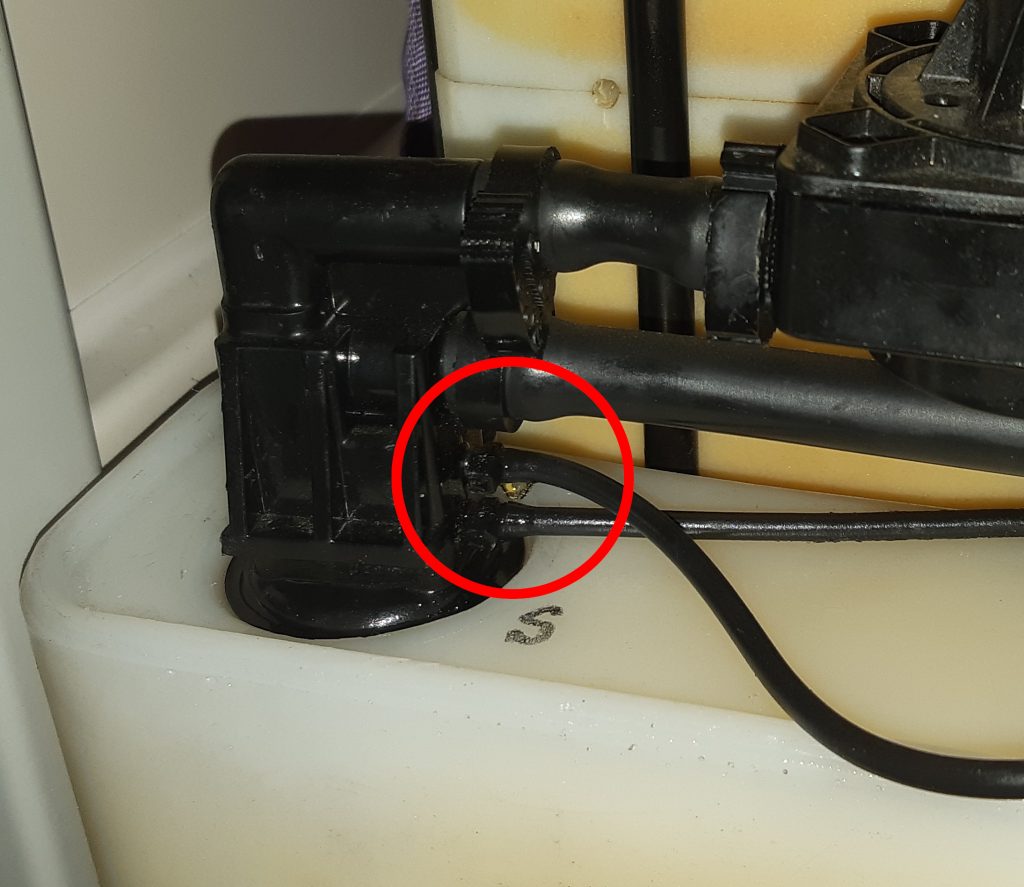

This small electrolyte leak was caught lower down in the battery, where the leak sensor is. Murray sucked the leaked electrolyte out of there, re-terminated that little hose and we were back in business. I was happy to learn that Redflow had obviously thought about the possibility of this type of failure and handled it. As I said to Murray at the time, we’d rather have a battery that leaks then turns itself off than a battery that catches fire!
Aside from those two interesting events, the rest of the year of operation was largely quite boring, which is exactly what one wants from a power system. As before I kept a small overnight scheduled charge and a larger late afternoon scheduled charge active on weekdays to ensure there was some power in the battery to use at peak (i.e. expensive) grid times. In spring and summer the afternoon charge is largely superfluous because the battery has usually been well filled up from the solar by then anyway, but there’s no harm in leaving it turned on. The one hack I did do during the year was to figure out a way to keep a small (I went with 15%) MinSoC in the battery at all times except for maintenance cycle evenings, and the morning after. This is more than enough to smooth out minor grid outages of a few minutes, and given our general load levels should be enough to run the house for more than an hour overnight if necessary, provided the hot water system and heating don’t decide to come on at the same time.
My earlier experiment along these lines involved a script that ran on the Cerbo twice a day to adjust scheduled charge settings in order to keep the battery at 100% SoC at all times except for peak electricity hours and maintenance cycle evenings. As mentioned in TANSTAAFL I ran that for all of July, August and most of September 2022. It worked fine, but ultimately I decided it was largely a waste of energy and money, especially when run during the winter months when there’s not much sun and you end up doing a lot of grid charging. This is a horribly inefficient way of getting power into the battery (AC to DC) versus charging the battery direct from solar PV. We did still use those scripts in the second year, but rather more judiciously, i.e. we kept an eye on the BOM forecasts as we always do, then occasionally activated the 100% charge when we knew severe weather and/or thunderstorms were on the way, those being the things most likely to cause extended grid outages. I also manually triggered maintenance on the battery earlier than strictly necessary several times when we expected severe weather in the coming days, to avoid having a maintenance cycle (and thus empty battery) coincide with potential outages. On most of those occasions this effort proved to be unnecessary. Bearing all that in mind, my general advice to anyone else with a single ZCell system (aside from maybe adding scheduled charges to time-shift expensive peak electricity) is to just leave it alone and let it do its thing. You’ll use most of your locally generated electricity onsite, you’ll save some money on your power bills, and you’ll avoid some, but not all, grid outages. This is a pretty good position to be in.
That said, I couldn’t resist messing around some more, hence my MinSoC experiment. Simon’s installation guide points out that “for correct system operation, the Settings->ESS menu ‘Min SoC’ value must be set to 0% in single-ZCell systems”. The issue here is that if MinSoC is greater than 0%, the Victron gear will try to charge the battery while the battery is simultaneously trying to empty itself during maintenance, which of course just isn’t going to work. My solution to this is the following script, which I run from a cron job on the Cerbo twice a day, once at midnight UTC and again at 06:00 UTC with the --check-maintenance flag set:
Midnight UTC corresponds to the end of our morning peak electricity time, and 06:00 UTC corresponds to the start of our afternoon peak. What this means is that after the morning peak finishes, the MinSoC setting will cause the system to automatically charge the battery to the value specified if it’s not up there already. Given it’s after the morning peak (10:00 AEST / 11:00 AEDT) this charge will likely come from solar PV, not the grid. When the script runs again just before the afternoon peak (16:00 AEST / 17:00 AEDT), MinSoC is set to either the value specified (effectively a no-op), or zero if it’s a maintenance day. This allows the battery to be discharged correctly in the evening on maintenance days, while keeping some charge every other day in case of emergencies. Unlike the script that tries for 100% SoC, this arrangement results in far less grid charging, while still giving protection from minor outages most of the time.
In case Simon is reading this now and is thinking “FFS, I wrote ‘MinSoC must be set to 0% in single-ZCell systems’ for a reason!” I should also add a note of caution. The script above detects ZCell maintenance cycles based solely on the configured maintenance time limit and the duration since last maintenance. It does not – and cannot – take into account occasions when the user manually forces maintenance, or situations in which a ZCell for whatever reason hypothetically decides to go into maintenance of its own accord. The latter shouldn’t generally happen, but it can. The point is, if you’re running this MinSoC script from a cron job, you really do still want to keep an eye on what the battery is doing each day, in case you need to turn that setting off and disable the cron job. If you’re not up for that I will reiterate my general advice from earlier: just leave the system alone – let it do its thing and you’ll (almost always) be perfectly fine. Or, get a second ZCell and you can ignore the last several paragraphs entirely.
Now, finally, let’s look at some numbers. The year periods here are a little sloppy for irritating historical reasons. 2018-2019, 2019-2020 and 2020-2021 are all August-based due to Aurora Energy’s previous quarterly billing cycle. The 2021-2022 year starts in late September partly because I had to wait until our new electricity meter was installed in September 2021, and partly because it let me include some nice screenshots when I started writing TANSTAAFL on September 25, 2022. I’ve chosen to make this year (2022-2023) mostly sane, in that it runs from October 1, 2022 through September 30, 2023 inclusive. This is only six days offset from the previous year, but notably makes it much easier to accurately correlate data from the VRM portal with our bills from Aurora. Overall we have five consecutive non-overlapping 12 month periods that are pretty close together. It’s not perfect, but I think it’s good enough to work with for our purposes here.
| YeaR | Grid In | Solar In | Total In | Loads | Export |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018-2019 | 9,031 | 6,682 | 15,713 | 11,827 | 3,886 |
| 2019-2020 | 9,324 | 6,468 | 15,792 | 12,255 | 3,537 |
| 2020-2021 | 7,582 | 6,347 | 13,929 | 10,358 | 3,571 |
| 2021-2022 | 8,531 | 5,640 | 14,171 | 10,849 | 754 |
| 2022-2023 | 8,936 | 5,744 | 14,680 | 11,534 | 799 |
Overall, 2022-2023 had a similar shape to 2021-2022, including the fact that in both these years we missed three weeks of solar generation in late summer. In 2022 this was due to replacing the MPPT, and in 2023 it was because we replaced the roof. In both cases our PV generation was lower than it should have been by an estimated 500-600kW. Hopefully nothing like this happens again in future years.
All of our numbers in 2022-2023 were a bit higher than in 2021-2022. We pulled 4.75% more power from the grid, generated 1.84% more solar, the total power going into the system (grid + solar) was 3.59% higher, our loads used 6.31% more power, and we exported 5.97% more power than the previous year.
I honestly don’t know why our loads used more power this year. Here’s a table showing our consumption for both years, and the differences each month (note that September 2022 is only approximate because of how the years don’t quite line up):
| Month | 2022 | 2023 | Diff |
|---|---|---|---|
| October | 988 | 873 | -115 |
| November | 866 | 805 | -61 |
| December | 767 | 965 | 198 |
| January | 822 | 775 | -47 |
| February | 638 | 721 | 83 |
| March | 813 | 911 | 98 |
| April | 775 | 1,115 | 340 |
| May | 953 | 1,098 | 145 |
| June | 1,073 | 1,149 | 76 |
| July | 1,118 | 1,103 | -15 |
| August | 966 | 1,065 | 99 |
| September | 1,070 | 964 | -116 |
Here’s a graph:
Did we use more cooling this December? Did we use more heating this April and May? I dug the nearest weather station’s monthly mean minimum and maximum temperatures out of the BOM Climate Data Online tool and found that there’s maybe a degree or so variance one way or the other each month year to year, so I don’t know what I can infer from that. All I can say is that something happened in December and April, but I don’t know what.
Another interesting thing is that what I referred to as “the energy cost of the system” in TANSTAAFL has gone down. That’s the kW figure below in the “what?” column, which is the difference between grid in + solar in – loads – export, i.e. the power consumed by the system itself. In 2021-2022, that was 2,568 kW, or about 18% of the total power that went into the system. In 2022-2023 it was down to 2,347kWh, or just under 16%:
| Year | Grid In | Solar In | Total In | Loads | Export | Total Out | what? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021-2022 | 8,531 | 5,640 | 14,171 | 10,849 | 754 | 11,603 | 2,568 |
| 2022-2023 | 8,936 | 5,744 | 14,680 | 11,534 | 799 | 12,333 | 2,347 |
I suspect the cause of this reduction is that we didn’t spend two and a half months doing lots of grid charging of the battery in 2022-2023. If that’s the case, this again points to the advisability of just letting the system do its thing and not messing with it too much unless you really know you need to.
The last set of numbers I have involve actual money. Here’s what our electricity bills looked like over the past five years:
| Year | From Grid | Total Bill | Cost/kWh |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018-2019 | 9,031 | $2,278.33 | $0.25 |
| 2019-2020 | 9,324 | $2,384.79 | $0.26 |
| 2020-2021 | 7,582 | $1,921.77 | $0.25 |
| 2021-2022 | 8,531 | $1,731.40 | $0.20 |
| 2022-2023 | 8,936 | $1,989.12 | $0.22 |
Note that cost/kWh as I have it here is simply the total dollar amount of our bills divided by the total power drawn from the grid (I’m deliberately ignoring the additional power we use that comes from the sun in this calculation). The bills themselves say “peak power costs $X, off-peak costs $Y, you get $Z back for power exported and there’s a daily supply charge of $SUCKS_TO_BE_YOU”, but that’s all noise. What ultimately matters in my opinion is what I call the effective cost per kilowatt hour, which is why those things are all smooshed together here. The important point is that with our existing solar array we were previously effectively paying about $0.25 per kWh for grid power. After getting the battery and switching to Peak & Off-Peak billing, that went down to $0.20/kWh – a reduction of 20%. Now we’ve inched back up to $0.22/kWh, but it turns out that’s just because power prices have increased. As far as I can tell Aurora Energy don’t publish historical pricing data, so as a public service, I’ll include what I’ve been able to glean from our prior bills here:
It’s nice that the feed-in tariff (i.e. what you get credited when you export power) has gone up quite a bit, but unless you’re somehow able to export 2-3x more power than you import, you’ll never get ahead of the ~20% increase in power prices over the last two years.
Having calculated the effective cost/kWh for grid power, I’m now going to do one more thing which I didn’t think to do during last year’s analysis, and that’s calculate the effective cost/kWh of running our loads, bearing in mind that they’re partially powered from the grid, and partially from the sun. I’ve managed to dig up some old Aurora bills from 2016-2017, back before we put the solar panels on. This should make for an interesting comparison.
| Year | From Grid | Total Bill | Grid $/kWh | Loads | Loads $/kWh |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016-2017 | 17,026 | $4,485.45 | $0.26 | 17,026 | $0.26 |
| 2018-2019 | 9,031 | $2,278.33 | $0.25 | 11,827 | $0.19 |
| 2019-2020 | 9,324 | $2,384.79 | $0.26 | 12,255 | $0.19 |
| 2020-2021 | 7,582 | $1,921.77 | $0.25 | 10,358 | $0.19 |
| 2021-2022 | 8,531 | $1,731.40 | $0.20 | 10,849 | $0.16 |
| 2022-2023 | 8,936 | $1,989.12 | $0.22 | 11,534 | $0.17 |
The first thing to note is the horrifying 17 megawatts we pulled in 2016-2017. Given the hot water and lounge room heat pump were on a separate tariff, I was able to determine that four of those megawatts (i.e. about 24% of our power usage) went on heating that year. Replacing the crusty old conventional electric hot water system with a Sanden heat pump hot water service cut that in half – subsequent years showed the heating/hot water tariff using about 2MW/year. We obviously also somehow reduced our loads by another ~3MW/year on top of that, but I can’t find the Aurora bills for 2017-2018 so I’m not sure exactly when that drop happened. My best guess is that I probably got rid of some old, always-on computer equipment.
The second thing to note is how the cost of running the loads drops. In 2016-2017 the grid cost/kWh is the same as the loads cost/kWh, because grid power is all we had. From 2018-2021 though, the load cost/kWh drops to $0.19, a saving of about 26%. It remains there until 2021-2022 when we got the battery and it dropped again to $0.16 (another 15% or so). So the big win was certainly putting the solar panels on and swapping the hot water system, with the battery being a decent improvement on top of that.
Further wins are going to come from decreasing our power consumption. In previous posts I had mentioned the need to replace panel heaters with heat pumps, and also that some of our aging computer equipment needed upgrading. We did finally get a heat pump installed in the master bedroom this year, and we replaced the old undersized lounge room heat pump with a new correctly sized unit. This happened on June 30 though, so will have had minimal impact on this years’ figures. Likewise an always-on computer that previously pulled ~100W is now better, stronger and faster in all respects, while only pulling ~50W. That will save us ~438kW of power per year, but given the upgrade happened in mid August, again we won’t see the full effects until later.
I’m looking forward to doing another one of these posts in a year’s time. Hopefully I will have nothing at all interesting to report.
I (relatively) recently went down the rabbit hole of trying out personal finance apps to help get a better grip on, well, the things you’d expect (personal finances and planning around them).
In the past, I’ve had an off-again-on-again relationship with GNUCash. I did give it a solid go for a few months in 2004/2005 it seems (I found my old files) and I even had the OFX exports of transactions for a limited amount of time for a limited number of bank accounts! Amazingly, there’s a GNUCash port to macOS, and it’ll happily open up this file from what is alarmingly close to 20 years ago.
Back in those times, running Linux on the desktop was even more of an adventure than it has been since then, and I always found GNUCash to be strange (possibly a theme with me and personal finance software), but generally fine. It doesn’t seem to have changed a great deal in the years since. You still have to manually import data from your bank unless you happen to be lucky enough to live in the very limited number of places where there’s some kind of automation for it.
So, going back to GNUCash was an option. But I wanted to survey the land of what was available, and if it was possible to exchange money for convenience. I am not big on the motivation to go and spend a lot of time on this kind of thing anyway, so it had to be easy for me to do so.
For my requirements, I basically had:
I viewed a mobile app (iOS) as a Nice to Have rather than essential. Given that, my shortlist was:
I’ve used it before, its web site at https://www.gnucash.org/ looks much the same as it always has. It’s Free and Open Source Software, and is thus well aligned with my values, and that’s a big step towards not having vendor lock-in.
I honestly could probably make it work. I wish it had the ability to import transactions from banks for anywhere I have ever lived or banked with. I also wish the UI got to be a bit more consistent and modern, and even remotely Mac like on the Mac version.
Honestly, if the deal was that a web service would pull bank transactions in exchange for ~$10/month and also fund GNUCash development… I’d struggle to say no.
Here’s an option that has been around forever – https://www.quicken.com/ – and one that I figured I should solidly look at. It’s actually one I even spent money on…. before requesting a refund. It’s Import/Export is so broken it’s an insult to broken software everywhere.
Did you know that Quicken doesn’t import the Quicken Interchange Format (QIF), and hasn’t since 2005?
Me, incredulously, when trying out quicken
I don’t understand why you wouldn’t support as many as possible formats that banks export your transaction data as. It cannot possibly be that hard to parse these things, nor can it possibly be code that requires a lot of maintenance.
This basically meant that I couldn’t import data from my Australian Banks. Urgh. This alone ruled it out.
It really didn’t build confidence in ever getting my data out. At every turn it seemed to be really keen on locking you into Quicken rather than having a good experience all-up.
This one was new to me – https://www.wiz.money/ – and had a fancy URL and everything. I spent a bunch of time trying MoneyWiz, and I concluded that it is pretty, but buggy. I had managed to create a report where it said I’d earned $0, but you click into it, and then it gives actual numbers. Not being self consistent and getting the numbers wrong, when this is literally the only function of said app (to get the numbers right), took this out of the running.
It did sync from my US and Australian banks though, so points there.
Intuit used to own Quicken until it sold it to H.I.G. Capital in 2016 (according to Wikipedia). I have no idea if that has had an impact as to the feature set / usability of Quicken, but they now have this Cloud-only product called Mint.
The big issue I had with Mint was that there didn’t seem to be any way to get your data out of it. It seemed to exemplify vendor lock-in. This seems to have changed a bit since I was originally looking, which is good (maybe I just couldn’t find it?). But with the cloud-only approach I wasn’t hugely comfortable with having everything there. It also seemed to be lacking a few features that I was begging to find useful in other places.
It is the only product that links with the Apple Card though. No idea why that is the case.
The price tag of $0 was pretty unbeatable, which does make me wonder where the money is made from to fund its development and maintenance. My guess is that it’s through commission on the various financial products advertised through it, and I dearly hope it is not through selling data on its users (I have no reason to believe it is, there’s just the popular habit of companies doing this).
This is what I’ve settled on. It seemed to be easy enough for me to figure out how to use, sync with an iPhone App, be a reasonable price, and be able to import and sync things from accounts that I have. Oddly enough, nothing can connect and pull things from the Apple Card – which is really weird. That isn’t a Banktivity thing though, that’s just universal (except for Intuit’s Mint).
I’ve been using it for a bit more than a year now, and am still pretty happy. I wish there was the ability to attach a PDF of a statement to the Statement that you reconcile. I wish I could better tune the auto match/classification rules, and a few other relatively minor things.
Periodically in life I’ve had the desire to be somewhat fit, or at least have the benefits that come with that such as not dying early and being able to navigate a mountain (or just the city of Seattle) on foot without collapsing. I have also found that holding myself accountable via data is pretty vital to me actually going and repeatedly doing something.
So, at some point I got myself a Garmin watch. The year was 2012 and it was a Garmin Forerunner 410. It had a standard black/grey LCD screen, GPS (where getting a GPS lock could be utterly infuriatingly slow), a sensor you attached to your foot, a sensor you strap to your chest for Heart Rate monitoring, and an ANT+ dongle for connecting to a PC to download your activities. There was even some open source software that someone wrote so I could actually get data off my watch on my Linux laptops. This wasn’t a smart watch – it was exclusively for wearing while exercising and tracking an activity, otherwise it was just a watch.
However, as I was ramping up to marathon distance running, one huge flaw emerged: I was not fast enough to run a marathon in the time that the battery in my Garmin lasted. IIRC it would end up dying around 3hr30min into something, which at the time was increasingly something I’d describe as “not going for too long of a run”. So, the search for a replacement began!
The year was 2017, and the Garmin fenix 5x attracted me for two big reasons: a battery life to be respected, and turn-by-turn navigation. At the time, I seldom went running with a phone, preferring a tiny SanDisk media play (RIP, they made a new version that completely sucked) and a watch. The attraction of being able to get better maps back to where I started (e.g. a hotel in some strange city where I didn’t speak the language) was very appealing. It also had (what I would now describe as) rudimentary smart-watch features. It didn’t have even remotely everything the Pebble had, but it was enough.
So, a (non-trivial) pile of money later (even with discounts), I had myself a shiny and virtually indestructible new Garmin. I didn’t even need a dongle to sync it anywhere – it could just upload via its own WiFi connection, or through Bluetooth to the Garmin Connect app to my phone. I could also (if I ever remembered to), plug in the USB cable to it and download the activities to my computer.
One problem: my skin rebelled against the Garmin fenix 5x after a while. Like, properly rebelled. If it wasn’t coming off, I wanted to rip it off. I tried all of the tricks that are posted anywhere online. Didn’t help. I even got tested for what was the most likely culprit (a Nickel allergy), and didn’t have one of them, so I (still) have no idea what I’m actually allergic to in it. It’s just that I cannot wear it constantly. Urgh. I was enjoying the daily smart watch uses too!
So, that’s one rather expensive watch that is special purpose only, and even then started to get to be a bit of an issue around longer activities. Urgh.
So the hunt began for a smart watch that I could wear constantly. This usually ends in frustration as anything I wanted was hundreds of $ and pretty much nobody listed what materials were in it apart from “stainless steel”, “may contain”, and some disclaimer about “other materials”, which wasn’t a particularly useful starting point for “it is one of these things that my skin doesn’t like”. As at least if the next one also turned out to cause me problems, I could at least have a list of things that I could then narrow down to what I needed to avoid.
So that was all annoying, with the end result being that I went a long time without really wearing a watch. Why? The search resumed periodically and ended up either with nothing, or totally nothing. That was except if I wanted to get further into some vendor lock-in.
Honestly, the only manufacturer of anything smartwatch like which actually listed everything and had some options was Apple. Bizarre. Well, since I already got on the iPhone bandwagon, this was possible. Rather annoyingly, they are very tied together and thus it makes it a bit of a vendor-lock-in if you alternate phone and watch replacement and at any point wish to switch platforms.
That being said though, it does work well and not irritate my skin. So that’s a bonus! If I get back into marathon level distance running, we’ll see how well it goes. But for more common distances that I’ve run or cycled with it… the accuracy seems decent, HR monitor never just sometimes decides I’m not exerting myself, and the GPS actually gets a lock in reasonable time. Plus it can pair with headphones and be the only thing I take out with me.
A few random notes about things that can make life on macOS (the modern one, as in, circa 2023) better for those coming from Linux.
For various reasons you may end up with Mac hardware with macOS on the metal rather than Linux. This could be anything from battery life of the Apple Silicon machines (and not quite being ready to jump on the Asahi Linux bandwagon), to being able to run the corporate suite of Enterprise Software (arguably a bug more than a feature), to some other reason that is also fine.
My approach to most of my development is to have a remote more powerful Linux machine to do the heavy lifting, or do Linux development on Linux, and not bank on messing around with a bunch of software on macOS that would approximate something on Linux. This also means I can move my GUI environment (the Mac) easily forward without worrying about whatever weird workarounds I needed to do in order to get things going for whatever development work I’m doing, and vice-versa.
Terminal emulator? iTerm2. The built in Terminal.app is fine, but there’s more than a few nice things in iTerm2, including tmux integration which can end up making it feel a lot more like a regular Linux machine. I should probably go read the tmux integration best practices before I complain about some random bugs I think I’ve hit, so let’s pretend I did that and everything is perfect.
I tend to use the Mac for SSHing to bigger Linux machines for most of my work. At work, that’s mostly to a Graviton 2 EC2 Instance running Amazon Linux with all my development environments on it. At home, it’s mostly a Raptor Blackbird POWER9 system running Fedora.
Running Linux locally? For all the use cases of containers, Podman Desktop or finch. There’s a GUI part of Podman which is nice, and finch I know about because of the relatively nearby team that works on it, and its relationship to lima. Lima positions itself as WSL2-like but for Mac. There’s UTM for a full virtual machine / qemu environment, although I rarely end up using this and am more commonly using a container or just SSHing to a bigger Linux box.
There’s XCode for any macOS development that may be needed (e.g. when you want that extra feature in UTM or something) I do use Homebrew to install a few things locally.
Have a read of Andrew‘s blog post on OpenBMC Development on an Apple M1 MacBook Pro too.
Last week I had occasion to test deploying ceph-csi on a k3s cluster, so that Kubernetes workloads could access block storage provided by an external Ceph cluster. I went with the upstream Ceph documentation, because assuming everything worked it’d then be really easy for me to say to others “just go do this”.
Everything did not work.
I’d gone through all the instructions, inserting my own Ceph cluster’s FSID and MON IP addresses in the right places, applied the YAML to deploy the provisioner and node plugins, and all the provisioner bits were running just fine, but the csi-rbdplugin pods were stuck in CrashLoopBackOff:
> kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE csi-rbdplugin-22zjr 1/3 CrashLoopBackOff 107 (3m55s ago) 2d csi-rbdplugin-pbtc2 1/3 CrashLoopBackOff 104 (3m33s ago) 2d csi-rbdplugin-provisioner-9dcfd56d7-c8s72 7/7 Running 28 (35m ago) 8d csi-rbdplugin-provisioner-9dcfd56d7-hcztz 7/7 Running 28 (35m ago) 8d csi-rbdplugin-provisioner-9dcfd56d7-w2ctc 7/7 Running 28 (35m ago) 8d csi-rbdplugin-r2rzr 1/3 CrashLoopBackOff 106 (3m39s ago) 2d
The csi-rbdplugin pod consists of three containers – driver-registrar, csi-rbdplugin, liveness-prometheus – and csi-rbdplugin wasn’t able to load the rbd kernel module:
> kubectl logs csi-rbdplugin-22zjr --container csi-rbdplugin I0726 10:25:12.862125 7628 cephcsi.go:199] Driver version: canary and Git version: d432421a88238a878a470d54cbf2c50f2e61cdda I0726 10:25:12.862452 7628 cephcsi.go:231] Starting driver type: rbd with name: rbd.csi.ceph.com I0726 10:25:12.865907 7628 mount_linux.go:284] Detected umount with safe 'not mounted' behavior E0726 10:25:12.872477 7628 rbd_util.go:303] modprobe failed (an error (exit status 1) occurred while running modprobe args: [rbd]): "modprobe: ERROR: could not insert 'rbd': Key was rejected by service\n" F0726 10:25:12.872702 7628 driver.go:150] an error (exit status 1) occurred while running modprobe args: [rbd]
Matching “modprobe: ERROR: could not insert ‘rbd’: Key was rejected by service” in the above was an error on each host’s console: “Loading of unsigned module is rejected”. These hosts all have secure boot enabled, so I figured it had to be something to do with that. So I logged into one of the hosts and ran modprobe rbd as root, but that worked just fine. No key errors, no unsigned module errors. And once I’d run modprobe rbd (and later modprobe nbd) on the host, the csi-rbdplugin container restarted and worked just fine.
So why wouldn’t modprobe work inside the container? /lib/modules from the host is mounted inside the container, the container has the right extra privileges… Clearly I needed to run a shell in the failing container to poke around inside when it was in CrashLoopBackOff state, but I realised I had no idea how to do that. I knew I could kubectl exec -it csi-rbdplugin-22zjr --container csi-rbdplugin -- /bin/bash but of course that only works if the container is actually running. My container wouldn’t even start because of that modprobe error.
Having previously spent a reasonable amount of time with podman, which has podman run, I wondered if there were a kubectl run that would let me start a new container using the upstream cephcsi image, but running a shell, instead of its default command. Happily, there is a kubectl run, so I tried it:
> kubectl run -it cephcsi --image=quay.io/cephcsi/cephcsi:canary --rm=true --command=true -- /bin/bash If you don't see a command prompt, try pressing enter. [root@cephcsi /]# modprobe rbd modprobe: FATAL: Module rbd not found in directory /lib/modules/5.14.21-150400.24.66-default [root@cephcsi /]# ls /lib/modules/ [root@cephcsi /]#
Ohhh, right, of course, that doesn’t have the host’s /lib/modules mounted. podman run lets me add volume mounts using -v options , so surely kubectl run will let me do that too.
At this point in the story, the notes I wrote last week include an awful lot of swearing.
See, kubectl run doesn’t have a -v option to add mounts, but what it does have is an --overrides option to let you add a chunk of JSON to override the generated pod. So I went back to the relevant YAML and teased out the bits I needed to come up with this monstrosity:
> kubectl run -it cephcsi-test \
--image=quay.io/cephcsi/cephcsi:canary --rm=true \
--overrides='{
"apiVersion": "v1",
"spec": {
"containers": [ {
"name": "cephcsi",
"command": ["/bin/bash"],
"stdin": true, "tty": true,
"image": "quay.io/cephcsi/cephcsi:canary",
"volumeMounts": [ {
"mountPath": "/lib/modules", "name": "lib-modules" }],
"securityContext": {
"allowPrivilegeEscalation": true,
"capabilities": { "add": [ "SYS_ADMIN" ] },
"privileged": true }
} ],
"volumes": [ {
"name": "lib-modules",
"hostPath": { "path": "/lib/modules", "type": "" }
} ]
} }'
But at least I could get a shell and reproduce the problem:
> kubectl run -it cephcsi-test [honking great horrible chunk of JSON] [root@cephcsi-test /]# ls /lib/modules/ 5.14.21-150400.24.66-default [root@cephcsi-test /]# modprobe rbd modprobe: ERROR: could not insert 'rbd': Key was rejected by service
A certain amount more screwing around looking at the source for modprobe and bits of the kernel confirmed that the kernel really didn’t think the module was signed for some reason (mod_verify_sig() was returning -ENODATA), but I knew these modules were fine, because I could load them on the host. Eventually I hit on this:
[root@cephcsi-test /]# ls /lib/modules/*/kernel/drivers/block/rbd* /lib/modules/5.14.21-150400.24.66-default/kernel/drivers/block/rbd.ko.zst
Wait, what’s that .zst extension? It turns out we (SUSE) have been shipping zstd-compressed kernel modules since – as best as I can tell – some time in 2021. modprobe on my SLE Micro 5.3 host of course supports this:
# grep PRETTY /etc/os-release PRETTY_NAME="SUSE Linux Enterprise Micro for Rancher 5.3" # modprobe --version kmod version 29 +ZSTD +XZ +ZLIB +LIBCRYPTO -EXPERIMENTAL
modprobe in the CentOS Stream 8 upstream cephcsi container does not:
[root@cephcsi-test /]# grep PRETTY /etc/os-release PRETTY_NAME="CentOS Stream 8" [root@cephcsi-test /]# modprobe --version kmod version 25 +XZ +ZLIB +OPENSSL -EXPERIMENTAL
Mystery solved, but I have to say the error messages presented were spectacularly misleading. I later tried with secure boot disabled, and got something marginally better – in that case modprobe failed with “modprobe: ERROR: could not insert ‘rbd’: Exec format error”, and dmesg on the host gave me “Invalid ELF header magic: != \x7fELF”. If I’d seen messaging like that in the first place I might have been quicker to twig to the compression thing.
Anyway, the point of this post wasn’t to rant about inscrutable kernel errors, it was to rant about how there’s no way anyone could be reasonably expected to figure out how to do that --overrides thing with the JSON to debug a container stuck in CrashLoopBackOff. Assuming I couldn’t possibly be the first person to need to debug containers in this state, I told my story to some colleagues, a couple of whom said (approximately) “Oh, I edit the pod YAML and change the container’s command to tail -f /dev/null or sleep 1d. Then it starts up just fine and I can kubectl exec into it and mess around”. Those things totally work, and I wish I’d thought to do that myself. The best answer I got though was to use kubectl debug to make a copy of the existing pod but with the command changed. I didn’t even know kubectl debug existed, which I guess is my reward for not reading the entire manual 
So, finally, here’s the right way to do what I was trying to do:
> kubectl debug csi-rbdplugin-22zjr -it \
--copy-to=csi-debug --container=csi-rbdplugin -- /bin/bash
[root@... /]# modprobe rbd
modprobe: ERROR: could not insert 'rbd': Key was rejected by service
(...do whatever other messing around you need to do, then...)
[root@... /]# exit
Session ended, resume using 'kubectl attach csi-debug -c csi-rbdplugin -i -t' command when the pod is running
> kubectl delete pod csi-debug
pod "csi-debug" deleted
In the above kubectl debug invocation, csi-rbdplugin-22zjr is the existing pod that’s stuck in CrashLoopBackOff, csi-debug is the name of the new pod being created, and csi-rbdplugin is the container in that pod that has its command replaced with /bin/bash, so you can mess around inside it.
The July 2023 meeting sparked multiple new topics including Linux security architecture, Debian ports of LoongArch and Risc-V as well as hardware design of PinePhone backplates.
On the practical side, Russell Coker demonstrated running different applications in isolated environment with bubblewrap sandbox, as well as other hardening techniques and the way they interact with the host system. Russell also discussed some possible pathways of hardening desktop Linux to reach the security level of modern Android. Yifei Zhan demonstrated sending and receiving messages with the PineDio USB LoRa adapter and how to inspect LoRa signal with off-the-shelf software defined radio receiver, and discussed how the driver situation for LoRa on Linux might be improved. Yifei then gave a demonstration on utilizing KVM on PinePhone Pro to run NetBSD and OpenBSD virtual machines, more details on running VMs on the PinePhone Pro can be found on this blog post from Yifei.
We also had some discussion of the current state of Mobian and Debian ecosystem, along with how to contribute to different parts of Mobian with a Mobian developer who joined us.
Somewhat a while ago now, I wrote about how every time I return to write some software for the Mac, the preferred language has changed. The purpose of this adventure was to get my photos out of the aging Shotwell and onto my (then new) Mac and the Apple Photos App.
I’ve had a pretty varied experience with photo management on Linux over the past couple of decades. For a while I used f-spot as it was the new hotness. At some point this became…. slow and crashy enough that it was unusable. Today, it appears that the GitHub project warns that current bugs include “Not starting”.
At some point (and via a method I have long since forgotten), I did manage to finally get my photos over to Shotwell, which was the new hotness at the time. That data migration was so long ago now I actually forget what features I was missing from f-spot that I was grumbling about. I remember the import being annoying though. At some point in time Shotwell was no longer was the new hotness and now there is GNOME Photos. I remember looking at GNOME Photos, and seeing no method of importing photos from Shotwell, so put it aside. Hopefully that situation has improved somewhere.
At some point Shotwell was becoming rather stagnated, and I noticed more things stopping to work rather than getting added features and performance. The good news is that there has been some more development activity on Shotwell, so hopefully my issues with it end up being resolved.
One recommendation for Linux photo management was digiKam, and one that I never ended up using full time. One of the reasons behind that was that I couldn’t really see any non manual way to import photos from Shotwell into it.
With tens of thousands of photos (~58k at the time of writing), doing things manually didn’t seem like much fun at all.
As I postponed my decision, I ended up moving my main machine over to a Mac for a variety of random reasons, and one quite motivating thing was the ability to have Photos from my iPhone magically sync over to my photo library without having to plug it into my computer and copy things across.
So…. how to get photos across from Shotwell on Linux to Photos on a Mac/iPhone (and also keep a very keen eye on how to do it the other way around, because, well, vendor lock-in isn’t great).
It would be kind of neat if I could just run Shotwell on the Mac and have some kind of import button, but seeing as there wasn’t already a native Mac port, and that Shotwell is written in Vala rather than something I know has a working toolchain on macOS…. this seemed like more work than I’d really like to take on.
Luckily, I remembered that Shotwell’s database is actually just a SQLite database pointing to all the files on disk. So, if I could work out how to read it accurately, and how to import all the relevant metadata (such as what Albums a photo is in, tags, title, and description) into Apple Photos, I’d be able to make it work.
So… is there any useful documentation as to how the database is structured?
Semi annoyingly, Shotwell is written in Vala, a rather niche programming language that while integrating with all the GObject stuff that GNOME uses, is largely unheard of. Luckily, the database code in Shotwell isn’t too hard to read, so was a useful fallback for when the documentation proves inadequate.
So, I armed myself with the following resources:
Programming the Mac side of things, it was a good excuse to start looking at Swift, so knowing I’d also need to read a SQLite database directly (rather than use any higher level abstraction), I armed myself with the following resources:
From here, I could work on getting the first half going, the ability to view my Shotwell database on the Mac (which is what I posted a screenshot of back in Feb 2022).
But also, I had to work out what I was doing on the other end of things, how would I import photos? It turns out there’s an API!
A bit of SwiftUI code:
import SwiftUI
import AppKit
import Photos
struct ContentView: View {
@State var favorite_checked : Bool = false
@State var hidden_checked : Bool = false
var body: some View {
VStack() {
Text("Select a photo for import")
Toggle("Favorite", isOn: $favorite_checked)
Toggle("Hidden", isOn: $hidden_checked)
Button("Import Photo")
{
let panel = NSOpenPanel()
panel.allowsMultipleSelection = false
panel.canChooseDirectories = false
if panel.runModal() == .OK {
let photo_url = panel.url!
print("selected: " + String(photo_url.absoluteString))
addAsset(url: photo_url, isFavorite: favorite_checked, isHidden: hidden_checked)
}
}
.padding()
}
}
}
struct ContentView_Previews: PreviewProvider {
static var previews: some View {
ContentView()
}
}
Combined with a bit of code to do the import (which does look a bunch like the examples in the docs):
import SwiftUI
import Photos
import AppKit
@main
struct SinglePhotoImporterApp: App {
var body: some Scene {
WindowGroup {
ContentView()
}
}
}
func addAsset(url: URL, isFavorite: Bool, isHidden: Bool) {
// Add the asset to the photo library.
let path = "/Users/stewart/Pictures/1970/01/01/1415446258647.jpg"
let url = URL(fileURLWithPath: path)
PHPhotoLibrary.shared().performChanges({
let addedImage = PHAssetChangeRequest.creationRequestForAssetFromImage(atFileURL: url)
addedImage?.isHidden = isHidden
addedImage?.isFavorite = isFavorite
}, completionHandler: {success, error in
if !success { print("Error creating the asset: \(String(describing: error))") } else
{
print("Imported!")
}
})
}
This all meant I could import a single photo. However, there were some limitations.
There’s the PHAssetCollectionChangeRequest to do things to Albums, so it would solve that problem, but I couldn’t for the life of me work out how to add/edit Titles and Descriptions.
It was so close!
So what did I need to do in order to import Titles and Descriptions? It turns out you can do that via AppleScript. Yes, that thing that launched in 1993 and has somehow survived the transition of m68k based Macs to PowerPC based Macs to Intel based Macs to ARM based Macs.

So, just to make it easier to debug what was going on, I started adding code to my ShotwellImporter tool that would generate snippets of AppleScript I could run and check that it was doing the right thing…. but then very quickly ran into a problem…. it appears that the AppleScript language interpreter on modern macOS has limits that you’d be more familiar with in 1993 than 2023, and I very quickly hit limits where the script would just error out before running (I was out of dictionary size allegedly).
But there’s a new option! Everything you can do with AppleScript you can now do with JavaScript – it’s just even less documented than AppleScript is! But it does work! I got to the point where I could generate JavaScript that imported photos, into all the relevant albums, and set title and descriptions.
A useful write up of using JavaScript rather than AppleScript to do things with Photos: https://mudge.name/2019/11/13/scripting-photos-for-macos-with-javascript/
More recent than when I was doing my hacking, https://alexwlchan.net/2023/managing-albums-in-photos/ is a good read.
With luck I’ll find some time to write up a bit of a walkthrough of my code, and push it up somewhere.
In my last post, I wrote about how I taught sesdev (originally a tool for deploying Ceph clusters on virtual machines) to deploy k3s, because I wanted a little sandbox in which I could break learn more about Kubernetes. It’s nice to be able to do a toy deployment locally, on a bunch of VMs, on my own hardware, in my home office, rather than paying to do it on someone else’s computer. Given the k3s thing worked, I figured the next step was to teach sesdev how to deploy Longhorn so I could break that learn more about that too.
Teaching sesdev to deploy Longhorn meant asking it to:
/dev/vdb on all the nodes that have extra disks, then mount that on /var/lib/longhorn.kubectl label node -l 'node-role.kubernetes.io/master!=true' node.longhorn.io/create-default-disk=true to ensure Longhorn does its storage thing only on the nodes that aren’t the k3s master.So, now I can do this:
> sesdev create k3s --deploy-longhorn
=== Creating deployment "k3s-longhorn" with the following configuration ===
Deployment-wide parameters (applicable to all VMs in deployment):
- deployment ID: k3s-longhorn
- number of VMs: 5
- version: k3s
- OS: tumbleweed
- public network: 10.20.78.0/24
Proceed with deployment (y=yes, n=no, d=show details) ? [y]: y
=== Running shell command ===
vagrant up --no-destroy-on-error --provision
Bringing machine 'master' up with 'libvirt' provider…
Bringing machine 'node1' up with 'libvirt' provider…
Bringing machine 'node2' up with 'libvirt' provider…
Bringing machine 'node3' up with 'libvirt' provider…
Bringing machine 'node4' up with 'libvirt' provider…
[... lots more log noise here - this takes several minutes... ]
=== Deployment Finished ===
You can login into the cluster with:
$ sesdev ssh k3s-longhorn
Longhorn will now be deploying, which may take some time.
After logging into the cluster, try these:
# kubectl get pods -n longhorn-system --watch
# kubectl get pods -n longhorn-system
The Longhorn UI will be accessible via any cluster IP address
(see the kubectl -n longhorn-system get ingress output above).
Note that no authentication is required.
…and, after another minute or two, I can access the Longhorn UI and try creating some volumes. There’s a brief period while the UI pod is still starting where it just says “404 page not found”, and later after the UI is up, there’s still other pods coming online, so on the Volume screen in the Longhorn UI an error appears: “failed to get the parameters: failed to get target node ID: cannot find a node that is ready and has the default engine image longhornio/longhorn-engine:v1.4.1 deployed“. Rest assured this goes away in due course (it’s not impossible I’m suffering here from rural Tasmanian internet lag pulling container images). Anyway, with my five nodes – four of which have an 8GB virtual disk for use by Longhorn – I end up with a bit less than 22GB storage available:
Now for the fun part. Longhorn is a distributed storage solution, so I thought it would be interesting to see how it handled a couple of types of failure. The following tests are somewhat arbitrary (I’m really just kicking the tyres randomly at this stage) but Longhorn did, I think, behave pretty well given what I did to it.
Volumes in Longhorn consist of replicas stored as sparse files on a regular filesystem on each storage node. The Longhorn documentation recommends using a dedicated disk rather than just having /var/lib/longhorn backed by the root filesystem, so that’s what sesdev does: /var/lib/longhorn is an ext4 filesystem mounted on /dev/vdb. Now, what happens to Longhorn if that underlying block device suffers some kind of horrible failure? To test that, I used the Longhorn UI to create a 2GB volume, then attached that to the master node:
Then, I ssh’d to the master node and with my 2GB Longhorn volume attached, made a filesystem on it and created a little file:
> sesdev ssh k3s-longhorn
Have a lot of fun...
master:~ # cat /proc/partitions
major minor #blocks name
253 0 44040192 vda
253 1 2048 vda1
253 2 20480 vda2
253 3 44016623 vda3
8 0 2097152 sda
master:~ # mkfs /dev/sda
mke2fs 1.46.5 (30-Dec-2021)
Discarding device blocks: done
Creating filesystem with 524288 4k blocks and 131072 inodes
Filesystem UUID: 3709b21c-b9a2-41c1-a6dd-e449bdeb275b
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912
Allocating group tables: done
Writing inode tables: done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
master:~ # mount /dev/sda /mnt
master:~ # echo foo > /mnt/foo
master:~ # cat /mnt/foo
foo
Then I went and trashed the block device backing one of the replicas:
> sesdev ssh k3s-longhorn node3 Have a lot of fun... node3:~ # ls /var/lib/longhorn engine-binaries longhorn-disk.cfg lost+found replicas unix-domain-socket node3:~ # dd if=/dev/urandom of=/dev/vdb bs=1M count=100 100+0 records in 100+0 records out 104857600 bytes (105 MB, 100 MiB) copied, 0.486205 s, 216 MB/s node3:~ # ls /var/lib/longhorn node3:~ # dmesg|tail -n1 [ 6544.197183] EXT4-fs error (device vdb): ext4_map_blocks:607: inode #393220: block 1607168: comm longhorn: lblock 0 mapped to illegal pblock 1607168 (length 1)
At this point, the Longhorn UI still showed the volume as green (healthy, ready, scheduled). Then, back on the master node, I tried creating another file:
master:~ # echo bar > /mnt/bar master:~ # cat /mnt/bar bar
That’s fine so far, but suddenly the Longhorn UI noticed that something very bad had happened:
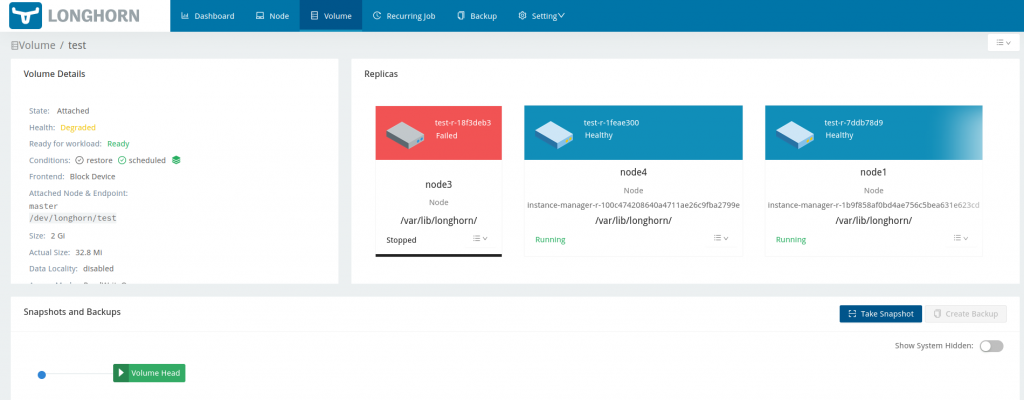
Ultimately node3 was rebooted and ended up stalled with the console requesting the root password for maintenance:
Meanwhile, Longhorn went and rebuilt a third replica on node2:
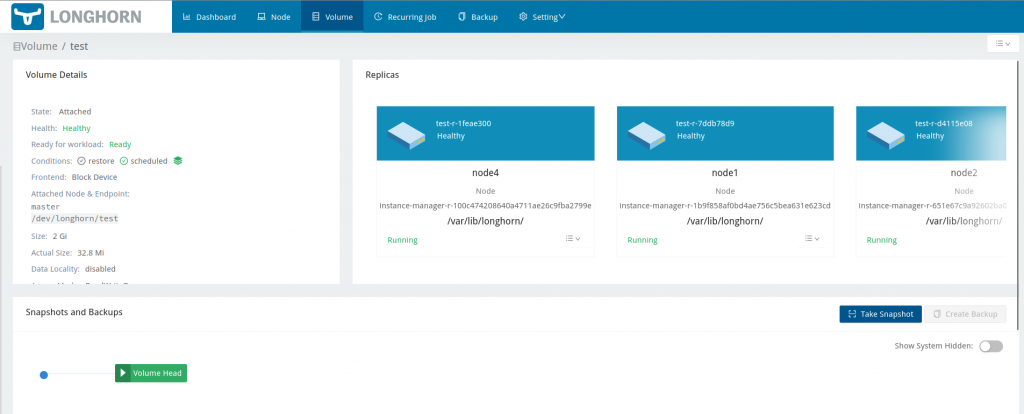
…and the volume remained usable the entire time:
master:~ # echo baz > /mnt/baz master:~ # ls /mnt bar baz foo lost+found
That’s perfect!
Looking at the Node screen we could see that node3 was still down:
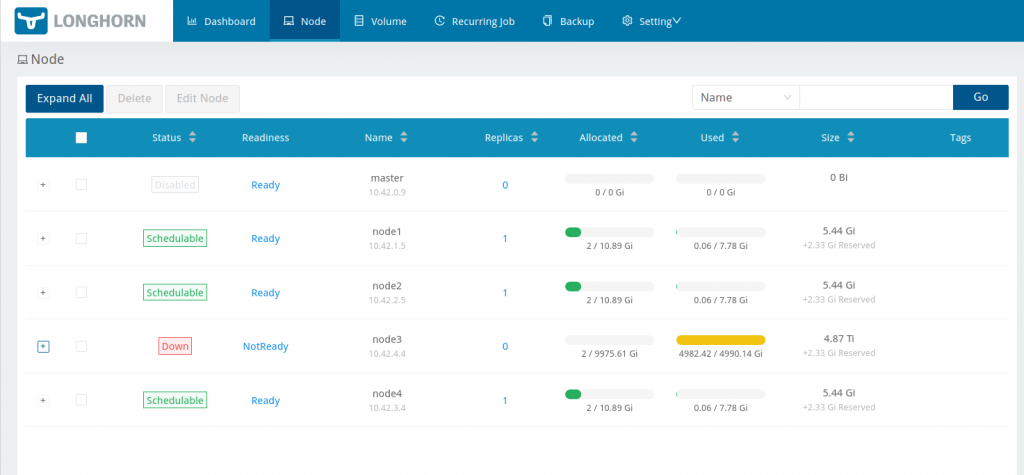
That’s OK, I was able to fix node3. I logged in on the console and ran mkfs.ext4 /dev/vdb then brought the node back up again.The disk remained unschedulable, because Longhorn was still expecting the ‘old’ disk to be there (I assume based on the UUID stored in /var/lib/longhorn/longhorn-disk.cfg) and of course the ‘new’ disk is empty. So I used the Longhorn UI to disable scheduling for that ‘old’ disk, then deleted it. Shortly after, Longhorn recognised the ‘new’ disk mounted at /var/lib/longhorn and everything was back to green across the board.
So Longhorn recovered well from the backing store of one replica going bad. Next I thought I’d try to break it from the other end by running a volume out of space. What follows is possibly not a fair test, because what I did was create a single Longhorn volume larger than the underlying disks, then filled that up. In normal usage, I assume one would ensure there’s plenty of backing storage available to service multiple volumes, that individual volumes wouldn’t generally be expected to get more than a certain percentage full, and that some sort of monitoring and/or alerting would be in place to warn of disk pressure.
With four nodes, each with a single 8GB disk, and Longhorn apparently reserving 2.33GB by default on each disk, that means no Longhorn volume can physically store more than a bit over 5.5GB of data (see the Size column in the previous screenshot). Given that the default setting for Storage Over Provisioning Percentage is 200, we’re actually allowed to allocate up to a bit under 11GB.
So I went and created a 10GB volume, attached that to the master node, created a filesystem on it, and wrote a whole lot of zeros to it:
master:~ # mkfs.ext4 /dev/sda mke2fs 1.46.5 (30-Dec-2021) [...] master:~ # mount /dev/sda /mnt master:~ # df -h /mnt Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/sda 9.8G 24K 9.3G 1% /mnt master:~ # dd if=/dev/zero of=/mnt/big-lot-of-zeros bs=1M status=progress 2357198848 bytes (2.4 GB, 2.2 GiB) copied, 107 s, 22.0 MB/s
While that dd was running, I was able to see the used space of the replicas increasing in the Longhorn UI:
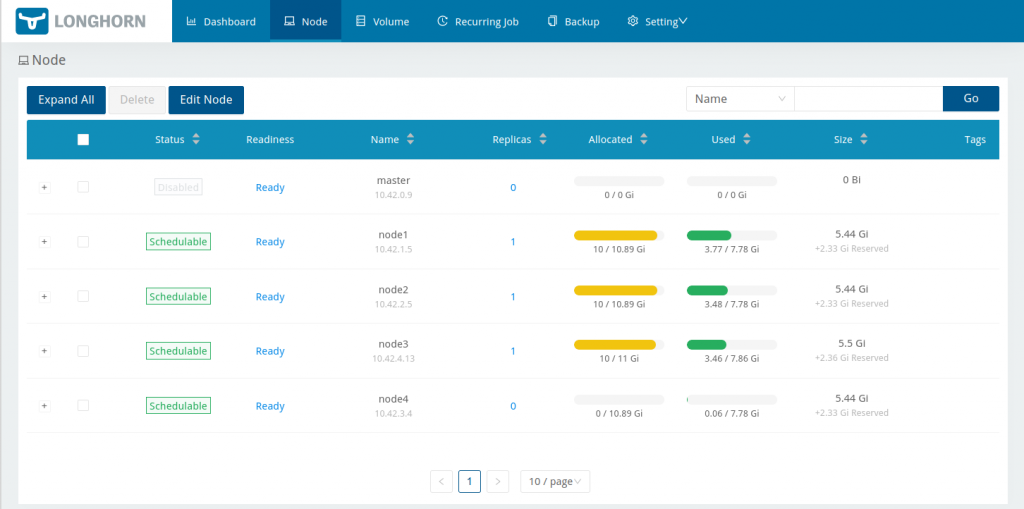
After a few more minutes, the dd stalled…
master:~ # dd if=/dev/zero of=/mnt/big-lot-of-zeros bs=1M status=progress 9039773696 bytes (9.0 GB, 8.4 GiB) copied, 478 s, 18.9 MB/s
…there was a lot of unpleasantness on the master node’s console…
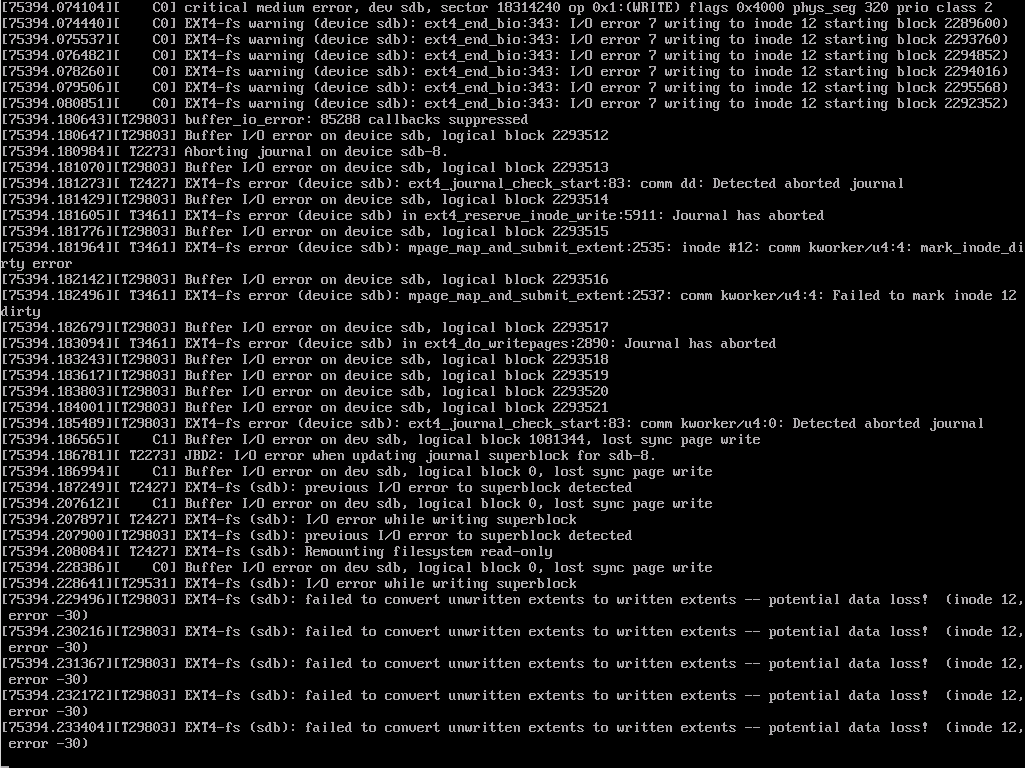
…the replicas became unschedulable due to lack of space…
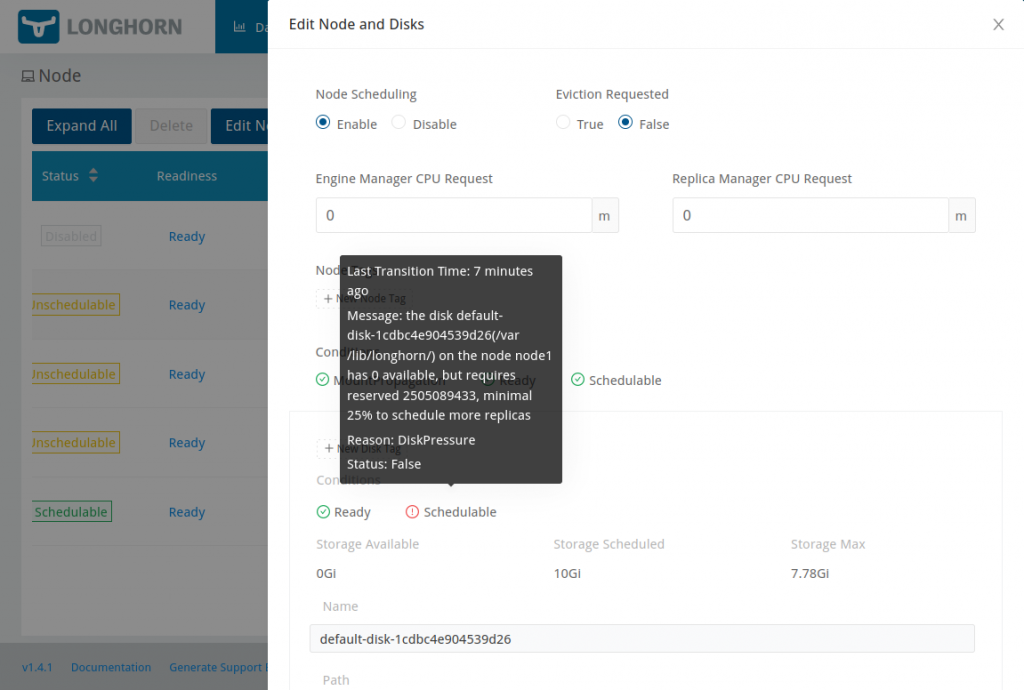
…and finally the volume faulted:
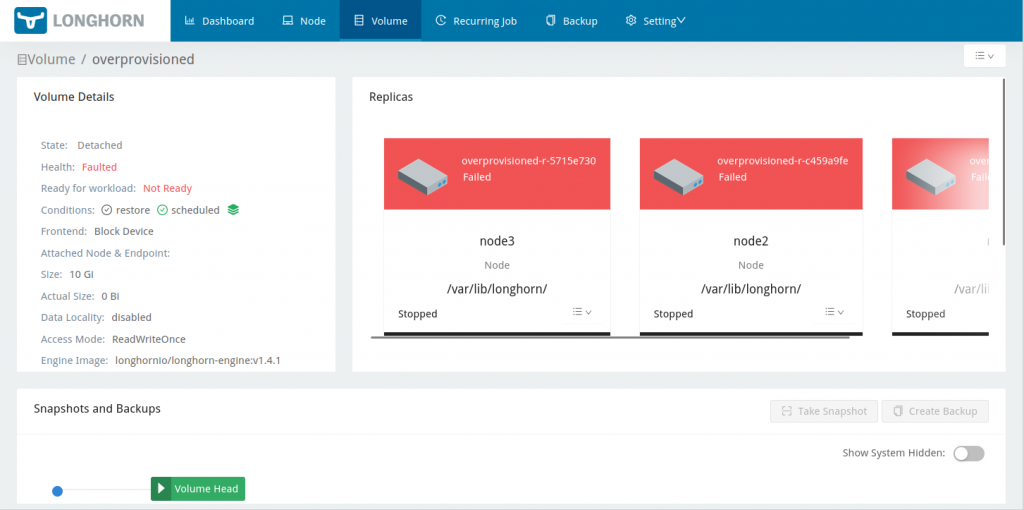
Now what?
It turns out that Longhorn will actually recover if we’re able to somehow expand the disks that store the replicas. This is probably a good argument for backing Longhorn with an LVM volume on each node in real world deployments, because then you could just add another disk and extend the volume onto it. In my case though, given it’s all VMs and virtual block devices, I can actually just enlarge those devices. For each node then, I:
qemu-img resize /var/lib/libvirt/images/k3s-longhorn_$NODE-vdb.qcow2 +8Gresize2fs /dev/vdb to take advantage of the extra disk space.After doing that to node1, Longhorn realised there was enough space there and brought node1’s replica of my 10GB volume back online. It also summarily discarded the other two replicas from the still-full disks on node2 and node3, which didn’t yet have enough free space to be useful:
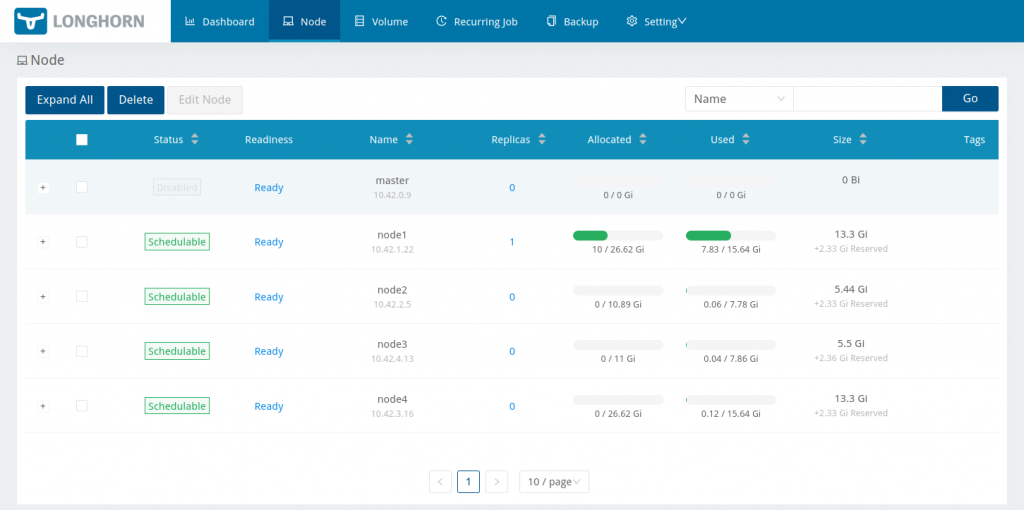
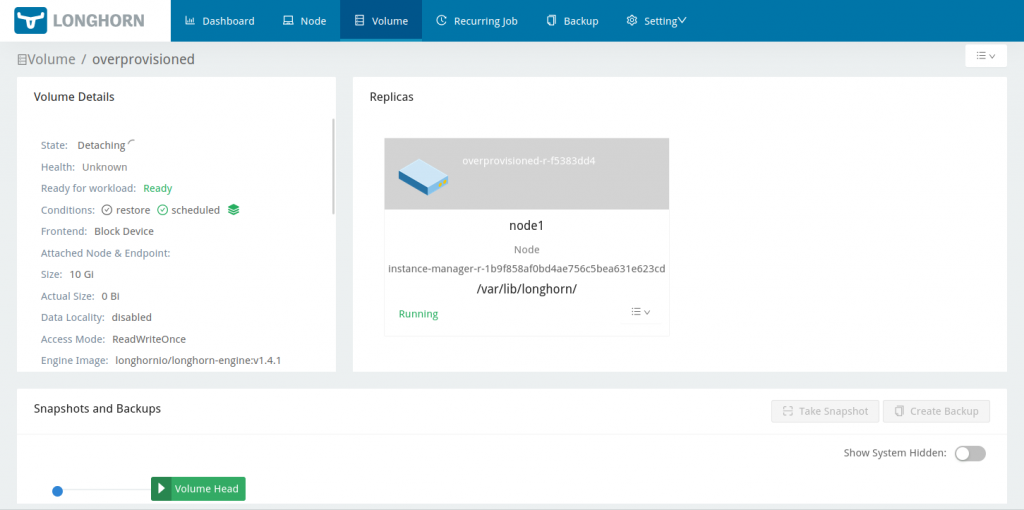
As I repeated the virtual disk expansion on the other nodes, Longhorn happily went off and recreated the missing replicas:
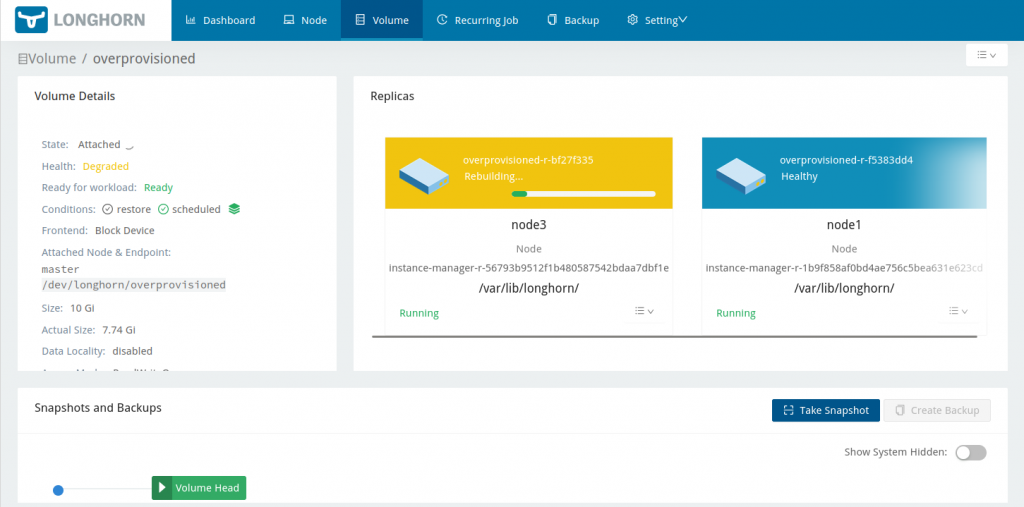
Finally I could re-attach the volume to the master node, and have a look to see how many of my zeros were actually written to the volume:
master:~ # cat /proc/partitions major minor #blocks name 254 0 44040192 vda 254 1 2048 vda1 254 2 20480 vda2 254 3 44016623 vda3 8 0 10485760 sda master:~ # mount /dev/sda /mnt master:~ # ls -l /mnt total 7839764 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 8027897856 May 3 04:41 big-lot-of-zeros drwx------ 2 root root 16384 May 3 04:34 lost+found
Recall that dd claimed to have written 9039773696 bytes before it stalled when the volume faulted, so I guess that last gigabyte of zeros is lost in the aether. But, recall also that this isn’t really a fair test – one overprovisioned volume deliberately being quickly and deliberately filled to breaking point vs. a production deployment with (presumably) multiple volumes that don’t fill quite so fast, and where one is hopefully paying at least a little bit of attention to disk pressure as time goes by.
It’s worth noting that in a situation where there are multiple Longhorn volumes, assuming one disk or LVM volume per node, the replicas will all share the same underlying disks, and once those disks are full it seems all the Longhorn volumes backed by them will fault. Given multiple Longhorn volumes, one solution – rather than expanding the underlying disks – is simply to delete a volume or two if you can stand to lose the data, or maybe delete some snapshots (I didn’t try the latter yet). Once there’s enough free space, the remaining volumes will come back online. If you’re really worried about this failure mode, you could always just disable overprovisioning in the first place – whether this makes sense or not will really depend on your workloads and their data usage patterns.
All in all, like I said earlier, I think Longhorn behaved pretty well given what I did to it. Some more information in the event log could perhaps be beneficial though. In the UI I can see warnings from longhorn-node-controller e.g. “the disk default-disk-1cdbc4e904539d26(/var/lib/longhorn/) on the node node1 has 3879731200 available, but requires reserved 2505089433, minimal 25% to schedule more replicas” and warnings from longhorn-engine-controller e.g. “Detected replica overprovisioned-r-73d18ad6 (10.42.3.19:10000) in error“, but I couldn’t find anything really obvious like “Dude, your disks are totally full!”
Later, I found more detail in the engine manager logs after generating a support bundle ([…] level=error msg=”I/O error” error=”tcp://10.42.4.34:10000: write /host/var/lib/longhorn/replicas/overprovisioned-c3b9b547/volume-head-003.img: no space left on device”) so the error information is available – maybe it’s just a matter of learning where to look for it.
In government we often speak about policy levers, but in the real world, a lever without a fulcrum is just a plank of wood. Levers are needed to lift a load, but without a fulcrum, you can’t move it very far. Fulcrums are needed to dramatically increase the impact of a lever without having to increase the effort/resource. Basically, levers without fulcrums are pretty ineffective.
Sometimes even ambitious change agendas can unintentionally adopt a levers-without-fulcrums pattern. For instance, setting up a team to innovate without normalising a culture of innovation across the organisation. Hiring or training extraordinary talent and then not letting them make any decisions or bring ideas to the table. Training staff on public engagement without creating an appetite for public input. Every lever needs a fulcrum.
Once you look for it, you can see this pattern everywhere.
So below are five of my favourite fulcrums to complement the usual policy levers you have today  These are all tried and tested in various governments. These fulcrums are: teaching public sector craft to all who work in (and with) the public sector, a responsible implementation mindset, servant leadership, structuring around outcomes, and finally the critical fulcrum of raised expectations.
These are all tried and tested in various governments. These fulcrums are: teaching public sector craft to all who work in (and with) the public sector, a responsible implementation mindset, servant leadership, structuring around outcomes, and finally the critical fulcrum of raised expectations.
Fulcrum 1: Teaching public service craft to all involved
All public servants used to be trained in public service craft. At some point, about 30 years ago, there was a change that mechanised the public sector (driven by New Public Management) and started bringing people in for a particular skillset (developer, accountant, lawyer, project manager, etc) with limited training on the context in which they’d be applying those skills. These days, generally only policy people are expected to be ‘trained’ in the ways of government, and even then, many public policy courses teach only the mechanics of public sector without the responsibilities or clear delineation of powers and accountabilities.
We have seen the results of this in shocking testimony throughout the Robodebt Royal Commission, as senior public servants demonstrated a complete misunderstanding (and sometimes abdication) of their responsibility to be trusted stewards acting both lawfully and in the best public interest, instead believing their job to just advise, and then loyally (blindly?) implement the decisions of the government of the day, whatever the cost, conflict, impact or legality. This culture issue is well articulated in the recent submission to the Robodebt Royal Commission by the UNSW Allens Hub and Australasian Society for Computers and the Law.
Similarly, political staffers need to be trained on the responsibilities, dignity and accountabilities of being in office (whether in Government or Opposition), and should be taught what a healthy relationship between Ministerial offices and departments looks like, as has been well articulated in Professor Andrew Podger’s well written recent analysis.
The reason public sector craft should be taught to all public servants, at all levels, is to ensure that everyone knows what good, responsible, ethical and lawful governance looks like, and is able to identify and hold the line when required. This ensures that good and high integrity governance weathers the storms of political change, while being capable of maintaining the trust and confidence of the Government, the Parliament and the People, because there is significant benefit in equally serving all three masters.
Fulcrum 2: A “responsible implementation” mindset
“Frank advice, fearless stewardship, responsible implementation�
There is a LOT of decision making to be made that doesn’t require Ministerial approval, where public servants at all levels can and should confidently exercise their delegations in accordance with the mandate and legislation.
Personally, I would like to change the old saying from “frank and fearless advice� to “frank advice, fearless stewardship, responsible implementation�, to help public servants, particularly policy folk, to realise the job is more than an advisory one. Stewardship is being added to the APS Values and will help ensure a more sustainable and public good mindset across the senior executive. Implementation is always where impact is felt, so responsible implementation is frankly more critical than good advice. Fearlessness should be about how the sector is maintaining its balance, integrity and trustworthiness in the face of adversity, influence and power.
In any case, the Government of the day generally only tweaks a small proportion of the whole mandate of the public sector, but public servants are expected to lawfully and responsibly administer all their obligations, not just the policy agenda of the Government of the day. Ministers (and Governments) can and do set “Big P� Policy, but where that policy conflicts with the law, legislation, constitution or frankly, with public benefit, then public servants have a responsibility to say no, not to just offer more advice but implement anyway.
The lack of training from fulcrum 1 has led to a situation where many public servants and ministerial staffers don’t know how they should interact. For instance, Ministers should ideally identify outcomes they wish to achieve, and ask departments to provide analysis and options, but Minister’s generally shouldn’t dictate solutions or delivery. Departments have a whole mandate to deliver outside of the Minister’s objectives, found in the legislative and constitutional foundations of the portfolio. Below is a little diagram I made to help folk understand where authorities lie and the actors and change mechanisms required for each. For example, there is significant authority and decision making around the operational policies and program implementation in the department itself, which doesn’t require continual Ministerial approvals.
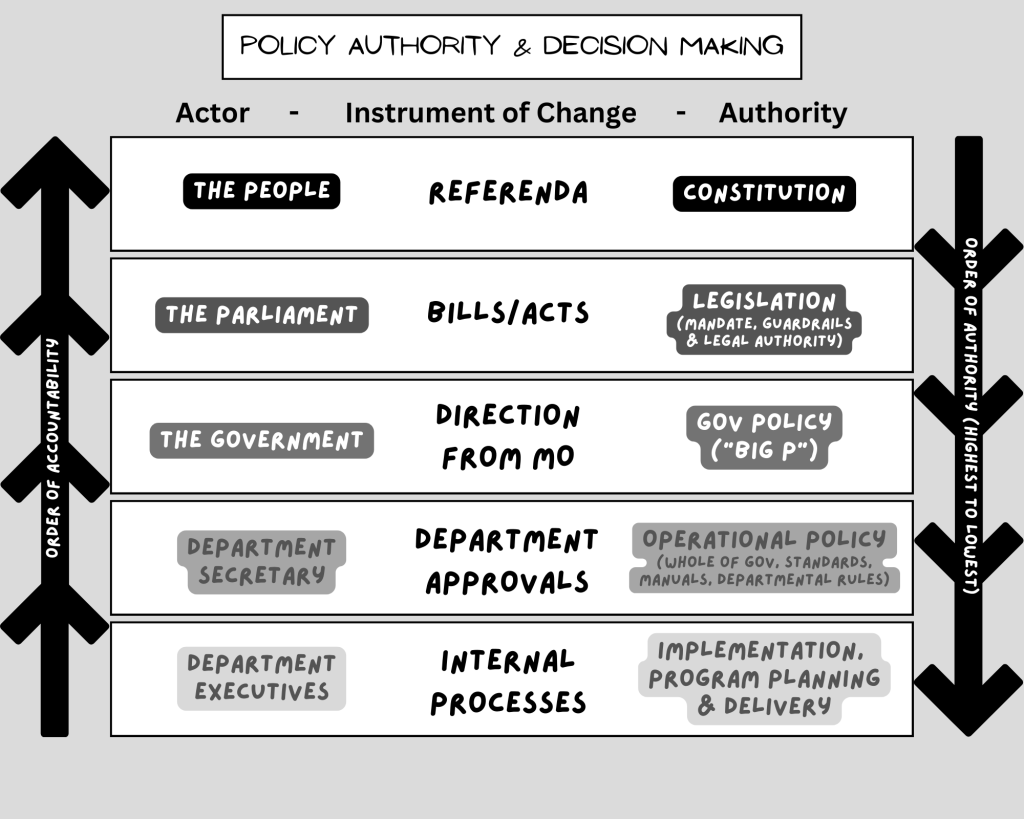
If more public servants used their full delegation to genuinely, openly and confidently serve the public, and refer continually to the mandate laid out in constitution and legislation, we would have better governance, improved public trust and dramatically better public outcomes.
Fulcrum 3: Servant Leadership
When I started working in the NSW Government as a senior executive, my new team asked me on my first day what my success criteria for them was. I thought for a moment, and answered: 1) that was have a measurably beneficial impact for the people/communities we serve; 2) that we are looked to and considered exemplars for how we work, not just what we deliver; and 3) that everyone in the team has joy every day at work. I truly believe that people should leave every workplace better than when they started.
Joy is a wonderful indicator for when people feel heard, empowered, working on meaningful stuff and valued. It shows people are busy but not burned out, delivering value and getting the balance roughly right. In the public sector where many people are driven by a deep desire to do good, joy is enabled by embracing and supporting that desire, and helping people bring their whole creative and brilliant selves to the job. An empowered and joyful team is a force of nature. So why are so many teams not joyful?
It is no secret that public sector leadership in recent decades has slowly devolved into a murky soup of micromanagement, distrust and politicisation. This is not because we have magically attracted such individuals pre-formed, but rather because we have normalised an executive environment with training and incentives that drives and rewards these behaviours. When a leader, at any level (team, branch, division, department) see their job as “managing� people, there is an inherently disrespectful and toxic presumption that people are not willing or capable of managing themselves. “Managing� people quickly leads to micromanaging people, leading to a very real sense of helplessness and disempowerment across the service.
People rising through the ranks have also been taught that “expertise� is a dirty word, and to really get anywhere you should become a “generalist�. This has led to an unhealthy and internalised disregard of internal experts, and mutual incomprehension between decision makers and those with the experience and expertise needed to inform decisions.
Equally problematic is the lack of public sector leadership development. Executives are often promoted or recruited through being highly capable at doing, but are not then taught how to empower others. Many courses teach execs to distrust their staff, to allocate tasks rather than outcomes, to focus on efficiency rather than public or policy outcomes, and to reward compliance over creativity.
There are solutions though. I have seen and adopted �Servant Leadership� as a powerful and effective fulcrum to shift and improve leadership culture in many public sectors around the world. It provides both a mindset/cultural shift and a method for building high performing teams capable of delivering real impact. Servant leadership reframes “leadership� as the act of empowering and supporting people to succeed, growing the confidence of staff and improving their capability and confidence to deliver.
Product management, done well, provides a good test for Servant Leaders. A senior program or project owner needs to be able to delegate decision making to product owners and managers, and to oversee and guide rather than direct. When product teams lose (or never truly gain) delegation of decision making, they are unable to design, deliver, manage, continuously improve or pivot products in response to changing needs or policy.
Servant leadership creates an active practice of listening, enabling and encouraging all staff to bring their best selves, creating the possibility of high performing and sustainable teams that can work smarter across disciplines, and can innovate and engage. Servant leadership actively delegates down, supporting staff to own outcomes along with relevant decision making to be at the right level, a critical requirement for better policy and service delivery outcomes.
Fulcrum 4: Structuring around outcomes
Whilst ever public servants have to provide a cost centre just to talk to each other (let alone work together), we will continue to see structural segmentation of disciplines, and a structural inability to be outcomes driven. There are small ways to structure around outcomes, even within highly segmented structures, like funding an outcome under one cost centre, and bringing together all the capabilities required for that outcome (rather than begging, borrowing, seconding, stealing or journaling), and building different disciplines and capability uplift into your project and programme budgets (such as 0.2 FTE from policy, or secondees from the frontline, or funding for service design that includes training for internal staff to learn for next time).
Whenever I build a government program, I ensure we identify and budget for the minimum viable set of capabilities to deliver the outcome end to end. We can always supplement with collaborations, vendors, partnerships, etc, but without the minimum viable capabilities represented in the team, then any delivery is always subject to the whims and pressures of someone else’s urgency laden prioritisation queue. We need to fund services for continuous improvement, rather than funding a launch. We need to fund end to end policy management, rather than blindfolded baton passing between different functions or departments. We need structures (and cost centres) that ensure full accountability for an outcome is supported by funding and multi-disciplinary capabilities to deliver the outcome.
Fulcrum 5: Raised expectations
The final fulcrum sounds simple, but is really the most important. Once of the most difficult to shift and self-fulfilling aspects of learned helplessness is when people allow themselves to continually expect the worst. Cynicism creates a form of acceptance and permission for poor behaviour and poor performance to continue, especially in the senior ranks.
When I entered the public sector over a decade ago, I had already seen this pattern from the outside, and I promised to never allow myself to not be surprised at things that make no sense. I ask questions, validate assumptions, look at actual versus intended impact and I encourage people to think about and aim for what will best serve the community, not to just tick the box. When I express surprise at something, people often say to me “but you’ve worked in government a while, surely you’ve seen this before�. I cheerfully tell them I made a conscious choice to not grow numb to systemic issues, often leading to great discussions about to redirect the energy of surprise and frustration into fixing the system, and the dangers of unintentionally propping up bad systems through low expectations.
So a critical but difficult fulcrum for genuine change needs and must be for all public servants to raise our expectations, at all levels. Expect more from yourself, your peers, your bosses, your department, your senior leadership, your Secretary. Don’t praise someone for being kind when that is a basic decency you should expect from everyone. Don’t be satisfied with an executive just listening to your ideas, unless they also give you agency to implement them. Have you noticed that our expectations of people seem to diminish the further up the hierarchy people climb? We should have the highest expectations of our most senior public servants. They should exemplify the very best stewardship, commitment to public good, integrity, culture, responsible administration and equally serving the Government, the Parliament and the People.
Raise your expectations, keep them high, and always, always, expect the best from people. You’d be surprised how many rise to that expectation  You’ll be surprised how powerful a fulcrum it can be.
You’ll be surprised how powerful a fulcrum it can be.
Over to you
These are five of my favourite fulcrums, what are yours? How have you already applied similar approaches in your own department? What does better public sector administration look like for you? Let’s get some sharing so we can create a better service together, and so that our policy, programme and other levers are more than planks.
We – that is to say the storage team at SUSE – have a tool we’ve been using for the past few years to help with development and testing of Ceph on SUSE Linux. It’s called sesdev because it was created largely for SES (SUSE Enterprise Storage) development. It’s essentially a wrapper around vagrant and libvirt that will spin up clusters of VMs running openSUSE or SLES, then deploy Ceph on them. You would never use such clusters in production, but it’s really nice to be able to easily spin up a cluster for testing purposes that behaves something like a real cluster would, then throw it away when you’re done.
I’ve recently been trying to spend more time playing with Kubernetes, which means I wanted to be able to spin up clusters of VMs running openSUSE or SLES, then deploy Kubernetes on them, then throw the clusters away when I was done, or when I broke something horribly and wanted to start over. Yes, I know there’s a bunch of other tools for doing toy Kubernetes deployments (minikube comes to mind), but given I already had sesdev and was pretty familiar with it, I thought it’d be worthwhile seeing if I could teach it to deploy k3s, a particularly lightweight version of Kubernetes. Turns out that wasn’t too difficult, so now I can do this:
> sesdev create k3s === Creating deployment "k3s" with the following configuration === Deployment-wide parameters (applicable to all VMs in deployment): deployment ID: k3s number of VMs: 5 version: k3s OS: tumbleweed public network: 10.20.190.0/24 Proceed with deployment (y=yes, n=no, d=show details) ? [y]: y === Running shell command === vagrant up --no-destroy-on-error --provision Bringing machine 'master' up with 'libvirt' provider... Bringing machine 'node1' up with 'libvirt' provider... Bringing machine 'node2' up with 'libvirt' provider... Bringing machine 'node3' up with 'libvirt' provider... Bringing machine 'node4' up with 'libvirt' provider... [... wait a few minutes (there's lots more log information output here in real life) ...] === Deployment Finished === You can login into the cluster with: $ sesdev ssh k3s
…and then I can do this:
> sesdev ssh k3s Last login: Fri Mar 24 11:50:15 CET 2023 from 10.20.190.204 on ssh Have a lot of fun… master:~ # kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION master Ready control-plane,master 5m16s v1.25.7+k3s1 node2 Ready 2m17s v1.25.7+k3s1 node1 Ready 2m15s v1.25.7+k3s1 node3 Ready 2m16s v1.25.7+k3s1 node4 Ready 2m16s v1.25.7+k3s1 master:~ # kubectl get pods -A NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE kube-system local-path-provisioner-79f67d76f8-rpj4d 1/1 Running 0 5m9s kube-system metrics-server-5f9f776df5-rsqhb 1/1 Running 0 5m9s kube-system coredns-597584b69b-xh4p7 1/1 Running 0 5m9s kube-system helm-install-traefik-crd-zz2ld 0/1 Completed 0 5m10s kube-system helm-install-traefik-ckdsr 0/1 Completed 1 5m10s kube-system svclb-traefik-952808e4-5txd7 2/2 Running 0 3m55s kube-system traefik-66c46d954f-pgnv8 1/1 Running 0 3m55s kube-system svclb-traefik-952808e4-dkkp6 2/2 Running 0 2m25s kube-system svclb-traefik-952808e4-7wk6l 2/2 Running 0 2m13s kube-system svclb-traefik-952808e4-chmbx 2/2 Running 0 2m14s kube-system svclb-traefik-952808e4-k7hrw 2/2 Running 0 2m14s
…and then I can make a mess with kubectl apply, helm, etc.
One thing that sesdev knows how to do is deploy VMs with extra virtual disks. This functionality is there for Ceph deployments, but there’s no reason we can’t turn it on when deploying k3s:
> sesdev create k3s --num-disks=2
> sesdev ssh k3s
master:~ # for node in \
$(kubectl get nodes -o 'jsonpath={.items[*].metadata.name}') ;
do echo $node ; ssh $node cat /proc/partitions ; done
master
major minor #blocks name
253 0 44040192 vda
253 1 2048 vda1
253 2 20480 vda2
253 3 44016623 vda3
node3
major minor #blocks name
253 0 44040192 vda
253 1 2048 vda1
253 2 20480 vda2
253 3 44016623 vda3
253 16 8388608 vdb
253 32 8388608 vdc
node2
major minor #blocks name
253 0 44040192 vda
253 1 2048 vda1
253 2 20480 vda2
253 3 44016623 vda3
253 16 8388608 vdb
253 32 8388608 vdc
node4
major minor #blocks name
253 0 44040192 vda
253 1 2048 vda1
253 2 20480 vda2
253 3 44016623 vda3
253 16 8388608 vdb
253 32 8388608 vdc
node1
major minor #blocks name
253 0 44040192 vda
253 1 2048 vda1
253 2 20480 vda2
253 3 44016623 vda3
253 16 8388608 vdb
253 32 8388608 vdc
As you can see this gives all the worker nodes an extra two 8GB virtual disks. I suspect this may make sesdev an interesting tool for testing other Kubernetes based storage systems such as Longhorn, but I haven’t tried that yet.
The decision to do this rather than build my own was complicated, and I'm going to mostly skip over the detail of that. At some time I might put it in another blog post. But for now it's enough to say that I'd accidentally cooked the motor in my Mark I, the work on the Mark II was going to take ages, and I was in the relatively fortunate situation of being able to afford the Experia if I sold my existing Triumph Tiger Sport and the parts for the Mark II.
For other complicated reasons I was planning to be in Sydney after the weekend that Bruce at Zen Motorcycles told me the bike would be arriving. Rather than have it freighted down, and since I would have room for my riding gear in our car, I decided to pick it up and ride it back on the Monday. In reconnoitering the route, we discovered that by pure coincidence Zen Motorcycles is on Euston Road in Alexandria, only 200 metres away from the entrance to WestConnex and the M8. So with one traffic light I could be out of Sydney.
I will admit to being more than a little excited that morning. Electric vehicles are still, in 2023, a rare enough commodity that waiting lists can be months long; I ordered this bike in October 2022 and it arrived in March 2023. So I'd had plenty of time to build my expectations. And likewise the thought of riding a brand new bike - literally one of the first of its kind in the country (it is the thirty-second Experia ever made!) - was a little daunting. I obtained PDF copies of the manual and familiarised myself with turning the cruise control on and off, as well as checking and setting the regen braking levels. Didn't want to stuff anything up on the way home.
There is that weird feeling in those situations of things being both very ordinary and completely unique. I met Bruce, we chatted, I saw the other Experia models in the store, met Ed - who had come down to chat with Bruce, and just happened to be the guy who rode a Harley Davidson Livewire from Perth to Sydney and then from Sydney to Cape Tribulation and back. He shared stories from his trip and tips on hypermiling. I signed paperwork, picked up the keys, put on my gear, prepared myself.
Even now I still get a bit choked up just thinking of that moment. Seeing that bike there, physically real, in front of me - after those months of anticipation - made the excitement real as well.
So finally, after making sure I wasn't floating, and making sure I had my ear plugs in and helmet on the right way round, I got on. Felt the bike's weight. Turned it on. Prepared myself. Took off. My partner followed behind, through the lights, onto the M8 toward Canberra. I gave her the thumbs up.
We planned to stop for lunch at Mittagong, while the NRMA still offers the free charger at the RSL there. One lady was charging her Nissan Leaf on the ChaDeMo side; shortly after I plugged in a guy arrived in his Volvo XC40 Recharge. He had the bigger battery and would take longer; I just needed a ten minute top up to get me to Marulan.
I got to Marulan and plugged in; a guy came thinking he needed to tell the petrol motorbike not to park in the electric vehicle bay, but then realised that the plug was going into my bike. Kate headed off, having charged up as well, and I waited another ten minutes or so to get a bit more charge. Then I rode back.
I stopped, only once more - at Mac's Reef Road. I turned off and did a U turn, then waited for the traffic to clear before trying the bike's acceleration. Believe me when I say this bike will absolutely do a 0-100km/hr in under four seconds! It is not a light bike, but when you pull on the power it gets up and goes.
Here is my basic review, given that experience and then having ridden it for about ten weeks around town.
The absolute best feature of the Energica Experia is that it is perfectly comfortable riding around town. Ease on the throttle and it gently takes off at the traffic lights and keeps pace with the traffic. Ease off, and it gently comes to rest with regenerative braking and a light touch on the rear brake after stopping to hold it still. If you want to take off faster, wind the throttle on more. It is not temperamental or twitchy, and you have no annoying gears and clutch to balance.
In fact, I feel much more confident lane filtering, because before I would have to have the clutch ready and be prepared to give the Tiger Sport lots of throttle lest I accidentally stall it in front of an irate line of traffic. With the Experia, I can simply wait peacefully - using no power - and then when the light goes green I simply twist on the throttle and I am away ahead of even the most aggressive car driver.
It is amazingly empowering.
I'm not going to bore you with the stats - you can probably look them up yourself if you care. The main thing to me is that it has DC fast charging, and watching 75KW go into a 22.5KWHr battery is just a little bit terrifying as well as incredibly cool. The stated range of 250km on a charge at highway speeds is absolutely correct, from my experience riding it down from Sydney. And that plus the fast charging means that I think it is going to be quite reasonable to tour on this bike, stopping off at fast or even mid-level chargers - even a boring 22KW charger can fill the battery up in an hour. The touring group I travel with stops often enough that if those stops can be top ups, I will not hold anyone up.
Some time in the near future I hope to have a nice fine day where I can take it out on the Cotter Loop. This is an 80km stretch of road that goes west of Canberra into the foothills of the Brindabella Ranges, out past the Deep Space Tracking Station and Tidbinbilla Nature Reserve. It's a great combination of curving country roads and hilly terrain, and reasonably well maintained as well. I did that on the Tiger Sport, with a GoPro, before I sold it - and if I can ever convince PiTiVi to actually compile the video from it I will put that hour's ride up on a platform somewhere.
I want to do that as much to show off Canberra's scenery as to show off the bike.
And if the CATL battery capacity improvement comes through to the rest of the industry, and we get bikes that can do 400km to 500km on a charge, then electric motorbike touring really will be no different to petrol motorbike touring. The Experia is definitely at the forefront of that change, but it is definitely possible on this bike.
Rustup (the community package manage for the Rust language) was starting to really suffer : CI times were up at ~ one hour.
We’ve made some strides in bringing this down.
The first thing, which achieved about a 30% reduction in test time was to stop recreating all the test context every time.
Rustup tests the download/installation/upgrade of distributions of Rust. To avoid downloading gigabytes in the test suite, the suite creates mocks of the published Rust artifacts. These mocks are GPG signed and compressed with multiple compression methods, both of which are quite heavyweight operations to perform – and not actually the interesting code under test to execute.
Previously, every test was entirely hermetic, and usually the server state was also unmodified.
There were two cases where the state was modified. One, a small number of tests testing error conditions such as GPG signature failures. And two, quite a number of tests that were testing temporal behaviour: for instance, install nightly at time A, then with a newer server state, perform a rustup update and check a new version is downloaded and installed.
We’re partway through this migration, but compare these two tests:
fn check_updates_some() {
check_update_setup(&|config| {
set_current_dist_date(config, "2015-01-01");
config.expect_ok(&["rustup", "update", "stable"]);
config.expect_ok(&["rustup", "update", "beta"]);
config.expect_ok(&["rustup", "update", "nightly"]);
set_current_dist_date(config, "2015-01-02");
config.expect_stdout_ok(
&["rustup", "check"],
for_host!(
r"stable-{0} - Update available : 1.0.0 (hash-stable-1.0.0) -> 1.1.0 (hash-stable-1.1.0)
beta-{0} - Update available : 1.1.0 (hash-beta-1.1.0) -> 1.2.0 (hash-beta-1.2.0)
nightly-{0} - Update available : 1.2.0 (hash-nightly-1) -> 1.3.0 (hash-nightly-2)
"
),
);
})
}
fn check_updates_some() {
test(&|config| {
config.with_scenario(Scenario::ArchivesV2_2015_01_01, &|config| {
config.expect_ok(&["rustup", "toolchain", "add", "stable", "beta", "nightly"]);
});
config.with_scenario(Scenario::SimpleV2, &|config| {
config.expect_stdout_ok(
&["rustup", "check"],
for_host!(
r"stable-{0} - Update available : 1.0.0 (hash-stable-1.0.0) -> 1.1.0 (hash-stable-1.1.0)
beta-{0} - Update available : 1.1.0 (hash-beta-1.1.0) -> 1.2.0 (hash-beta-1.2.0)
nightly-{0} - Update available : 1.2.0 (hash-nightly-1) -> 1.3.0 (hash-nightly-2)
"
),
);
})
})
}
The former version mutates the date with set_current_dist_date; the new version uses two scenarios, one for the earlier time, and one for the later time. This permits the server state to be constructed only once. On a per-test basis it can move as much as 50% of the time out of the test.
The next major gain was moving from having 14 separate integration test binaries to just one. This reduces the link cost of linking the test binaries, all of which link in the same library. It also permits us to see unused functions in our test support library, which helps with cleaning up cruft rather than having it accumulate.
Part of the test suite for each test is setting up an installed rustup environment. Why not start from scratch every time? Well, we obviously have tests that do that, but most tests are focused on steps beyond the new-user case. Setting up an installed rustup environment has a few steps, but particular ones are copying a binary of rustup into the test sandbox, and hard linking it under various names: cargo, rustc, rustup etc.
A debug build of rustup is ~20MB. Running 400 tests means about 8GB of IO; on some platforms most of that IO won’t hit disk, on others it will.
In review now is a PR that changes the initial copy to a hardlink: we hardlink the rustup-init built by cargo into each test, and then hardlink that to the various binaries. That saves 8GB of IO, which isn’t much from some perspectives, but it adds pressure on the page cache, and is wasted work. One wrinkle is a very low max-links limit on NTFS of 1023; to mitigate that we count the links made to rustup-init and generate a new inode for the original to avoid failures happening.
In GitHub actions this lowers our test time to 19m for Linux, 24m for Windows, which is a lot better but not great.
I plan on experimenting with separate actions for building release artifacts and doing CI tests – at the moment we have the same action do both, but they don’t share artifacts in the cache in any meaningful way, so we can probably gain parallelism there, as well as turning off release builds entirely for CI.
We should finish the cached test context work and use it everywhere.
Also we’re looking at having less integration tests and more narrow close to the code tests.
I have long said “Long Malaysians, Short Malaysia” in conversation to many. Maybe it took me a while to tweet it, but this was the first example: Dec 29, 2021. I’ve tweeted it a lot more since.
Malaysia has a 10th Prime Minister, but in general, it is a very precarious partnership. Consider it, same shit, different day?
5/n: Otherwise, there will be no change.
So change via “purported democracy” is never going to happen with a country like Malaysia, rotten to the core. It is a crazy dream.
You succeed, despite of. Davka.
Reboot, or bust.
Good luck, Malaysia.
— Colin Charles (@bytebot) August 18, 2021
I just have to get off the Malaysian news diet. Malaysians elsewhere, are generally very successful. Malaysians suffering by their daily doldrums, well, they just need to wake up, see the light, and succeed.
In the end, as much as people paraphrase, ask not what the country can do for you, legitimately, this is your life, and you should be taking good care of yourself and your loved ones. You succeed, despite of. Politics and the state happens, regardless of.
Me, personally? Ideas are abound for how to get Malaysians who see the light, to succeed elsewhere. And if I read, and get angry at something (tweet rage?), I’m going to pop RM50 into an investment account, which should help me get off this poor habit. I’ll probably also just cut subscriptions to Malaysian news things… Less exposure, is actually better for you. I can’t believe that it has taken me this long to realise this.
Time to build.
I did poorly blogging last year. Oops. I think to myself when I read, This Thing Still On?, I really have to do better in 2023. Maybe the catalyst is the fact that Twitter is becoming a shit show. I doubt people will leave the platform in droves, per se, but I think we are coming back to the need for decentralised blogs again.
I have 477 days to becoming 40. I ditched the Hobonich Techo sometime in 2022, and just focused on the Field Notes, and this year, I’ve got a Monocle x Leuchtturm1917 + Field Notes combo (though it seems my subscription lapsed Winter 2022, I should really burn down the existing collection, and resubscribe).
2022 was pretty amazing. Lots of work. Lots of fun. 256 days on the road (what a number), 339,551km travelled, 49 cities, 20 countries.
The getting back into doing, and not being afraid of experimenting in public is what 2023 is all about. The Year of The Rabbit is upon us tomorrow, hence why I don’t mind a little later Hello 2023 :)
Get back into the habit of doing. And publishing by learning and doing. No fear. Not that I wasn’t doing, but its time to be prolific with what’s been going on.
I better remember that.
TL;DR: An overview of my insights from FWD50 2022, including the talk I gave, and the responses to the questions submitted to my talk  In short, it was awesome! Apologies for the long post!
In short, it was awesome! Apologies for the long post!
Every year I attend (or participate in) FWD50, a Canadian conference that I consider the world’s best government transformation event. It is such a special conference because it purposefully doesn’t specialise in just one domain (like the plethora or data, digital, procurement or other events I normally see), but rather it brings together all disciplines around burning questions of the day, and how might the public sector become fundamentally better for the people and communities it serves. FWD50 manages to simultaneously be a social platform for public servants to connect, evolve and be brave together, as well as being something of a petri dish where everyone can participate in co-creating a fundamentally more humane approach to public service. The participants are highly diverse in all respects, with over a hundred government jurisdictions represented from around the world, and thought leadership exhibited from up and down the usual hierarchy chain, embracing the expertise and experience that we all have to share. Some of the most mindblowing sessions often come from junior public servants 
FWD50 is the brainchild of the Croll siblings, Alistair and Rebecca, with a small army of conference experts and public servant volunteers. I can’t recommend this event enough, and the leadership the Crolls have shown, not just in what they’ve built, but in how they continue to deliver it through kind, inclusive, collegial and respectful sharing and provocations. They and their army of awesomeness have also managed to grow and evolve through the pandemic, simultaneously running an in person AND online event, drawing from all the lessons of the last few years, and delivering something both excellent and exemplary for organisations trying to work through their post-COVID existential crisis 
It was also an opportunity for me to connect with colleagues and friends in the Canadian Government, including my old DECD (Digital Experience and Client Data) team at Service Canada. It was SUCH a delight, such a joy, to meet, hug, and hear about how the team are going, including Aaron Jaffrey, who took over leading DECD. I could not have asked for a better person to take care of this very special team, thanks again Aaron! DECD continue to design and deliver amazing things, to be an exemplar for purpose-led, kind and calm culture, and to truly put people at the centre of the design. I miss you all and continue to be your biggest fan 
Below are a few take aways and lessons from the event, shared in the hope they will be helpful, and to encourage more folk to tune in to the discussions and content from FWD50 as a provocation to help plan holistic government transformation in all your own teams 
 When you think someone else energises you, you are potentially missing the vital role you play in the equation
When you think someone else energises you, you are potentially missing the vital role you play in the equation 
I was surprised by the enormous gap I observed between senior executives and the broader community of public servants, a gap so large it had an almost tangible weight. I’ve always believed change can only happen when you first change your mind. For most public servants, COVID has fundamentally changed our minds. The pandemic irrefutably proved that our systems, structures, processes and ways of working are not capable of responding effectively or humanely to the speed of change/need in the modern world. Sure, we can leverage all kinds of emergency superpowers to push things through in weeks/months instead of years, but we always revert to “normal� after the emergency, and in any case, the more pressure there is, the more insular we become in how we operate.
We have entered a time of continuous emergencies, and most public servants intuitively know that we need to fundamentally rethink how we do public administration and governance in a mission, purpose and values oriented way. Though many of the talks at FWD50 touched upon the changed world since COVID (check out the agenda here), they seemed to fall into three broad patterns: disruptive reform, building public trust, and what I’ll cheekily call “Hello 2019â€�.Â
We heard incredible stories of disruptive reform in Ukraine, US Veteran Affairs, the importance of a “moonshot� mindset from X, policy transformation, and what “winning� could look like if we be more purpose and outcomes driven. We heard about efforts and models to improve public trust and confidence, to identify and meeting public expectations (beyond a “customer� imperative), how to design for legitimacy, to value and engage employees in a transformation agenda, how to govern AI, and the need to consider the undeniable (but usually overlooked) relationship between the quality of government services and public trust.
But we also heard several “Hello 2019” talks that would have been completely great 3 years ago, but felt just a little out of touch with the heightened expectations and new challenges from almost 3 years of COVID. The talks about “we just need some better platformsâ€�, or “policy should just focus on deliveryâ€�, or “it all starts with digital identityâ€�. It’s not to say these aren’t important topics to explore, but it felt almost like there is a new gravity in place, where most public servants and the people we serve want us to urgently focus on the why, not just the what or how. In the grand scheme of things, it is easy to deliver new digital stuff, but public sectors need to create the ways and means for people to thrive in ambiguity, to navigate complexity, to be socially included and supported when things go wrong, and to live well, even through rolling crises. If public institutions can’t deliver values based and meaningful public good, and do so in alignment with public values and expectations, then tech, tools, platforms, design and other mechanisms for “howâ€� will continue to distract us from delivering on our purpose.
I feel like for all the trauma we have experienced over the last few years, COVID has acted as a form of necessary intervention on several fronts:
So when I see talks that basically feel like “Hello 2019�, it feels like either a missed opportunity, or perhaps like the speaker is slightly out of step with the changed environment they occupy, which is a real pity.
I suggest it is imperative that we all work diligently to change the systems we work within to reflect the change we have had in our minds, rather than allowing our minds to be reverted to the old world. This is not something to wait for others to do, or to “hopeâ€� for. Just get on with it, and be the change you want to see  Â
Â

This workshop was just excellent, and one of my favourites this year. It was run by the Think Digital and Code for Canada crews with a few public servant volunteers. They invited participants to share barriers, using an expanded version of the old “Culture eats Strategy for Breakfast� idea. Their proposal was that Incentives eat Culture, and Structure eats Incentives, both of which I have certainly observed in my time working in and with public sectors. I thought it was a profound sentiment and one worth considering in any program or project. Often we get caught up with the issues created by fixing behaviours through better culture, or the lack of a “light on the hill� that strategy is supposed to provide, but both can be undermined or perverted by incentives and structure. For example, an efficiency agenda will always incentivise saving money for the sake of saving money, which always kills opportunities to deliver genuine or purpose driven public good, let alone new value to the public.
Similarly, the current structure of most government departments was adopted during the NPM (New Public Management) years. It created functional segmentation of disciplines, which has led to a structural barrier to being outcomes focused. Basically, your policy people don’t walk to data, don’t talk to tech, don’t talk to program, etc etc. Collaboration is only possible with a hard won and years in the making cost centre, and cross functional engagement happens at the 11th hour (if at all) rather than from the first minute. Structures shape incentives by the function of your team, and this is most obvious when you talk to IT Departments who have been largely asked to just be efficient for the sake of efficiency, creating a huge barrier between those doing, and the policy or mandate outcomes that their department is responsible for.
This framing was VERY helpful, and I’m thankful to Ryan, Dorothy, Winter and Luke for the wonderful session 
My main talk this year focused on how to build trustworthy systems in the special context of government (slides here). I started by talking about why trust is critical for public sectors, and how trust is earned, not asked for. Public trust and confidence in public institutions is a necessary foundation for all that we administer and deliver in their name. Without trust, public sectors and governments everywhere run the risk of losing perceived and then actual legitimacy, leading to instability and chaos. I then talked about the key ingredients for trust: operating in good faith, with integrity, and as expected by the people/person we deal with. Good faith can be demonstrated in the public sector through a systemic and measurable commitment to human-centred and humane outcomes, strong governance. High integrity of gov can be demonstrated by operating in a way that is demonstrably lawful, accurate, high veracity, assured, consistently applied and appealable. Meeting public expectations of gov means reflecting public expectations, values and needs, doing no harm, being transparent and operating within relevant legal, social, moral and jurisdictional limitations of power.
I then used three use cases to apply this approach:
My final thought was we need a few additional tools in our toolbox to realise the vision and value of truly trustworthy and legitimate public services in the 21st century:
The questions submitted for my talk are below with answers 

Honestly I have found that being as open as possible helps build trust to best navigate those waters. We should be open about that balance, as much as we can be, and people don’t expect everything they say to be unthinkingly implemented, but they do expect to be heard. So open up channels for regular communication, for relationship building, for trust building, and you’ll get better policy, better services, better governance, and you’ll get more trust to deal with the things you can’t be as open about. Here is a blog post I wrote about balancing the three masters we all serve: the Government of the day, the Parliament, and the People 
By being politically neutral and having a voice for the public sector. People will always be wary of politics, but they should be able to trust their public institutions. So have a voice, demonstrate your commitment and stewardship of the best public good, and maintain that healthy separation of politics and public sector. In Canada you have that lovely bridge demonstrating the division of power. Do your part to always do the right thing, not what’s politically expedient. And ensure you talk about the work of your department directly to the public. If you are only communicating through the lens of political speeches or media releases, you will likely have a problem 
I think it is entirely reasonable for governments to ensure how they interact with companies includes requirements of openness and accountability. But it is hard to regulate behaviours in companies, some will be open by default, some won’t. But you can make certain things a requirement of contracts with companies that can at least ensure the ones who you work directly with meet the requirements of good government, good accountability, and meet the public trust test. But as above, the best way the public sector can grow trust is to have a voice of it’s own. People assume the worst of the public sector because a) it’s everyone’s favourite punching bag, and b) it has unmatched power in a society so people should have some distrust. The onus on the public sector to earn trust is higher than on companies, which is as it should be. So earn that trust by being trustworthy, rather than needing to expose the disfunction of others around us  All organisations have disfunction, and we can all learn from each other, but have confidence in our value to society.
All organisations have disfunction, and we can all learn from each other, but have confidence in our value to society.
Great question! Honestly just starting is good, but if you ask citizens what they think, then whatever you choose will be reflective of their hopes and fears. It doesn’t need to be the best one, just start. If your jurisdiction is struggling with homelessness, make that your first measure. Similarly for employment, or health indicators, or perhaps trust in government?  This “Trust in Australian Public Services� report provides a good blueprint for baselining and monitoring changes in public trust over time.
This “Trust in Australian Public Services� report provides a good blueprint for baselining and monitoring changes in public trust over time.

 Involve them in the design, delivery and oversight of such systems. Isn’t isn’t just about understanding user needs, it is about including different perspectives in the decision making and governance.
Involve them in the design, delivery and oversight of such systems. Isn’t isn’t just about understanding user needs, it is about including different perspectives in the decision making and governance.
 2) always ask the hard questions: how will this benefit the public? how will we know if it is creating harm? Use my questions from the talk as epics in yoru product/policy backlog
2) always ask the hard questions: how will this benefit the public? how will we know if it is creating harm? Use my questions from the talk as epics in yoru product/policy backlog  and 3) Take just a little time to imagine what good looks like, to connect with others who are similarly values-driven, and to always, in everything you do, try to bring about something better for people. This last one sounds fluffy, but you’d be surprised how much it influences every concrete action, plan, decision etc in your life.
and 3) Take just a little time to imagine what good looks like, to connect with others who are similarly values-driven, and to always, in everything you do, try to bring about something better for people. This last one sounds fluffy, but you’d be surprised how much it influences every concrete action, plan, decision etc in your life. Every time you create an example of genuine and valuable participatory governance, you will create a new baseline for people to build upon. Just do it.
Every time you create an example of genuine and valuable participatory governance, you will create a new baseline for people to build upon. Just do it. Drop me an email or DM!
Drop me an email or DM!I like using Catalyst Cloud to host some of my personal sites. In the past I used to use CAcert for my TLS certificates, but more recently I've been using Let's Encrypt for my TLS certificates as they're trusted in all browsers. Currently the LoadBalancer as a Service (LBaaS) in Catalyst Cloud doesn't have built in support for Let's Encrypt. I could use an apache2/nginx proxy and handle the TLS termination there and have that manage the Let's Encrypt lifecycle, but really, I'd rather use LBaaS.
So I thought I'd set about working out how to get Dehydrated (the Let's Encrypt client I've been using) to drive LBaaS (known as Octavia). I figured this would be of interest to other people using Octavia with OpenStack in general, not just Catalyst Cloud.
There's a few things you need to do. These instructions are specific to Debian:
As we're using HTTP-01 Challenge Type here, you need to have the LoadBalancer forwarding port 80 to your website to allow for the challenge response. It is good practice to have a redirect to HTTPS, here's an example virtual host for Apache:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName www.example.com
ServerAlias example.com
RewriteEngine On
RewriteRule ^/.well-known/ - [L]
RewriteRule ^/(.*)$ https://www.example.com/$1 [R=301,L]
<Location />
Require all granted
</Location>
</VirtualHost>
You all also need this in /etc/apache2/conf-enabled/letsencrypt.conf:
Alias /.well-known/acme-challenge /var/lib/dehydrated/acme-challenges
<Directory /var/lib/dehydrated/acme-challenges>
Options None
AllowOverride None
# Apache 2.x
<IfModule !mod_authz_core.c>
Order allow,deny
Allow from all
</IfModule>
# Apache 2.4
<IfModule mod_authz_core.c>
Require all granted
</IfModule>
</Directory>
And that should be all that you need to do. Now, when Dehydrated updates your certificate, it should update your LoadBalancer as well!
Sample hook.sh:deploy_cert() {
local DOMAIN="${1}" KEYFILE="${2}" CERTFILE="${3}" FULLCHAINFILE="${4}" \
CHAINFILE="${5}" TIMESTAMP="${6}"
shift 6
# File contents should be:
# export OS_PASSWORD='your password in here'
. /etc/dehydrated/catalystcloud/password
# OpenRC file from the Catalyst Cloud dashboard
. /etc/dehydrated/catalystcloud/openrc.sh --no-token
# UUID of the LoadBalancer to be managed
LB_LISTENER='xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx'
# Barbican uses P12 files, we need to make one.
P12=$(readlink -f $KEYFILE \
| sed -E 's/privkey-([0-9]+)\.pem/barbican-\1.p12/')
openssl pkcs12 -export -inkey $KEYFILE -in $CERTFILE -certfile \
$FULLCHAINFILE -passout pass: -out $P12
# Keep track of existing certs for this domain (hopefully no more than 100)
EXISTING_URIS=$(openstack secret list --limit 100 \
-c Name -c 'Secret href' -f json \
| jq -r ".[]|select(.Name | startswith(\"$DOMAIN\"))|.\"Secret href\"")
# Upload the new cert
NOW=$(date +"%s")
openstack secret store --name $DOMAIN-$TIMESTAMP-$NOW -e base64 \
-t "application/octet-stream" --payload="$(base64 < $P12)"
NEW_URI=$(openstack secret list --name $DOMAIN-$TIMESTAMP-$NOW \
-c 'Secret href' -f value) \
|| unset NEW_URI
# Change LoadBalancer to use new cert - if the old one was the default,
# change the default. If the old one was in the SNI list, update the
# SNI list.
if [ -n "$EXISTING_URIS" ]; then
DEFAULT_CONTAINER=$(openstack loadbalancer listener show $LB_LISTENER \
-c default_tls_container_ref -f value)
for URI in $EXISTING_URIS; do
if [ "x$URI" = "x$DEFAULT_CONTAINER" ]; then
openstack loadbalancer listener set $LB_LISTENER \
--default-tls-container-ref $NEW_URI
fi
done
SNI_CONTAINERS=$(openstack loadbalancer listener show $LB_LISTENER \
-c sni_container_refs -f value | sed "s/'//g" | sed 's/^\[//' \
| sed 's/\]$//' | sed "s/,//g")
for URI in $EXISTING_URIS; do
if echo $SNI_CONTAINERS | grep -q $URI; then
SNI_CONTAINERS=$(echo $SNI_CONTAINERS | sed "s,$URI,$NEW_URI,")
openstack loadbalancer listener set $LB_LISTENER \
--sni-container-refs $SNI_CONTAINERS
fi
done
# Remove old certs
for URI in $EXISTING_URIS; do
openstack secret delete $URI
done
fi
}
HANDLER="$1"; shift
#if [[ "${HANDLER}" =~ ^(deploy_challenge|clean_challenge|sync_cert|deploy_cert|deploy_ocsp|unchanged_cert|invalid_challenge|request_failure|generate_csr|startup_hook|exit_hook)$ ]]; then
if [[ "${HANDLER}" =~ ^(deploy_cert)$ ]]; then
"$HANDLER" "$@"
fi
We’ve done this a number of times over the last decade, from OSDC to LCA. The idea is to provide a free psychologist or counsellor at an in-person conference. Attendees can do an anonymous booking by taking a stickynote (with the timeslot) from a signup sheet, and thus get a free appointment.
Many people find it difficult taking the first (very important) step towards getting professional help, and we’ve received good feedback that this approach indeed assists.
So far we’ve always focused on open source conferences. Now we’re moving into information security! First BrisSEC 2022 (Friday 29 April at the Hilton in Brisbane, QLD) and then AusCERT 2022 (10-13 May at the Star Hotel, Gold Coast QLD). The awesome and geek friendly Dr Carla Rogers will be at both events.
How does this get funded? Well, we’ve crowdfunded some, nudged sponsors, most mostly it gets picked up by the conference organisers (aka indirectly by the sponsors, mostly).
If you’re a conference organiser, or would like a particular upcoming conference to offer this service, do drop us a line and we’re happy to chase it up for you and help the organisers to make it happen. We know how to run that now.
In-person is best. But for virtual conferences, sure contact us as well.
The post Free psychologist service at conferences: April 2022 update first appeared on BlueHackers.org.The hack day didn’t go as well as I hoped, but didn’t go too badly. There was smaller attendance than hoped and the discussion was mostly about things other than FLOSS. But everyone who attended had fun and learned interesting things so generally I think it counts as a success. There was discussion on topics including military hardware, viruses (particularly Covid), rocketry, and literature. During the discussion one error in a Wikipedia page was discussed and hopefully we can get that fixed.
I think that everyone who attended will be interested in more such meetings. Overall I think this is a reasonable start to the Hack Day meetings, when I previously ran such meetings they often ended up being more social events than serious hacking events and that’s OK too.
One conclusion that we came to regarding meetings is that they should always be well announced in email and that the iCal file isn’t useful for everyone. Discussion continues on the best methods of announcing meetings but I anticipate that better email will get more attendance.
TL;DR – I’ve taken on a new role, and this blog post explains why and how I came to the decision I did  Please scroll to the bottom or see my LinkedIn page if you just want to jump to the job.
Please scroll to the bottom or see my LinkedIn page if you just want to jump to the job.
If you’re reading this blog, you probably already know that I am passionate about and professionally committed to genuine and systemic reform/renewal of the public sector. I have spent the last decade in public service, and a decade before that in the tech sector, mostly focused on how to create better government services and policies, with digital/data transformation often providing a useful means for much needed reform.
I have written extensively about the many barriers facing systemic reform of the public sector, including on my blog. I know most public servants want change, but at this exact point in time there is a pressing need to:
So when I left Service Canada, I realised I most want to focus on three key areas to address these pressing needs, to hopefully help make a real difference:
 What does a blend of participatory and representative democracy look like, that gets the best of both?
What does a blend of participatory and representative democracy look like, that gets the best of both? Rampant automation often undermines or misses the opportunity for better, more equitable, more ethical or more humane services and policies, so exploring and demonstrating the opportunities for service and workforce augmentation would be quite timely. Exploring and growing the understanding of human augmentation is also important as we will need to collectively deal with the potential implications for social cohesion when body hacking becomes more mainstream, given the human form is considered everything from sacred to irrelevant, depending on your culture and personal comfort or beliefs.
Rampant automation often undermines or misses the opportunity for better, more equitable, more ethical or more humane services and policies, so exploring and demonstrating the opportunities for service and workforce augmentation would be quite timely. Exploring and growing the understanding of human augmentation is also important as we will need to collectively deal with the potential implications for social cohesion when body hacking becomes more mainstream, given the human form is considered everything from sacred to irrelevant, depending on your culture and personal comfort or beliefs.So, having decided these are the three areas I’d like to focus on, I had to consider where could I work to explore them? Where could possibly provide the breadth of opportunities to explore, build, influence, strategise and collaborate on public sector transformation? Sadly, many departments are pushed to stay within their wheelhouse and have become highly reactive to politics, and it is hard to drive a 5 or 10 year cross portfolio and systemic transformation agenda (let alone a 50 year vision!) within the constraints of an election cycle. Ideally, we need public institutions that are stable, operationally independent and confident stewards for long term public good, but this is a chicken and egg issue.
So I decided to work from the outside for a little while. A public service sabbatical of sorts, where I can contribute my expertise in the public domain, explore and demonstrate what “good� could look like, help build the demand and ambition for change (with executives, politics and the public), participate in community initiatives and grow my own experience. I plan to return to the sector to help drive systemic change when demand supports it 
I’m pleased to say that after months of considering some very interesting and exciting options across different sectors, I was approached for a role as a Strategic Advisor with AWS, working with a small team called Strategic Development that works with the public sector across Australia, New Zealand and Oceania. Our focus is on supporting public institutions to dream big and explore new horizons, to achieve long term policy outcomes and sustainable public good, and to develop genuinely transformative plans with practical roadmaps to get there. As a team of accomplished public servants, we all understand the domain and want to help support and champion the sector and all public servants  I think I can both contribute a lot and learn a lot from this role, and it gives me a strong basis to drive my three objectives.
I think I can both contribute a lot and learn a lot from this role, and it gives me a strong basis to drive my three objectives.
I will continue to work in the open, not just because it is my preference, but for peer review, collaboration and so you can all help me to keep it real and stay on track with the mission  Thanks to all those who advised me on this decision, and I hope to join a number of government advisory groups and boards where I can usefully contribute.
Thanks to all those who advised me on this decision, and I hope to join a number of government advisory groups and boards where I can usefully contribute.
Please get in touch with me on piagov [at] amazon.com if you’d like to chat about any of the above!  I’m looking forward to collaborating on ambitious and transformative initiatives that create more mission oriented, values driven, humane and participatory public sectors across the region
I’m looking forward to collaborating on ambitious and transformative initiatives that create more mission oriented, values driven, humane and participatory public sectors across the region 
In other news, my family had to return to Australia. Sick family + NZ travel policies at the time = having to move country again, but luckily the family member has recovered and we are now only a flight away from family  We decided if we were in Aus that we wanted to live somewhere glorious so we moved to Broome (WA), which has been just wonderful. I’ll be traveling for events and conferences, but am always available online and I’m looking forward to reconnecting with the Australian tech/data and public sectors after the last few years in NZ with the Canadian Government.
We decided if we were in Aus that we wanted to live somewhere glorious so we moved to Broome (WA), which has been just wonderful. I’ll be traveling for events and conferences, but am always available online and I’m looking forward to reconnecting with the Australian tech/data and public sectors after the last few years in NZ with the Canadian Government.
The March 2022 meeting went reasonably well. Everyone seemed to have fun and learn useful things about computers. After 2 hours my Internet connection dropped out which stopped the people who were using VMs from doing the tutorial. Fortunately most people seemed ready for a break so we ended the meeting. The early and abrupt ending of the meeting was a disappointment but it wasn’t too bad, the meeting would probably only have gone for another half hour otherwise.
The BigBlueButton system was shown to be effective for training when one person got confused with the Debian package configuration options for Postfix and they were able to share the window with everyone else to get advice. I was also confused by that stage.
The main feature of the meeting was training in setting up a mailserver with Postfix, here are the lecture notes for it [1]. The consensus at the end of the meeting was that people wanted more of that for the April meeting. So for the April meeting I will add to the Postfix Training to include SpamAssassin, SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. For the start of the next meeting instead of providing bare Debian installations for the VMs I’ll provide a basic Postfix/Dovecot setup so people can get straight into SpamAssassin etc.
For the May meeting training on SE Linux was requested.
Towards the end of the meeting we discussed Matrix and federated social media. LUV has a Matrix server and I can give accounts to anyone who’s involved in FOSS in the Australia and New Zealand area. For Mastodon the NZOSS Mastodon server [2] seems like a good option. I have an account there to try Mastodon, my Mastodon address is @etbe@mastodon.nzoss.nz .
We are going to make Matrix a primary communication method for the Flounder group, the room is #flounder:luv.asn.au . My Matrix address is @etbe:luv.asn.au .
We now have a mailing list see https://lists.linux.org.au/mailman/listinfo/flounder for information, the address to post to the list is flounder@lists.linux.org.au..
We also have a new URL for the blog and events. See the right sidebar for the link to the iCal file which can be connected to Google Calendar and most online calendaring systems.
We just had the first Flounder meeting which went well. Had some interesting discussion of storage technology, I learnt a few new things. Some people did the ZFS training and BTRFS training and we had lots of interesting discussion.
Andrew Pam gave a summary of new things in Linux and talked about the sites lwn.net, gamingonlinux.com, and cnx-software.com that he uses to find Linux news. One thing he talked about is the latest developments with SteamDeck which is driving Linux support in Steam games. The site protondb.com tracks Linux support in Steam games.
We had some discussion of BPF, for an introduction to that technology see the BPF lecture from LCA 2022.
The next meeting (Saturday 5th of March 1PM Melbourne time) will focus on running your own mail server which is always of interest to people who are interested in system administration and which is probably of more interest than usual because of Google forcing companies with “a legacy G Suite subscription” to transition to a more expensive “Business family” offering.
I “recently” wrote about obtaining a new (to me, actually quite old) computer over in The Apple Power Macintosh 7200/120 PC Compatible (Part 1). This post is a bit of a detour, but may help others understand why some images they download from the internet don’t work.
Disk partitioning is (of course) a way to divide up a single disk into multiple volumes (partitions) for different uses. While the idea is similar, computer platforms over the ages have done this in a variety of different ways, with varying formats on disk, and varying limitations. The ones that you’re most likely to be familiar with are the MBR partitioning scheme (from the IBM PC), and the GPT partitioning scheme (common for UEFI systems such as the modern PC and Mac). One you’re less likely to be familiar with is the Apple Partition Map scheme.
The way all IBM PCs and compatibles worked from the introduction of MS-DOS 2.0 in 1983 until some time after 2005 was the Master Boot Record partitioning scheme. It was outrageously simple: of the first 512 byte sector of a disk, the first 446 bytes was for the bootstrapping code (the “boot sector”), the last 2 bytes were for the magic two bytes telling the BIOS this disk was bootable, and the other 64 bytes were four entries of 16 bytes, each describing a disk partition. The Wikipedia page is a good overview of what it all looks like. Since “four partitions should be enough for anybody” wasn’t going to last, DOS 3.2 introduced “extended partitions” which was just using one of those 4 partitions as another similar data structure that could point to more partitions.
In the 1980s (similar to today), the Macintosh was, of course, different. The Apple Partition Map is significantly more flexible than the MBR on PCs. For a start, you could have more than four partitions! You could actually have a lot more than four partitions, as the Apple Partition Map is a single 512-byte sector for each partition, and the partition map is itself a partition. Instead of being block 0 (like the MBR is), it actually starts at block 1, and is contiguous (The Driver Descriptor Record is what’s at block 0). So, once created, it’s hard to extend. Typically it’d be created as 64×512-byte entries, for 32kb… which turns out is actually about enough for anyone.
The Inside Macintosh reference on the SCSI Manager goes through more detail as to these structures. If you’re wondering what language all the coding examples are in, it’s Pascal – which was fairly popular for writing Macintosh applications in back in the day.
But the actual partition map isn’t the “interesting” part of all this (and yes, the quotation marks are significant here), because Macs are pretty darn finicky about what disks to boot off, which gets to be interesting if you’re trying to find a CD-ROM image on the internet from which to boot, and then use to install an Operating System from.
… the preferred programming language changes.
I never programmed a 1980s Macintosh actually in the 1980s. It was sometime in the early 1990s that I first experienced Microsoft Basic for the Macintosh. I’d previously (unknowingly at the time as it was branded Commodore) experienced Microsoft BASIC on the Commodore 16, Commodore 64, and even the Apple ][, but the Macintosh version was something else. It let you do some pretty neat things such as construct a GUI with largely the same amount of effort as it took to construct a Text based UI on the micros I was familiar with.
Okay, to be fair, I’d also dabbled in Microsoft QBasic that came bundled with MS-DOS of the era, which let you do a whole bunch of graphics – so you could theoretically construct a GUI with it. Something I did attempt to do. Programming on the Mac was so much easier to construct a GUI.
Of course, Microsoft Basic wasn’t the preferred way to program on the Macintosh. At that time it was largely Pascal, with C being something that also existed – but you were going to see Pascal in Inside Macintosh. It was probably somewhat fortuitous that I’d poked at Pascal a bit as something alternate to look at in the high school computing classes. I can only remember using TurboPascal on DOS systems and never actually writing Pascal on the Macintosh.
By the middle part of the 1990s though, I was firmly incompetently writing C on the Mac. No doubt the quality of my code increased after I’d done some university courses actually covering the language rather than the only practical way I had to attempt to write anything useful being looking at Inside Macintosh examples in Pascal and “C for Dummies” which was very not-Macintosh. Writing C on UNIX/Linux was a lot easier – everything was made for it, including Actual Documentation!
Anyway, in the early 2000s I ran MacOS X for a bit on my white iBook G3, and did a (very) small amount of any GUI / Project Builder (the precursor to Xcode) related development – instead largely focusing on command line / X11 things. The latest coolness being to use Objective-C to program applications (unless you were bringing over your Classic MacOS Carbon based application, then you could still write C). Enter some (incompetent) Objective-C coding!
Then Apple went to x86, so the hardware ceased being interesting, and I had no reason to poke at it even as a side effect of having hardware that could run the software stack. Enter a long-ass time of Debian, Ubuntu, and Fedora on laptops.
Come 2022 though, and (for reasons I should really write up), I’m poking at a Mac again and it’s now Swift as the preferred way to write apps. So, I’m (incompetently) hacking away at Swift code. I have to admit, it’s pretty nice. I’ve managed to be somewhat productive in a relative short amount of time, and all the affordances in the language gear towards the kind of safety that is a PITA when coding in C.
So this is my WIP utility to be able to import photos from a Shotwell database into the macOS Photos app:

There’s a lot of rough edges and unknowns left, including how to actually do the import (it looks like there’s going to be Swift code doing AppleScript things as the PhotoKit API is inadequate). But hey, some incompetent hacking in not too much time has a kind-of photo browser thing going on that feels pretty snappy.
Recently I read Michael Snoyman’s post on combining Axum, Hyper, Tonic and Tower. While his solution worked, it irked me – it seemed like there should be a much tighter solution possible.
I can deep dive into the code in a later post perhaps, but I think there are four points of difference. One, since the post was written Axum has started boxing its routes : so the enum dispatch approach taken, which delivers low overheads actually has no benefits today.
Two, while writing out the entire type by hand has some benefits, async code is much more pithy.
Thirdly, the code in the post is entirely generic, except the routing function itself.
And fourth, the outer Service<AddrStream> is an unnecessary layer to abstract over: given the similar constraints – the inner Service must take Request<..>, it is possible to just not use a couple of helpers and instead work directly with Service<Request...>.
So, onto a pithier version.
First, the app server code itself.
use std::{convert::Infallible, net::SocketAddr};
use axum::routing::get;
use hyper::{server::conn::AddrStream, service::make_service_fn};
use hyper::{Body, Request};
use tonic::async_trait;
use demo::echo_server::{Echo, EchoServer};
use demo::{EchoReply, EchoRequest};
struct MyEcho;
#[async_trait]
impl Echo for MyEcho {
async fn echo(
&self,
request: tonic::Request<EchoRequest>,
) -> Result<tonic::Response<EchoReply>, tonic::Status> {
Ok(tonic::Response::new(EchoReply {
message: format!("Echoing back: {}", request.get_ref().message),
}))
}
}
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() {
let addr = SocketAddr::from(([0, 0, 0, 0], 3000));
let axum_service = axum::Router::new().route("/", get(|| async { "Hello world!" }));
let grpc_service = tonic::transport::Server::builder()
.add_service(EchoServer::new(MyEcho))
.into_service();
let both_service =
demo_router::Router::new(axum_service, grpc_service, |req: &Request<Body>| {
Ok::<bool, Infallible>(
req.headers().get("content-type").map(|x| x.as_bytes())
== Some(b"application/grpc"),
)
});
let make_service = make_service_fn(move |_conn: &AddrStream| {
let both_service = both_service.clone();
async { Ok::<_, Infallible>(both_service) }
});
let server = hyper::Server::bind(&addr).serve(make_service);
if let Err(e) = server.await {
eprintln!("server error: {}", e);
}
}
Note the Router: it takes the two services and Fn to determine which to use on any given request. Then we just drop that composed service into make_service_fn and we’re done.
Next up we have the Router implementation. This is generic across any two Service<Request<...>> types as long as they are both Into<Bytes> for their Data, and Into<Box<dyn Error>> for errors.
use std::{future::Future, pin::Pin, task::Poll};
use http_body::combinators::UnsyncBoxBody;
use hyper::{body::HttpBody, Body, Request, Response};
use tower::Service;
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct Router<First, Second, F> {
first: First,
second: Second,
discriminator: F,
}
impl<First, Second, F> Router<First, Second, F> {
pub fn new(first: First, second: Second, discriminator: F) -> Self {
Self {
first,
second,
discriminator,
}
}
}
impl<First, Second, FirstBody, FirstBodyError, SecondBody, SecondBodyError, F, FErr>
Service<Request<Body>> for BinaryRouter<First, Second, F>
where
First: Service<Request<Body>, Response = Response<FirstBody>>,
First::Error: Into<Box<dyn std::error::Error + Send + Sync>> + 'static,
First::Future: Send + 'static,
First::Response: 'static,
Second: Service<Request<Body>, Response = Response<SecondBody>>,
Second::Error: Into<Box<dyn std::error::Error + Send + Sync>> + 'static,
Second::Future: Send + 'static,
Second::Response: 'static,
F: Fn(&Request<Body>) -> Result<bool, FErr>,
FErr: Into<Box<dyn std::error::Error + Send + Sync>> + Send + 'static,
FirstBody: HttpBody<Error = FirstBodyError> + Send + 'static,
FirstBody::Data: Into<bytes::Bytes>,
FirstBodyError: Into<Box<dyn std::error::Error + Send + Sync>> + 'static,
SecondBody: HttpBody<Error = SecondBodyError> + Send + 'static,
SecondBody::Data: Into<bytes::Bytes>,
SecondBodyError: Into<Box<dyn std::error::Error + Send + Sync>> + 'static,
{
type Response = Response<
UnsyncBoxBody<
<hyper::Body as HttpBody>::Data,
Box<dyn std::error::Error + Send + Sync + 'static>,
>,
>;
type Error = Box<dyn std::error::Error + Send + Sync + 'static>;
type Future =
Pin<Box<dyn Future<Output = Result<Self::Response, Self::Error>> + Send + 'static>>;
fn poll_ready(
&mut self,
cx: &mut std::task::Context<'_>,
) -> std::task::Poll<Result<(), Self::Error>> {
match self.first.poll_ready(cx) {
Poll::Ready(Ok(())) => match self.second.poll_ready(cx) {
Poll::Ready(Ok(())) => Poll::Ready(Ok(())),
Poll::Ready(Err(e)) => Poll::Ready(Err(e.into())),
Poll::Pending => Poll::Pending,
},
Poll::Ready(Err(e)) => Poll::Ready(Err(e.into())),
Poll::Pending => Poll::Pending,
}
}
fn call(&mut self, req: Request<Body>) -> Self::Future {
let discriminant = { (self.discriminator)(&req) };
let (first, second) = if matches!(discriminant, Ok(false)) {
(Some(self.first.call(req)), None)
} else if matches!(discriminant, Ok(true)) {
(None, Some(self.second.call(req)))
} else {
(None, None)
};
let f = async {
Ok(match discriminant.map_err(Into::into)? {
true => second
.unwrap()
.await
.map_err(Into::into)?
.map(|b| b.map_data(Into::into).map_err(Into::into).boxed_unsync()),
false => first
.unwrap()
.await
.map_err(Into::into)?
.map(|b| b.map_data(Into::into).map_err(Into::into).boxed_unsync()),
})
};
Box::pin(f)
}
}
Interesting things here – I use boxed_unsync to abstract over the body concrete type, and I implement the future using async code rather than as a separate struct. It becomes much smaller even after a few bits of extra type constraining.
One thing that flummoxed me for a little was the need to capture the future for the underlying response outside of the async block. Failing to do so provokes a 'static requirement which was tricky to debug. Fortunately there is a bug on making this easier to diagnose in rustc already. The underlying problem is that if you create the async block, and then dereference self, the type for impl of .first has to live an arbitrary time. Whereas by capturing the future immediately, only the impl of the future has to live an arbitrary time, and that doesn’t then require changing the signature of the function.
This is almost worth turning into a crate – I couldn’t see an existing one when I looked, though it does end up rather small – < 100 lines. What do you all think?
The first meeting will start at 1PM Australian Eastern time (Melbourne/Sydney) which is +1100 on Saturday the 5th of February.
I will start the video chat an hour early in case someone makes a timezone mistake and gets there an hour before it starts. If anyone else joins early we will have random chat until the start time (deliberately avoiding topics worthy of the main meeting). The link http://b.coker.com.au will redirect to the meeting URL on the day.
The first scheduled talk is a summary and discussion of free software related news. Anyone who knows of something new that excites them is welcome to speak about it.
The main event is discussion of storage technology and hands-on training on BTRFS and ZFS for those who are interested. Here are the ZFS training notes and here are the BTRFS training notes. Feel free to do the training exercises on your own VM before the meeting if you wish.
Then discussion of the future of the group and the use of FOSS social media. While social media is never going to be compulsory some people will want to use it to communicate and we could run some servers for software that is considered good (lots of server capacity is available).
Finally we have to plan future meetings and decide on which communication methods are desired.
The BBB instance to be used for the video conference is sponsored by NZOSS and Catalyst Cloud.
I’m attending the https://linux.conf.au/ conference online this weekend, which is always a good opportunity for some sideline hacking.
I found something boneheaded doing that today.
There have been a few times while inventing the OpenHMD Rift driver where I’ve noticed something strange and followed the thread until it made sense. Sometimes that leads to improvements in the driver, sometimes not.
In this case, I wanted to generate a graph of how long the computer vision processing takes – from the moment each camera frame is captured until poses are generated for each device.
To do that, I have a some logging branches that output JSON events to log files and I write scripts to process those. I used that data and produced:
Two things caught my eye in this graph. The first is the way the baseline latency (pink lines) increases from ~20ms to ~58ms. The 2nd is the quantisation effect, where pose latencies are clearly moving in discrete steps.
Neither of those should be happening.
Camera frames are being captured from the CV1 sensors every 19.2ms, and it takes that 17-18ms for them to be delivered across the USB. Depending on how many IR sources the cameras can see, figuring out the device poses can take a different amount of time, but the baseline should always hover around 17-18ms because the fast “device tracking locked” case take as little as 1ms.
Did you see me mention 19.2ms as the interframe period? Guess what the spacing on those quantisation levels are in the graph? I recognised it as implying that something in the processing is tied to frame timing when it should not be.
This 2nd graph helped me pinpoint what exactly was going on. This graph is cut from the part of the session where the latency has jumped up. What it shows is a ~1 frame delay between when the frame is received (frame-arrival-finish-local-ts) before the initial analysis even starts!
That could imply that the analysis thread is just busy processing the previous frame and doesn’t get start working on the new one yet – but the graph says that fast analysis is typically done in 1-10ms at most. It should rarely be busy when the next frame arrives.
This is where I found the bone headed code – a rookie mistake I wrote when putting in place the image analysis threads early on in the driver development and never noticed.
There are 3 threads involved:
These 3 threads communicate using frame worker queues passing frames between each other. Each analysis thread does this pseudocode:
while driver_running:
Pop a frame from the queue
Process the frame
Sleep for new frame notification
The problem is in the 3rd line. If the driver is ever still processing the frame in line 2 when a new frame arrives – say because the computer got really busy – the thread sleeps anyway and won’t wake up until the next frame arrives. At that point, there’ll be 2 frames in the queue, but it only still processes one – so the analysis gains a 1 frame latency from that point on. If it happens a second time, it gets later by another frame! Any further and it starts reclaiming frames from the queues to keep the video capture thread fed – but it only reclaims one frame at a time, so the latency remains!
The fix is simple:
while driver_running:
Pop a frame
Process the frame
if queue_is_empty():
sleep for new frame notification
Doing that for both the fast and long analysis threads changed the profile of the pose latency graph completely.
This is a massive win! To be clear, this has been causing problems in the driver for at least 18 months but was never obvious from the logs alone. A single good graph is worth a thousand logs.
What does this mean in practice?
The way the fusion filter I’ve built works, in between pose updates from the cameras, the position and orientation of each device are predicted / updated using the accelerometer and gyro readings. Particularly for position, using the IMU for prediction drifts fairly quickly. The longer the driver spends ‘coasting’ on the IMU, the less accurate the position tracking is. So, the sooner the driver can get a correction from the camera to the fusion filter the less drift we’ll get – especially under fast motion. Particularly for the hand controllers that get waved around.
Poses are now being updated up to 40ms earlier and the baseline is consistent with the USB transfer delay.
You can also visibly see the effect of the JPEG decoding support I added over Christmas. The ‘red’ camera is directly connected to USB3, while the ‘khaki’ camera is feeding JPEG frames over USB2 that then need to be decoded, adding a few ms delay.
The latency reduction is nicely visible in the pose graphs, where the ‘drop shadow’ effect of pose updates tailing fusion predictions largely disappears and there are fewer large gaps in the pose observations when long analysis happens (visible as straight lines jumping from point to point in the trace):
Yes, the blog is still on. January 2004 I moved to WordPress, and it is still here January 2022. I didn’t write much last year (neither here, not experimenting with the Hey blog). I didn’t post anything to Instagram last year either from what I can tell, just a lot of stories.
August 16 2021, I realised I was 1,000 days till May 12 2024, which is when I become 40. As of today, that leads 850 days. Did I squander the last 150 days? I’m back to writing almost daily in the Hobonichi Techo (I think last year and the year before were mostly washouts; I barely scribbled anything offline).
I got a new Apple Watch Series 7 yesterday. I can say I used the Series 4 well (79% battery life), purchased in the UK when I broke my Series 0 in Edinburgh airport.
TripIt stats for last year claimed 95 days on the road. This is of course, a massive joke, but I’m glad I did get to visit London, Lisbon, New York, San Francisco, Los Angeles without issue. I spent a lot of time in Kuantan, a bunch of Langkawi trips, and also, I stayed for many months at the Grand Hyatt Kuala Lumpur during the May lockdowns (I practically stayed there all lockdown).
With 850 days to go till I’m 40, I have plenty I would like to achieve. I think I’ll write a lot more here. And elsewhere. Get back into the habit of doing. And publishing by learning and doing. No fear. Not that I wasn’t doing, but its time to be prolific with what’s been going on.
On the 6th October, a public consultation about a Digital Strategy for Aotearoa New Zealand opened for feedback and participation. Contributions close 10th November, and I thought I’d share a few thoughts, and encourage you all to contribute  I also wrote a paper on two major issues I see facing us here, Service Delivery and Public Trust in New Zealand Aotearoa: a Discussion Paper which might be of interest, I hope these thoughts are helpful and I want to thank DIA and MBIE for engaging so openly on this topic. It provides a good opportunity to create a genuinely bold and visionary approach that serves us well into the future
I also wrote a paper on two major issues I see facing us here, Service Delivery and Public Trust in New Zealand Aotearoa: a Discussion Paper which might be of interest, I hope these thoughts are helpful and I want to thank DIA and MBIE for engaging so openly on this topic. It provides a good opportunity to create a genuinely bold and visionary approach that serves us well into the future 
The discussion paper paints a vision of Aotearoa New Zealand being a world leading digital nation built on trust, known for the ethical deployment of new technologies, and it defines success as predominantly:Â
The rest of the paper however, seems to focus almost mostly on the productivity goal, for example, talking about trust as “We have the right foundations to sell our products and services to the world with confidence, while all New Zealanders embrace the digital future because they feel safe and secureâ€�. “Embracing the digital future” ignores that we are in a digital present, and ignores also the current stress, fears and uncertainty that many feel, as they are actively gamed online today. Ethical deployment of tech also needs defining, because what you can’t describe, measure or monitor for will not lead to an ethical outcome. For instance, to my mind, ethical means all decisions or actions taken are traceable back to a legal authority, are explainable, and are easily appealable by the people affected, and independently auditable. Ethical means a program, policy, service, etc demonstrably and measurable contributes to wellbeing, and does no harm. Define it how you wish, but defining it is critical to assuring it 
This paper seems very focused on “digitalâ€� as just the adopting of technologies, but doesn’t really address what is needed to live well in a digital age. I would hope the draft digital strategy that is developed as a result of this engagement addresses the fact that to be meaningful, a digital strategy for Aotearoa New Zealand needs to address the paradigm shifts, future state, and the necessary systemic and structural changes needed to live well and thrive in a digital age.Â
Whatever measures are created (there should be clear measures for all three themes) must be applied to all initiatives. If a department is funded to do something in the trust theme, then they must be accountable for demonstrating how that initiative contributes to the trust measures, as well as being accountable for how that initiative contributes to Wellbeing measures. Otherwise we’ll continue to see a lack of systemic pressure to drive the intended outcomes.
I suggest adding the following, which are critical components for a digitally inclusive, equitable and consistent ecosystem.
To address social exclusion, I suggest you adopt all the recommendations from the Citizen Advice Bureau recent submission here https://www.cab.org.nz/assets/Documents/Face-to-Face-with-Digital-Exclusion-/FINAL-CABNZ-collated-submission-to-Petitions-Committee.pdf.
There needs to be strategic investment in computer science as an area of hypothesis led research, looking at national issues. The regular use of computer science as just a means to commercialise something misses the critical need for research into bleeding edge and emergent opportunities/challenges as a critical pipeline for innovation across all sectors. Such research and input is also critical to inform government policies, services, infrastructure and regulation in an evidence based and non commercially motivated way.
Once again time has passed, and another update on Oculus Rift support feels due! As always, it feels like I’ve been busy with work and not found enough time for Rift CV1 hacking. Nevertheless, looking back over the history since I last wrote, there’s quite a lot to tell!
In general, the controller tracking is now really good most of the time. Like, wildly-swing-your-arms-and-not-lose-track levels (most of the time). The problems I’m hunting now are intermittent and hard to identify in the moment while using the headset – hence my enthusiasm over the last updates for implementing stream recording and a simulation setup. I’ll get back to that.
Since I last wrote, the tracking improvements have mostly come from identifying and rejecting incorrect measurements. That is, if I have 2 sensors active and 1 sensor says the left controller is in one place, but the 2nd sensor says it’s somewhere else, we’ll reject one of those – choosing the pose that best matches what we already know about the controller. The last known position, the gravity direction the IMU is detecting, and the last known orientation. The tracker will now also reject observations for a time if (for example) the reported orientation is outside the range we expect. The IMU gyroscope can track the orientation of a device for quite a while, so can be relied on to identify strong pose priors once we’ve integrated a few camera observations to get the yaw correct.
It works really well, but I think improving this area is still where most future refinements will come. That and avoiding incorrect pose extractions in the first place.
The above plot is a sample of headset tracking, showing the extracted poses from the computer vision vs the pose priors / tracking from the Kalman filter. As you can see, there are excursions in both position and orientation detected from the video, but these are largely ignored by the filter, producing a steadier result.
This plot shows the left controller being tracked during a Beat Saber session. The controller tracking plot is quite different, because controllers move a lot more than the headset, and have fewer LEDs to track against. There are larger gaps here in the timeline while the vision re-acquires the device – and in those gaps you can see the Kalman filter interpolating using IMU input only (sometimes well, sometimes less so).
Another nice thing I did is changes in the way the search for a tracked device is made in a video frame. Before starting looking for a particular device it always now gets the latest estimate of the previous device position from the fusion filter. Previously, it would use the estimate of the device pose as it was when the camera exposure happened – but between then and the moment we start analysis more IMU observations and other camera observations might arrive and be integrated into the filter, which will have updated the estimate of where the device was in the frame.
This is the bit where I think the Kalman filter is particularly clever: Estimates of the device position at an earlier or later exposure can improve and refine the filter’s estimate of where the device was when the camera captured the frame we’re currently analysing! So clever. That mechanism (lagged state tracking) is what allows the filter to integrate past tracking observations once the analysis is done – so even if the video frame search take 150ms (for example), it will correct the filter’s estimate of where the device was 150ms in the past, which ripples through and corrects the estimate of where the device is now.
To improve the identification of devices better, I measured the actual angle from which LEDs are visible (about 75 degrees off axis) and measured the size. The pose matching now has a better idea of which LEDs should be visible for a proposed orientation and what pixel size we expect them to have at a particular distance.
I fixed a bug in the output pose smoothing filter where it would glitch as you turned completely around and crossed the point where the angle jumps from +pi to -pi or vice versa.
I got a wide-angle hi-res webcam and took photos of a checkerboard pattern through the lens of my headset, then used OpenCV and panotools to calculate new distortion and chromatic aberration parameters for the display. For me, this has greatly improved. I’m waiting to hear if that’s true for everyone, or if I’ve just fixed it for my headset.
Config blocks! A long time ago, I prototyped code to create a persistent OpenHMD configuration file store in ~/.config/openhmd. The rift-kalman-filter branch now uses that to store the configuration blocks that it reads from the controllers. The first time a controller is seen, it will load the JSON calibration block as before, but it will now store it in that directory – removing a multiple second radio read process on every subsequent startup.
To go along with that, I have an experimental rift-room-config branch that creates a rift-room-config.json file and stores the camera positions after the first startup. I haven’t pushed that to the rift-kalman-filter branch yet, because I’m a bit worried it’ll cause surprising problems for people. If the initial estimate of the headset pose is wrong, the code will back-project the wrong positions for the cameras, which will get written to the file and cause every subsequent run of OpenHMD to generate bad tracking until the file is removed. The goal is to have a loop that monitors whether the camera positions seem stable based on the tracking reports, and to use averaging and resetting to correct them if not – or at least to warn the user that they should re-run some (non-existent) setup utility.
The final big ticket item was a rewrite of how the USB video frame capture thread collects pixels and passes them to the analysis threads. This now does less work in the USB thread, so misses fewer frames, and also I made it so that every frame is now searched for LEDs and blob identities tracked with motion vectors, even when no further analysis will be done on that frame. That means that when we’re running late, it better preserves LED blob identities until the analysis threads can catch up – increasing the chances of having known LEDs to directly find device positions and avoid searching. This rewrite also opened up a path to easily support JPEG decode – which is needed to support Rift Sensors connected on USB 2.0 ports.
I mentioned the recording simulator continues to progress. Since the tracking problems are now getting really tricky to figure out, this tool is becoming increasingly important. So far, I have code in OpenHMD to record all video and tracking data to a .mkv file. Then, there’s a simulator tool that loads those recordings. Currently it is capable of extracting the data back out of the recording, parsing the JSON and decoding the video, and presenting it to a partially implemented simulator that then runs the same blob analysis and tracking OpenHMD does. The end goal is a Godot based visualiser for this simulation, and to be able to step back and forth through time examining what happened at critical moments so I can improve the tracking for those situations.
To make recordings, there’s the rift-debug-gstreamer-record branch of OpenHMD. If you have GStreamer and the right plugins (gst-plugins-good) installed, and you set env vars like this, each run of OpenHMD will generate a recording in the target directory (make sure the target dir exists):
export OHMD_TRACE_DIR=/home/user/openhmd-traces/
export OHMD_FULL_RECORDING=1
The next things that are calling to me are to improve the room configuration estimation and storage as mentioned above – to detect when the poses a camera is reporting don’t make sense because it’s been bumped or moved.
I’d also like to add back in tracking of the LEDS on the back of the headset headband, to support 360 tracking. I disabled those because they cause me trouble – the headband is adjustable relative to the headset, so the LEDs don’t appear where the 3D model says they should be and that causes jitter and pose mismatches. They need special handling.
One last thing I’m finding exciting is a new person taking an interest in Rift S and starting to look at inside-out tracking for that. That’s just happened in the last few days, so not much to report yet – but I’ll be happy to have someone looking at that while I’m still busy over here in CV1 land!
As always, if you have any questions, comments or testing feedback – hit me up at thaytan@noraisin.net or on @thaytan Twitter/IRC.
Thank you to the kind people signed up as Github Sponsors for this project!
For a long time computer manufacturers have tried to differentiate themselves and their products from their competitors with fancy names with odd capitalisation and spelling. But as an author, using these names does a disservice to the reader: how are they to know that DEC is pronounced as if it was written Dec ("deck").
It's time we pushed back, and wrote for our readers, not for corporations.
It's time to use standard English rules for these Corporate Fancy Names. Proper names begin with a capital, unlike "ciscoSystems®" (so bad that Cisco itself moved away from it). Words are separated by spaces, so "Cisco Systems". Abbreviations and acronyms are written in lower case if they are pronounced as a word, in upper case if each letter is pronounced: so "ram" and "IBM®".
So from here on in I'll be using the following:
I'd encourage you to try this in your own writing. It does look odd for the first time, but the result is undeniably more readable. If we are not writing to be understood by our audience then we are nothing more than an unpaid member of some corporation's marketing team.
I gave the talk On The Use and Misuse of Decorators as part of PyConline AU 2021, the second in annoyingly long sequence of not-in-person PyCon AU events. Here’s some code samples that you might be interested in:
@property implementationThis shows a demo of @property-style getters. Setters are left as an exercise :)
def demo_property(f):
f.is_a_property = True
return f
class HasProperties:
def __getattribute__(self, name):
ret = super().__getattribute__(name)
if hasattr(ret, "is_a_property"):
return ret()
else:
return ret
class Demo(HasProperties):
@demo_property
def is_a_property(self):
return "I'm a property"
def is_a_function(self):
return "I'm a function"
a = Demo()
print(a.is_a_function())
print(a.is_a_property)
@run (The Scoped Block)@run is a decorator that will run the body of the decorated function, and then store the result of that function in place of the function’s name. It makes it easier to assign the results of complex statements to a variable, and get the advantages of functions having less leaky scopes than if or loop blocks.
def run(f):
return f()
@run
def hello_world():
return "Hello, World!"
print(hello_world)
@apply (Multi-line stream transformers)def apply(transformer, iterable_):
def _applicator(f):
return(transformer(f, iterable_))
return _applicator
@apply(map, range(100)
def fizzbuzzed(i):
if i % 3 == 0 and i % 5 == 0:
return "fizzbuzz"
if i % 3 == 0:
return "fizz"
elif i % 5 == 0:
return "buzz"
else:
return str(i)
def html(f):
builder = HtmlNodeBuilder("html")
f(builder)
return builder.build()
class HtmlNodeBuilder:
def __init__(self, tag_name):
self.tag_name = tag_name
self.nodes = []
def node(self, f):
builder = HtmlNodeBuilder(f.__name__)
f(builder)
self.nodes.append(builder.build())
def text(self, text):
self.nodes.append(text)
def build(self):
nodes = "\n".join(self.nodes)
return f"<{self.tag_name}>\n{nodes}\n</{self.tag_name}>"
@html
def document(b):
@b.node
def head(b):
@b.node
def title(b):
b.text("Hello, World!")
@b.node
def body(b):
for i in range(10, 0, -1):
@b.node
def p(b):
b.text(f"{i}")
This is an incomplete implementation of a code registry for handling simple text processing tasks:
```python
def register(self, input, output):
def _register_code(f):
self.registry[(input, output)] = f
return f
return _register_code
in_type = (iterable[str], (WILDCARD, ) out_type = (Counter, (WILDCARD, frequency))
@registry.register(in_type, out_type) def count_strings(strings):
return Counter(strings)
@registry.register( (iterable[str], (WILDCARD, )), (iterable[str], (WILDCARD, lowercase)) ) def words_to_lowercase(words): …
@registry.register( (iterable[str], (WILDCARD, )), (iterable[str], (WILDCARD, no_punctuation)) ) def words_without_punctuation(words): …
def find_steps( self, input_type, input_attrs, output_type, output_attrs ):
hand_wave()
def give_me(self, input, output_type, output_attrs):
steps = self.find_steps(
type(input), (), output_type, output_attrs
)
temp = input
for step in steps:
temp = step(temp)
return temp
A while ago, I wrote a post about how to build and test my Oculus CV1 tracking code in SteamVR using the SteamVR-OpenHMD driver. I have updated those instructions and moved them to https://noraisin.net/diary/?page_id=1048 – so use those if you’d like to try things out.
The pandemic continues to sap my time for OpenHMD improvements. Since my last post, I have been working on various refinements. The biggest visible improvements are:
Adding velocity and acceleration reporting is needed in VR apps that support throwing things. It means that throwing objects and using gravity-grab to fetch objects works in Half-Life: Alyx, making it playable now.
The rewrite to the pose transformation code fixed problems where the rotation of controller models in VR didn’t match the rotation applied in the real world. Controllers would appear attached to the wrong part of the hand, and rotate around the wrong axis. Movements feel more natural now.
My focus going forward is on fixing glitches that are caused by tracking losses or outliers. Those problems happen when the computer vision code either fails to match what the cameras see to the device LED models, or when it matches incorrectly.
Tracking failure leads to the headset view or controllers ‘flying away’ suddenly. Incorrect matching leads to controllers jumping and jittering to the wrong pose, or swapping hands. Either condition is very annoying.
Unfortunately, as the tracking has improved the remaining problems get harder to understand and there is less low-hanging fruit for improvement. Further, when the computer vision runs at 52Hz, it’s impossible to diagnose the reasons for a glitch in real time.
I’ve built a branch of OpenHMD that uses GStreamer to record the CV1 camera video, plus IMU and tracking logs into a video file.
To go with those recordings, I’ve been working on a replay and simulation tool, that uses the Godot game engine to visualise the tracking session. The goal is to show, frame-by-frame, where OpenHMD thought the cameras, headset and controllers were at each point in the session, and to be able to step back and forth through the recording.
Right now, I’m working on the simulation portion of the replay, that will use the tracking logs to recreate all the poses.
I’ve been asked more than once what it was like at the beginning of Ubuntu, before it was a company, when an email from someone I’d never heard of came into my mailbox.
We’re coming up on 20 years now since Ubuntu was founded, and I had cause to do some spelunking into IMAP archives recently… while there I took the opportunity to grab the very first email I received.
The Ubuntu long shot succeeded wildly. Of course, we liked to joke about how spammy those emails where: cold-calling a raft of Debian developers with job offers, some of them were closer to phishing attacks :). This very early one – I was the second employee (though I started at 4 days a week to transition my clients gradually) – was less so.
I think its interesting though to note how explicit a gamble this was framed as: a time limited experiment, funded for a year. As the company scaled this very rapidly became a hiring problem and the horizon had to be pushed out to 2 years to get folk to join.
And of course, while we started with arch in earnest, we rapidly hit significant usability problems, some of which were solvable with porcelain and shallow non-architectural changes, and we built initially patches, and then the bazaar VCS project to tackle those. But others were not: for instance, I recall exceeding the 32K hard link limit on ext3 due to a single long history during a VCS conversion. The sum of these challenges led us to create the bzr project, a ground up rethink of our version control needs, architecture, implementation and user-experience. While ultimately git has conquered all, bzr had – still has in fact – extremely loyal advocates, due to its laser sharp focus on usability.
Anyhow, here it is: one of the original no-name-here-yet, aka Ubuntu, introductory emails (with permission from Mark, of course). When I clicked through to the website Mark provided there was a link there to a fantastical website about a space tourist… not what I had expected to be reading in Adelaide during LCA 2004.
From: Mark Shuttleworth <xxx@xxx>
To: Robert Collins <xxx@xxx>
Date: Thu, 15 Jan 2004, 04:30
Tom Lord gave me your email address, I believe he’s
already sent you the email that I sent him so I’m sure
you have some background.
In short, I am going to fund some open source
development for a year. This is part of a new project
that I will be getting off the ground in the coming
weeks. I don’t know where it will lead, it’s flying in
the face of a stiff breeze but I think at the end of
the day it will at least fund a few very good open
source developers for a full year to work on the
projects they like most.
One of the pieces of the puzzle is high end source
code management. I’ll be looking to build an
infrastructure that will manage source code for
between 100 and 8000 open source projects (yes,
there’s a big difference between the two, I don’t know
at which end of the spectrum we will be at the end of
the year but our infrastructure will have to at least
be capable of scaling to the latter within two years)
with upwards of 2000 developers, drawing code from a
variety of sources, playing with it and spitting it
out regularly in nice packages.
Arch and Subversion seem to be the two leading
contenders for “next generation open source sccm”. I’d
be interested in your thoughts on the two of them, and
how they stack up. I’m looking to hire one person who
will lead that part of the effort. They’ll work alone
from home, and be responsible for two things. First,
extending the tool (arch or svn) in ways that help the
project. Such extensions will be released under an
open source licence, and hopefully embraced by the
tools maintainers and included in the mainline code
for the tool. And second, they will be responsible for
our large-scale implementation of SCCM, using that
tool, and building the management scripts and other
infrastructure to support such a large, and hopefully
highly automated, set of repositories.
Would you be interested in this position? What
attributes and experience do you think would make you
a great person to have on the team? What would your
salary expectation be, as a monthly figure, for a one
year contract full time?
I’m currently on your continent, well, just off it. On
Lizard Island, up North. Am headed today for Brisbane,
then on the 17th to Launceston via Melbourne. If you
happen to be on any of those stops, would you be
interested in meeting up to discuss it further?
If you’re curious you can find out a bit more about me
at www.markshuttleworth.com. This project is much
lower key than some of what you’ll find there. It’s a
very long shot indeed. But if at worst all that
happens is a bunch of open source work gets funded at
my expense I’ll feel it was money well spent.
Cheers,
Mark
=====
—
“Good judgement comes from experience, and often experience
comes from bad judgement” – Rita Mae Brown

I have always liked cryptography, and public-key cryptography in particularly. When Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) first came out in 1991, I not only started using it, also but looking at the documentation and the code to see how it worked. I created my own implementation in C using very small keys, just to better understand.
Cryptography has been running a race against both faster and cheaper computing power. And these days, with banking and most other aspects of our lives entirely relying on secure communications, it’s a very juicy target for bad actors.
About 5 years ago, the National (USA) Institute for Science and Technology (NIST) initiated a search for cryptographic algorithmic that should withstand a near-future world where quantum computers with a significant number of qubits are a reality. There have been a number of rounds, which mid 2020 saw round 3 and the finalists.
This submission caught my eye some time ago: Classic McEliece, and out of the four finalists it’s the only one that is not lattice-based [wikipedia link].
For Public Key Encryption and Key Exchange Mechanism, Prof Bill Buchanan thinks that the winner will be lattice-based, but I am not convinced.

Tiny side-track, you may wonder where does the McEleice name come from? From mathematician Robert McEleice (1942-2019). McEleice developed his cryptosystem in 1978. So it’s not just named after him, he designed it. For various reasons that have nothing to do with the mathematical solidity of the ideas, it didn’t get used at the time. He’s done plenty cool other things, too. From his Caltech obituary:
He made fundamental contributions to the theory and design of channel codes for communication systems—including the interplanetary telecommunication systems that were used by the Voyager, Galileo, Mars Pathfinder, Cassini, and Mars Exploration Rover missions.
Back to lattices, there are both unknowns (aspects that have not been studied in exhaustive depth) and recent mathematical attacks, both of which create uncertainty – in the crypto sphere as well as for business and politics. Given how long it takes for crypto schemes to get widely adopted, the latter two are somewhat relevant, particularly since cyber security is a hot topic.
Lattices are definitely interesting, but given what we know so far, it is my feeling that systems based on lattices are more likely to be proven breakable than Classic McEleice, which come to this finalists’ table with 40+ years track record of in-depth analysis. Mind that all finalists are of course solid at this stage – but NIST’s thoughts on expected developments and breakthroughs is what is likely to decide the winner. NIST are not looking for shiny, they are looking for very very solid in all possible ways.
Prof Buchanan recently published implementations for the finalists, and did some benchmarks where we can directly compare them against each other.
We can see that Classic McEleice’s key generation is CPU intensive, but is that really a problem? The large size of its public key may be more of a factor (disadvantage), however the small ciphertext I think more than offsets that disadvantage.
As we’re nearing the end of the NIST process, in my opinion, fast encryption/decryption and small cyphertext, combined with the long track record of in-depth analysis, may still see Classic McEleice come out the winner.
The post Classic McEleice and the NIST search for post-quantum crypto first appeared on Lentz family blog.Living in California, I’ve (sadly) grown accustomed to needing to keep track of our local air quality index (AQI) ratings, particularly as we live close to places where large wildfires happen every other year.
Last year, Josh and I bought a PurpleAir outdoor air quality meter, which has been great. We contribute our data to a collection of very local air quality meters, which is important, since the hilly nature of the North Bay means that the nearest government air quality ratings can be significantly different to what we experience here in Petaluma.
I recently went looking to pull my PurpleAir sensor data into my Home Assistant setup. Unfortunately, the PurpleAir API does not return the AQI metric for air quality, only the raw PM2.5/PM5/PM10 numbers. After some searching, I found a nice template sensor solution on the Home Assistant forums, which I’ve modernised by adding the AQI as a sub-sensor, and adding unique ID fields to each useful sensor, so that you can assign them to a location.
You’ll end up with sensors for raw PM2.5, the PM2.5 AQI value, the US EPA air quality category, air pressure, relative humidity and air pressure.
First up, visit the PurpleAir Map, find the sensor you care about, click “get this widget�, and then “JSON�. That will give you the URL to set as the resource key in purpleair.yaml.
In HomeAssistant, add the following line to your configuration.yaml:
sensor: !include purpleair.yaml
and then add the following contents to purpleair.yaml
- platform: rest
name: 'PurpleAir'
# Substitute in the URL of the sensor you care about. To find the URL, go
# to purpleair.com/map, find your sensor, click on it, click on "Get This
# Widget" then click on "JSON".
resource: https://www.purpleair.com/json?key={KEY_GOES_HERE}&show={SENSOR_ID}
# Only query once a minute to avoid rate limits:
scan_interval: 60
# Set this sensor to be the AQI value.
#
# Code translated from JavaScript found at:
# https://docs.google.com/document/d/15ijz94dXJ-YAZLi9iZ_RaBwrZ4KtYeCy08goGBwnbCU/edit#
value_template: >
{{ value_json["results"][0]["Label"] }}
unit_of_measurement: ""
# The value of the sensor can't be longer than 255 characters, but the
# attributes can. Store away all the data for use by the templates below.
json_attributes:
- results
- platform: template
sensors:
purpleair_aqi:
unique_id: 'purpleair_SENSORID_aqi_pm25'
friendly_name: 'PurpleAir PM2.5 AQI'
value_template: >
{% macro calcAQI(Cp, Ih, Il, BPh, BPl) -%}
{{ (((Ih - Il)/(BPh - BPl)) * (Cp - BPl) + Il)|round|float }}
{%- endmacro %}
{% if (states('sensor.purpleair_pm25')|float) > 1000 %}
invalid
{% elif (states('sensor.purpleair_pm25')|float) > 350.5 %}
{{ calcAQI((states('sensor.purpleair_pm25')|float), 500.0, 401.0, 500.0, 350.5) }}
{% elif (states('sensor.purpleair_pm25')|float) > 250.5 %}
{{ calcAQI((states('sensor.purpleair_pm25')|float), 400.0, 301.0, 350.4, 250.5) }}
{% elif (states('sensor.purpleair_pm25')|float) > 150.5 %}
{{ calcAQI((states('sensor.purpleair_pm25')|float), 300.0, 201.0, 250.4, 150.5) }}
{% elif (states('sensor.purpleair_pm25')|float) > 55.5 %}
{{ calcAQI((states('sensor.purpleair_pm25')|float), 200.0, 151.0, 150.4, 55.5) }}
{% elif (states('sensor.purpleair_pm25')|float) > 35.5 %}
{{ calcAQI((states('sensor.purpleair_pm25')|float), 150.0, 101.0, 55.4, 35.5) }}
{% elif (states('sensor.purpleair_pm25')|float) > 12.1 %}
{{ calcAQI((states('sensor.purpleair_pm25')|float), 100.0, 51.0, 35.4, 12.1) }}
{% elif (states('sensor.purpleair_pm25')|float) >= 0.0 %}
{{ calcAQI((states('sensor.purpleair_pm25')|float), 50.0, 0.0, 12.0, 0.0) }}
{% else %}
invalid
{% endif %}
unit_of_measurement: "bit"
purpleair_description:
unique_id: 'purpleair_SENSORID_description'
friendly_name: 'PurpleAir AQI Description'
value_template: >
{% if (states('sensor.purpleair_aqi')|float) >= 401.0 %}
Hazardous
{% elif (states('sensor.purpleair_aqi')|float) >= 301.0 %}
Hazardous
{% elif (states('sensor.purpleair_aqi')|float) >= 201.0 %}
Very Unhealthy
{% elif (states('sensor.purpleair_aqi')|float) >= 151.0 %}
Unhealthy
{% elif (states('sensor.purpleair_aqi')|float) >= 101.0 %}
Unhealthy for Sensitive Groups
{% elif (states('sensor.purpleair_aqi')|float) >= 51.0 %}
Moderate
{% elif (states('sensor.purpleair_aqi')|float) >= 0.0 %}
Good
{% else %}
undefined
{% endif %}
entity_id: sensor.purpleair
purpleair_pm25:
unique_id: 'purpleair_SENSORID_pm25'
friendly_name: 'PurpleAir PM 2.5'
value_template: "{{ state_attr('sensor.purpleair','results')[0]['PM2_5Value'] }}"
unit_of_measurement: "μg/m3"
entity_id: sensor.purpleair
purpleair_temp:
unique_id: 'purpleair_SENSORID_temperature'
friendly_name: 'PurpleAir Temperature'
value_template: "{{ state_attr('sensor.purpleair','results')[0]['temp_f'] }}"
unit_of_measurement: "°F"
entity_id: sensor.purpleair
purpleair_humidity:
unique_id: 'purpleair_SENSORID_humidity'
friendly_name: 'PurpleAir Humidity'
value_template: "{{ state_attr('sensor.purpleair','results')[0]['humidity'] }}"
unit_of_measurement: "%"
entity_id: sensor.purpleair
purpleair_pressure:
unique_id: 'purpleair_SENSORID_pressure'
friendly_name: 'PurpleAir Pressure'
value_template: "{{ state_attr('sensor.purpleair','results')[0]['pressure'] }}"
unit_of_measurement: "hPa"
entity_id: sensor.purpleair
I had difficulty getting the AQI to display as a numeric graph when I didn’t set a unit. I went with bit, and that worked just fine. 🤷�♂�
So, this idea has been brewing for a while now… try and watch all of Doctor Who. All of it. All 38 seasons. Today(ish), we started. First up, from 1963 (first aired not quite when intended due to the Kennedy assassination): An Unearthly Child. The first episode of the first serial.
A lot of iconic things are there from the start: the music, the Police Box, embarrassing moments of not quite remembering what time one is in, and normal humans accidentally finding their way into the TARDIS.
I first saw this way back when a child, where they were repeated on ABC TV in Australia for some anniversary of Doctor Who (I forget which one). Well, I saw all but the first episode as the train home was delayed and stopped outside Caulfield for no reason for ages. Some things never change.
Of course, being a show from the early 1960s, there’s some rougher spots. We’re not about to have the picture of diversity, and there’s going to be casual racism and sexism. What will be interesting is noticing these things today, and contrasting with my memory of them at the time (at least for episodes I’ve seen before), and what I know of the attitudes of the time.
“This year-ometer is not calculating properly” is a very 2020 line though (technically from the second episode).
Multi-architecture is not something that most people think about - everyone assumes that the only architecture that counts is x86_64, but that's not the case!
In my job at Red Hat I care about making sure that software running on ppc64le, arm64 and s390x behaves just the same as it does on x86_64, which brings me to containers. Did you know that container images are architecture specific?
It makes sense, right? Containers contain software, and often software is architecture specific. When you pull down a container, you never specify an architecture to use. So how does that work? And more importantly to us developers, how do I ensure my containers are multiarch-aware and "just work" no matter which platform we are running on?
For the purposes of this post, I'm going to be using podman and quay.io, but you could just as easily use docker and dockerhub. I much prefer the serviceless design of podman, but that's up to you.
[Aside: From here on in I'm going to use the term amd64 in lieu of x86_64. You can read more about that here. Likewise you might be wondering why we use arm64 instead of aarch64, you can read about that too. And if that's not enough, here's a nice link on golang architectures]
To begin with, let's build a simple Flask python application. Something that is super trivial, but can demonstrate software running in a container. To that end, I present you moo-chop. It just prints a hello world message in a random colour, like this:
It’s been a while since my last post about tracking support for the Oculus Rift in February. There’s been big improvements since then – working really well a lot of the time. It’s gone from “If I don’t make any sudden moves, I can finish an easy Beat Saber level” to “You can’t hide from me!” quality.
Equally, there are still enough glitches and corner cases that I think I’ll still be at this a while.
Here’s a video from 3 weeks ago of (not me) playing Beat Saber on Expert+ setting showing just how good things can be now:
Strap in. Here’s what I’ve worked on in the last 6 weeks:
Most of the biggest improvements have come from improving the computer vision algorithm that’s matching the observed LEDs (blobs) in the camera frames to the 3D models of the devices.
I split the brute-force search algorithm into 2 phases. It now does a first pass looking for ‘obvious’ matches. In that pass, it does a shallow graph search of blobs and their nearest few neighbours against LEDs and their nearest neighbours, looking for a match using a “Strong” match metric. A match is considered strong if expected LEDs match observed blobs to within 1.5 pixels.
Coupled with checks on the expected orientation (matching the Gravity vector detected by the IMU) and the pose prior (expected position and orientation are within predicted error bounds) this short-circuit on the search is hit a lot of the time, and often completes within 1 frame duration.
In the remaining tricky cases, where a deeper graph search is required in order to recover the pose, the initial search reduces the number of LEDs and blobs under consideration, speeding up the remaining search.
I also added an LED size model to the mix – for a candidate pose, it tries to work out how large (in pixels) each LED should appear, and use that as a bound on matching blobs to LEDs. This helps reduce mismatches as devices move further from the camera.
When a brute-force search for pose recovery completes, the system now knows the identity of various blobs in the camera image. One way it avoids a search next time is to transfer the labels into future camera observations using optical-flow tracking on the visible blobs.
The problem is that even sped-up the search can still take a few frame-durations to complete. Previously LED labels would be transferred from frame to frame as they arrived, but there’s now a unique ID associated with each blob that allows the labels to be transferred even several frames later once their identity is known.
One of the problems with reverse engineering is the guesswork around exactly what different values mean. I was looking into why the controller movement felt “swimmy” under fast motions, and one thing I found was that the interpretation of the gyroscope readings from the IMU was incorrect.
The touch controllers report IMU angular velocity readings directly as a 16-bit signed integer. Previously the code would take the reading and divide by 1024 and use the value as radians/second.
From teardowns of the controller, I know the IMU is an Invensense MPU-6500. From the datasheet, the reported value is actually in degrees per second and appears to be configured for the +/- 2000 °/s range. That yields a calculation of Gyro-rad/s = Gyro-°/s * (2000 / 32768) * (?/180) – or a divisor of 938.734.
The 1024 divisor was under-estimating rotation speed by about 10% – close enough to work until you start moving quickly.
If we don’t find a device in the camera views, the fusion filter predicts motion using the IMU readings – but that quickly becomes inaccurate. In the worst case, the controllers fly off into the distance. To avoid that, I added a limit of 500ms for ‘coasting’. If we haven’t recovered the device pose by then, the position is frozen in place and only rotation is updated until the cameras find it again.
I implemented a 1-Euro exponential smoothing filter on the output poses for each device. This is an idea from the Project Esky driver for Project North Star/Deck-X AR headsets, and almost completely eliminates jitter in the headset view and hand controllers shown to the user. The tradeoff is against introducing lag when the user moves quickly – but there are some tunables in the exponential filter to play with for minimising that. For now I’ve picked some values that seem to work reasonably.
Communications with the touch controllers happens through USB radio command packets sent to the headset. The main use of radio commands in OpenHMD is to read the JSON configuration block for each controller that is programmed in at the factory. The configuration block provides the 3D model of LED positions as well as initial IMU bias values.
Unfortunately, reading the configuration block takes a couple of seconds on startup, and blocks everything while it’s happening. Oculus saw that problem and added a checksum in the controller firmware. You can read the checksum first and if it hasn’t changed use a local cache of the configuration block. Eventually, I’ll implement that caching mechanism for OpenHMD but in the meantime it still reads the configuration blocks on each startup.
As an interim improvement I rewrote the radio communication logic to use a state machine that is checked in the update loop – allowing radio communications to be interleaved without blocking the regularly processing of events. It still interferes a bit, but no longer causes a full multi-second stall as each hand controller turns on.
The hand controllers have haptic feedback ‘rumble’ motors that really add to the immersiveness of VR by letting you sense collisions with objects. Until now, OpenHMD hasn’t had any support for applications to trigger haptic events. I spent a bit of time looking at USB packet traces with Philipp Zabel and we figured out the radio commands to turn the rumble motors on and off.
In the Rift CV1, the haptic motors have a mode where you schedule feedback events into a ringbuffer – effectively they operate like a low frequency audio device. However, that mode was removed for the Rift S (and presumably in the Quest devices) – and deprecated for the CV1.
With that in mind, I aimed for implementing the unbuffered mode, with explicit ‘motor on + frequency + amplitude’ and ‘motor off’ commands sent as needed. Thanks to already having rewritten the radio communications to use a state machine, adding haptic commands was fairly easy.
The big question mark is around what API OpenHMD should provide for haptic feedback. I’ve implemented something simple for now, to get some discussion going. It works really well and adds hugely to the experience. That code is in the https://github.com/thaytan/OpenHMD/tree/rift-haptics branch, with a SteamVR-OpenHMD branch that uses it in https://github.com/thaytan/SteamVR-OpenHMD/tree/controller-haptics-wip
I’d say the biggest problem right now is unexpected tracking loss and incorrect pose extractions when I’m not expecting them. Especially my right controller will suddenly glitch and start jumping around. Looking at a video of the debug feed, it’s not obvious why that’s happening:
To fix cases like those, I plan to add code to log the raw video feed and the IMU information together so that I can replay the video analysis frame-by-frame and investigate glitches systematically. Those recordings will also work as a regression suite to test future changes.
The Kalman filter I have implemented works really nicely – it does the latency compensation, predicts motion and extracts sensor biases all in one place… but it has a big downside of being quite expensive in CPU. The Unscented Kalman Filter CPU cost grows at O(n^3) with the size of the state, and the state in this case is 43 dimensional – 22 base dimensions, and 7 per latency-compensation slot. Running 1000 updates per second for the HMD and 500 for each of the hand controllers adds up quickly.
At some point, I want to find a better / cheaper approach to the problem that still provides low-latency motion predictions for the user while still providing the same benefits around latency compensation and bias extraction.
To generate a convincing illusion of objects at a distance in a headset that’s only a few centimetres deep, VR headsets use some interesting optics. The LCD/OLED panels displaying the output get distorted heavily before they hit the users eyes. What the software generates needs to compensate by applying the right inverse distortion to the output video.
Everyone that tests the CV1 notices that the distortion is not quite correct. As you look around, the world warps and shifts annoyingly. Sooner or later that needs fixing. That’s done by taking photos of calibration patterns through the headset lenses and generating a distortion model.
The camera feeds are captured using a custom user-space UVC driver implementation that knows how to set up the special synchronisation settings of the CV1 and DK2 cameras, and then repeatedly schedules isochronous USB packet transfers to receive the video.
Occasionally, some people experience failure to re-schedule those transfers. The kernel rejects them with an out-of-memory error failing to set aside DMA memory (even though it may have been running fine for quite some time). It’s not clear why that happens – but the end result at the moment is that the USB traffic for that camera dies completely and there’ll be no more tracking from that camera until the application is restarted.
Often once it starts happening, it will keep happening until the PC is rebooted and the kernel memory state is reset.
Tracking generally works well when the cameras get a clear shot of each device, but there are cases like sighting down the barrel of a gun where we expect that the user will line up the controllers in front of one another, and in front of the headset. In that case, even though we probably have a good idea where each device is, it can be hard to figure out which LEDs belong to which device.
If we already have a good tracking lock on the devices, I think it should be possible to keep tracking even down to 1 or 2 LEDs being visible – but the pose assessment code will have to be aware that’s what is happening.
April 14th marks 2 years since I first branched off OpenHMD master to start working on CV1 tracking. How hard can it be, I thought? I’ll knock this over in a few months.
Since then I’ve accumulated over 300 commits on top of OpenHMD master that eventually all need upstreaming in some way.
One thing people have expressed as a prerequisite for upstreaming is to try and remove the OpenCV dependency. The tracking relies on OpenCV to do camera distortion calculations, and for their PnP implementation. It should be possible to reimplement both of those directly in OpenHMD with a bit of work – possibly using the fast LambdaTwist P3P algorithm that Philipp Zabel wrote, that I’m already using for pose extraction in the brute-force search.
I’ve picked the top issues to highlight here. https://github.com/thaytan/OpenHMD/issues has a list of all the other things that are still on the radar for fixing eventually.
At some point soon, I plan to put a pin in the CV1 tracking and look at adapting it to more recent inside-out headsets like the Rift S and WMR headsets. I implemented 3DOF support for the Rift S last year, but getting to full positional tracking for that and other inside-out headsets means implementing a SLAM/VIO tracking algorithm to track the headset position.
Once the headset is tracking, the code I’m developing here for CV1 to find and track controllers will hopefully transfer across – the difference with inside-out tracking is that the cameras move around with the headset. Finding the controllers in the actual video feed should work much the same.
This development happens mostly in my spare time and partly as open source contribution time at work at Centricular. I am accepting funding through Github Sponsorships to help me spend more time on it – I’d really like to keep helping Linux have top-notch support for VR/AR applications. Big thanks to the people that have helped get this far.
Today, 30 March, is World Bipolar Day.
Why that particular date? It’s Vincent van Gogh’s birthday (1853), and there is a fairly strong argument that the Dutch painter suffered from bipolar (among other things).
The image on the side is Vincent’s drawing “Worn Out” (from 1882), and it seems to capture the feeling rather well – whether (hypo)manic, depressed, or mixed. It’s exhausting.
Bipolar is complicated, often undiagnosed or misdiagnosed, and when only treated with anti-depressants, it can trigger the (hypo)mania – essentially dragging that person into that state near-permanently.
Hypo-mania is the “lesser” form of mania that distinguishes Bipolar I (the classic “manic depressive” syndrome) from Bipolar II. It’s “lesser” only in the sense that rather than someone going so hyper they may think they can fly (Bipolar I is often identified when someone in manic state gets admitted to hospital – good catch!) while with Bipolar II the hypo-mania may actually exhibit as anger. Anger in general, against nothing in particular but potentially everyone and everything around them. Or, if it’s a mixed episode, anger combined with strong negative thoughts. Either way, it does not look like classic mania. It is, however, exhausting and can be very debilitating.
Bipolar II people often present to a doctor while in depressed state, and GPs (not being psychiatrists) may not do a full diagnosis. Note that D.A.S. and similar test sheets are screening tools, they are not diagnostic. A proper diagnosis is more complex than filling in a form some questions (who would have thought!)
If you have a diagnosis of depression, only from a GP, and are on medication for this, I would strongly recommend you also get a referral to a psychiatrist to confirm that diagnosis.
Our friends at the awesome Black Dog Institute have excellent information on bipolar, as well as a quick self-test – if that shows some likelihood of bipolar, go get that referral and follow up ASAP.
I will be writing more about the topic in the coming time.
The post World bipolar day 2021 first appeared on BlueHackers.org.This post documented an older method of building SteamVR-OpenHMD. I moved them to a page here. That version will be kept up to date for any future changes, so go there.
I’ve had a few people ask how to test my OpenHMD development branch of Rift CV1 positional tracking in SteamVR. Here’s what I do:
git clone --recursive https://github.com/ChristophHaag/SteamVR-OpenHMD.git
cd subprojects/openhmd git remote add thaytan-github https://github.com/thaytan/OpenHMD.git git fetch thaytan-github git checkout -b rift-kalman-filter thaytan-github/rift-kalman-filter cd ../../
meson to build and register the SteamVR-OpenHMD binaries. You may need tmeson first (see below):meson -Dbuildtype=release build ninja -C build ./install_files_to_build.sh ./register.sh
./build/subprojects/openhmd/openhmd_simple_example

I prefer the Meson build system here. There’s also a cmake build for SteamVR-OpenHMD you can use instead, but I haven’t tested it in a while and it sometimes breaks as I work on my development branch.
If you need to install meson, there are instructions here – https://mesonbuild.com/Getting-meson.html summarising the various methods.
I use a copy in my home directory, but you need to make sure ~/.local/bin is in your PATH
pip3 install --user meson
I spent some time this weekend implementing a couple of my ideas for improving the way the tracking code in OpenHMD filters and rejects (or accepts) possible poses when trying to match visible LEDs to the 3D models for each device.
In general, the tracking proceeds in several steps (in parallel for each of the 3 devices being tracked):
The goal is to always assign the correct LEDs to the correct device (so you don’t end up with the right controller in your left hand), and to avoid going back to the expensive brute-force search to re-acquire devices as much as possible
What I’ve been working on this week is steps 1 and 3 – initial acquisition of correct poses, and fast validation / refinement of the pose in each video frame, and I’ve implemented two new strategies for that.
The first new strategy is to reject candidate poses that don’t closely match the known direction of gravity for each device. I had a previous implementation of that idea which turned out to be wrong, so I’ve re-worked it and it helps a lot with device acquisition.
The IMU accelerometer and gyro can usually tell us which way up the device is (roll and pitch) but not which way they are facing (yaw). The measure for ‘known gravity’ comes from the fusion Kalman filter covariance matrix – how certain the filter is about the orientation of the device. If that variance is small this new strategy is used to reject possible poses that don’t have the same idea of gravity (while permitting rotations around the Y axis), with the filter variance as a tolerance.
The 2nd strategy is based around tracking with fewer LED correspondences once a tracking lock is acquired. Initial acquisition of the device pose relies on some heuristics for how many LEDs must match the 3D model. The general heuristic threshold I settled on for now is that 2/3rds of the expected LEDs must be visible to acquire a cold lock.
With the new strategy, if the pose prior has a good idea where the device is and which way it’s facing, it allows matching on far fewer LED correspondences. The idea is to keep tracking a device even down to just a couple of LEDs, and hope that more become visible soon.
While this definitely seems to help, I think the approach can use more work.
With these two new approaches, tracking is improved but still quite erratic. Tracking of the headset itself is quite good now and for me rarely loses tracking lock. The controllers are better, but have a tendency to “fly off my hands” unexpectedly, especially after fast motions.
I have ideas for more tracking heuristics to implement, and I expect a continuous cycle of refinement on the existing strategies and new ones for some time to come.
For now, here’s a video of me playing Beat Saber using tonight’s code. The video shows the debug stream that OpenHMD can generate via Pipewire, showing the camera feed plus overlays of device predictions, LED device assignments and tracked device positions. Red is the headset, Green is the right controller, Blue is the left controller.
Initial tracking is completely wrong – I see some things to fix there. When the controllers go offline due to inactivity, the code keeps trying to match LEDs to them for example, and then there are some things wrong with how it’s relabelling LEDs when they get incorrect assignments.
After that, there are periods of good tracking with random tracking losses on the controllers – those show the problem cases to concentrate on.
These lack of updates are also likely because I’ve been quite caught up with stuff.
Monday I had a steak from Bay Leaf Steakhouse for dinner. It was kind of weird eating it from packs, but then I’m reminded you could do this in economy class. Tuesday I wanted to attempt to go vegetarian and by the time I was done with a workout, the only place was a chap fan shop (Leong Heng) where I had a mixture of Chinese and Indian chap fan. The Indian stall is run by an ex-Hyatt staff member who immediately recognised me! Wednesday, Alice came to visit, so we got to Hanks, got some alcohol, and managed a smorgasbord of food from Pickers/Sate Zul/Lila Wadi. Night ended very late, and on Thursday, visited Hai Tian for their famous salted egg squid and prawns in a coconut shell. Friday was back to being normal, so I grabbed a pizza from Mint Pizza (this time I tried their Aussie variant). Saturday, today, I hit up Rasa Sayang for some matcha latte, but grabbed food from Classic Pilot Cafe, which Faeeza owns! It was the famous salted egg chicken, double portion, half rice.
As for workouts, I did sign up for Mantas but found it pretty hard to do, timezone wise. I did spend a lot of time jogging on the beach (this has been almost a daily affair). Monday I also did 2 MD workouts, Tuesday 1 MD workout, Wednesday half a MD workout, Thursday I did a Ping workout at Pwrhouse (so good!), Friday 1 MD workout, and Saturday an Audrey workout at Pwrhouse and 1 MD workout.
Wednesday I also found out that Rasmus passed away. Frankly, there are no words.
Thursday, my Raspberry Pi 400 arrived. I set it up in under ten minutes, connecting it to the TV here. It “just works”. I made a video, which I should probably figure out how to upload to YouTube after I stitch it together. I have to work on using it a lot more.
COVID-19 cases are through the roof in Malaysia. This weekend we’ve seen two days of case breaking records, with today being 5,728 (yesterday was something close). Nutty. Singapore suspended the reciprocal green lane (RGL) agreement with Malaysia for the next 3 months.
I’ve managed to finish Bridgerton. I like the score. Finding something on Netflix is proving to be more difficult, regardless of having a VPN. Honestly, this is why Cable TV wins… linear programming that you’re just fed.
Stock market wise, I’ve been following the GameStop short squeeze, and even funnier is the Top Glove one, that they’re trying to repeat in Malaysia. Bitcoin seems to be doing “reasonably well” and I have to say, I think people are starting to realise decentralised services have a future. How do we get there?
What an interesting week, I look forward to more productive time. I’m still writing in my Hobonichi Techo, so at least that’s where most personal stuff ends up, I guess?
I hit an important OpenHMD milestone tonight – I completed a Beat Saber level using my Oculus Rift CV1!
I’ve been continuing to work on integrating Kalman filtering into OpenHMD, and on improving the computer vision that matches and tracks device LEDs. While I suspect noone will be completing Expert levels just yet, it’s working well enough that I was able to play through a complete level of Beat Saber. For a long time this has been my mental benchmark for tracking performance, and I’m really happy 
Check it out:
I should admit at this point that completing this level took me multiple attempts. The tracking still has quite a tendency to lose track of controllers, or to get them confused and swap hands suddenly.
I have a list of more things to work on. See you at the next update!